Abstract
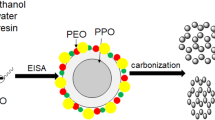
In the present work, mesoporous carbon monoliths with worm-hole structure had been synthesized through hydrothermal reaction by using amphiphilic triblock copolymer F127 and P123 as templates and resole as carbon precursor. Synthesis conditions, carbonization temperature and pore structure were studied by Fourier transform infrared, thermogravimetric analysis, transmission electron microscopy and N2 adsorption–desorption. The results indicated that the ideal pyrolysis temperature of the template is 450 °C. The organic ingredients were almost removed after further carbonized at 600 °C and the mesoporous carbon monoliths with worm-hole structure were obtained. The mesoporous carbon synthesized with P123 as single template exhibited larger pore size (6.6 nm), higher specific surface area (747 m2 g−1), lower pore ratio (45.9 %) in comparison with the mesoporous carbon synthesized with F127 as single template (with the corresponding value of 4.9 nm, 681 m2 g−1, 49.6 %, respectively), and also exhibited wider pore size distribution and lower structure regularity. Moreover, the higher mass ratio of template P123/resole induced similar pore size, larger specific surface area and lower pore ratio at the same synthesizing condition. It was also found that the textural structure of mesoporous carbon was affect by calcination atmosphere.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Ryoo, S.H. Joo, S. Jun, Synthesis of highly ordered carbon molecular sieves via template-mediated structural transformation. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 7743 (1999)
J. Lee, J. Kim, T. Hyeon, Recent progress in the synthesis of porous carbon materials. Adv. Mater. 32, 339 (2011)
J. Fan, T. Wang, C. Yu et al., Ordered, nanostructured tin-based oxides/carbon composite as the negative-electrode material for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 16, 1432 (2004)
J.S. Lee, S.H. Joo, R. Ryoo, Synthesis of mesoporous silicas of controlled pore wall thickness and their replication to ordered nanoporous carbons with various pore diameters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 1156 (2002)
X. Zhuang, Y. Wan, C.M. Feng et al., Highly efficient adsorption of bulky dye molecules in wastewater on ordered mesoporous carbons. Chem. Mater. 21, 706 (2009)
G.P. Hao, W.C. Li, D. Qian et al., Structurally designed synthesis of mechanically stable poly (benzoxazine-co-resol)-based porous carbon monoliths and their application as high-performance CO2 capture sorbents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 11378 (2011)
X. Yuan, S.P. Zhuo, W. Xing et al., Aqueous dye adsorption on ordered mesoporous carbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 310, 83 (2007)
H.I. Lee, Y. Jung, S. Kim et al., Preparation and application of chelating polymer–mesoporous carbon composite for copper-ion adsorption. Carbon 47, 1043 (2009)
Y. Wan, H.Y. Wang, Q.F. Zhao et al., Ordered Mesoporous Pd/Silica–carbon as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst for coupling reaction of chlorobenzene in Aqueous Media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 4541 (2009)
S.H. Joo, S.J. Choi, I. Oh et al., Ordered nanoporous arrays of carbon supporting high dispersions of platinum nanoparticles. Nature 412, 169 (2001)
C. Minchev, H. Huwe, T. Tsoncheva et al., Iron oxide modified mesoporous carbons: physicochemical and catalytic study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 81, 333 (2005)
S. Zhu, H. Zhou, M. Hibino et al., Synthesis of MnO2 nanoparticles confined in ordered mesoporous carbon using a sonochemical method. Adv. Funct. Mater. 15, 381 (2005)
J. Roggenbuck, M. Tiemann, Ordered mesoporous magnesium oxide with high thermal stability synthesized by exotemplating using CMK-3 carbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 1096 (2005)
J.H. Knox, B. Kaur, G.R. Millward, Structure and performance of porous graphitic carbon in liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 352, 3 (1986)
J.H. Knox, K.K. Unger, H. Mueller, Prospects for carbon as packing material in high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 6, 1 (1983)
C. Liang, K. Hong, G.A. Guiochon, Synthesis of a large-scale highly ordered porous carbon film by self-assembly of block copolymers. (2004). doi:10.1002/anie.200461051
S. Tanaka, N. Nishiyama, Y. Egashira et al., Synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbons with channel structure from an organic–organic nanocomposite. Chem. Commun. 16, 2125 (2005)
Y. Meng, D. Gu, F. Zhang, et al. Ordered mesoporous polymers and homologous carbon frameworks: amphiphilic surfactant templating and direct transformation. (2005). doi:10.1002/anie.200501561
Z. Lei, Y. Zhang, H. Wang et al., Fabrication of well-ordered macroporous active carbon with a microporous framework. J. Mater. Chem. 11, 1975 (2001)
Y. Meng, D. Gu, F. Zhang et al., A family of highly ordered mesoporous polymer resin and carbon structures from organic–organic self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 18, 4447 (2006)
F. Zhang, Y. Meng, D. Gu et al., An aqueous cooperative assembly route to synthesize ordered mesoporous carbons with controlled structures and morphology. Chem. Mater. 18, 5279 (2006)
C. Liang, S. Dai, Synthesis of mesoporous carbon materials via enhanced hydrogen-bonding interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 5316 (2006)
F. Liu, H. Zhang, L. Zhu et al., High-temperature hydrothermal synthesis of magnetically active, ordered mesoporous resin and carbon monoliths with reusable adsorption for organic dye. Adsorption 19, 39 (2013)
Muhammad, M.A. Khan, S.Y. Thomas. Desorption of β-carotene from mesoporous carbon coated monolith Isotherm, kinetics and regeneration studies. Chem. Eng. J. 173, 474 (2011)
Y.S. Kim, X.F. Guo, G.J. Kim, Synthesis of carbon monolith with bimodal meso/macroscopic pore structure and its application in asymmetric catalysis. Catal. Today 150, 91 (2010)
Z. Wang, A. Stein, Morphology control of carbon, silica, andcarbon/silica nanocomposites: from 3D ordered macro-/mesoporous monoliths to shaped mesoporous particles. Chem. Mater. 20, 1029 (2008)
G.P. Hao, W.C. Li, S. Wang et al., Lysine-assisted rapid synthesis of crack-free hierarchical carbon monolithis with a hexagonal array of mesopores. Carbon 49, 3762 (2011)
Y. Huang, H.Q. Cai, D. Feng et al., One-step hydrothermal synthesis of ordered mesostructured carbonaceous monoliths with hierarchical porosities. Chem. Commun. 21, 2641 (2008)
L.L. Meng, M.J. Wang, H.M. Yang, Catalytic effect of alkali carbonates on CO2 gasification of Pingshuo coal. Min. Sci. Technol. 21, 587 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shanxi Province of China (Program No. 2015JM2058) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51373135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, J., Xiang, Y., Cao, J. et al. Worm-hole structured mesoporous carbon monoliths synthesized with amphiphilic triblock copolymer. J Porous Mater 23, 1431–1438 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0203-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0203-2