Abstract
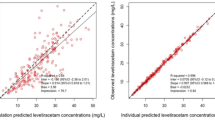
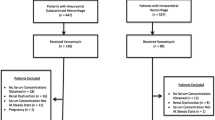
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, a naturally-occurring antagonist to the pro-inflammatory cytokine Interleukin-1, is already in clinical use. In experimental models of stroke, Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in cerebrospinal fluid has been associated with cerebral neuroprotection and in a phase I clinical trial in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage it crosses the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. The aims of the current work were to design a dose-ranging clinical study in patients and to analyse the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid data obtained using a population pharmacokinetic modelling approach. The study was designed using prior information: a published population pharmacokinetic model and associated parameter estimates. Simulations were carried out to identify combinations of intravenous bolus and 4 h infusion doses that could achieve a concentration of 100 ng/ml in cerebrospinal fluid within approximately 30 min. The most informative time points for plasma and cerebrospinal fluid were obtained prospectively; optimisation identified five sampling time points that were included in the 15 time points in the present study design. All plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentration data from previous and current studies were combined for updated analysis. The result of the simulations showed that a dosage regimen of 500 mg intravenous bolus and 10 mg/kg/h could achieve the target concentration, however four other regimens that represent a stepwise increase in maximum concentration were also selected. Analysis of the updated data showed improvement in parameter accuracy and predictive performance of the model; the percentage relative standard errors for fixed and random-effects parameters were <15 and 35 % respectively. A dose-ranging study was successfully designed using modelling and simulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soler EP, Ruiz VC (2010) Epidemiology and risk factors of cerebral ischemia and ischemic heart diseases: similarities and differences. Curr Cardiol Rev 6:138–149
Touzani O, Boutin H, Chuquet J, Rothwell N (1999) Potential mechanisms of interleukin-1 involvement in cerebral ischaemia. J Neuroimmunol 100:203–215
Banwell V, Sena ES, Macleod MR (2009) Systematic review and stratified meta-analysis of the efficacy of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in animal models of stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 18:269–276
Clark SR, McMahon CJ, Gueorguieva I, Rowland M, Scarth S, Georgiou R, Tyrrell PJ, Hopkins SJ, Rothwell NJ (2008) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist penetrates human brain at experimentally therapeutic concentrations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:387–394
Gueorguieva I, Clark SR, McMahon CJ, Scarth S, Rothwell NJ, Tyrell PJ, Hopkins SJ, Rowland M (2008) Pharmacokinetic modelling of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of patients following subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br J Clin Pharmacol 65:317–325
Stroke Therapy Academic Industry R, II (2001) Recommendations for clinical trial evaluation of acute stroke therapies. Stroke 32:1598–1606
Deng YZ, Reeves MJ, Jacobs BS, Birbeck GL, Kothari RU, Hickenbottom SL, Mullard AJ, Wehner S, Maddox K, Majid A, R PCNAS (2006) IV tissue plasminogen activator use in acute stroke—experience from a statewide registry. Neurology 66:306–312
Saver JL (2006) Time is brain–quantified. Stroke 37:263–266
Lalonde RL, Kowalski KG, Hutmacher MM, Ewy W, Nichols DJ, Milligan PA, Corrigan BW, Lockwood PA, Marshall SA, Benincosa LJ, Tensfeldt TG, Parivar K, Amantea M, Glue P, Koide H, Miller R (2007) Model-based drug development. Clin Pharmacol Ther 82:21–32
Holford NH, Kimko HC, Monteleone JP, Peck CC (2000) Simulation of clinical trials. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40:209–234
Ogungbenro K, Dokoumetzidis A, Aarons L (2009) Application of optimal design methodologies in clinical pharmacology experiments. Pharm Stat 8:239–252
Nyberg J, Bazzoli C, Ogungbenro K, Aliev A, Leonov S, Duffull S, Hooker AC, Mentre F (2015) Methods and software tools for design evaluation in population pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics studies. Br J Clin Pharmacol 79:6–17
Beal S, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann A, Bauer RJ (2009) NONMEM user’s guides (1989–2009). Icon Development Solutions, Ellicott City
Gueorguieva I, Ogungbenro K, Graham G, Glatt S, Aarons L (2007) A program for individual and population optimal design for univariate and multivariate response pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 86:51–61
Galea J, Ogungbenro K, Hulme S, Greenhalgh A, Aarons L, Scarth S, Hutchinson P, Grainger S, King A, Hopkins SJ, Rothwell N, Tyrrell P (2011) Intravenous anakinra can achieve experimentally effective concentrations in the central nervous system within a therapeutic time window: results of a dose-ranging study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:439–447
Lindbom L, Ribbing J, Jonsson EN (2004) Perls-speaks-NONMEM (PsN)—a Perl module for NONMEM related programming. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 75:85–94
Lindbom L, Pihlgren P, Jonsson N (2005) PsN-Toolkit—a collection of computer intensive statistical methods for non-linear mixed effect modeling using NONMEM. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 79:241–257
Hutchinson PJ, O’Connell MT, Rothwell NJ, Hopkins SJ, Nortje J, Carpenter KLH, Timofeev I, Al-Rawi PG, Menon DK, Pickard JD (2007) Inflammation in human brain injury: intracerebral concentrations of IL-1α, IL-1β, and their endogenous inhibitor IL-1ra. J Neurotrauma 24:1545–1557
Mathiesen T, Andersson B, Loftenius A, von Holst H (1993) Increased interleukin-6 levels in cerebrospinal fluid following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 78:562–567
Hopkins SJ, McMahon CJ, Singh N, Galea J, Hoadley M, Scarth S, Patel H, Vail A, Hulme S, Rothwell NJ, King AT, Tyrrell PJ (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma cytokines after subarachnoid haemorrhage: CSF interleukin-6 may be an early marker of infection. J Neuroinflammation 9:255
Rothwell NJ, Luheshi GN (2000) Interleukin 1 in the brain: biology, pathology and therapeutic target. Trends Neurosci 23:618–625
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Amgen Inc (CA, USA) for providing IL-1Ra, anakinra as Kineret®, the Medical Research Council (MRC; UK) for funding the study, and Salford Royal Foundation Trust for funding and sponsoring the study, the patients that participated in this study and the neurosurgical team at Salford Royal Foundation Trust and Addenbrooke’s Hospital for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
NJR is a non-executive director of AstraZeneca plc, but this has no relation with the present study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogungbenro, K., Hulme, S., Rothwell, N. et al. Study design and population pharmacokinetic analysis of a phase II dose-ranging study of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 43, 1–12 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-015-9450-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-015-9450-0