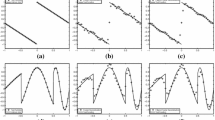
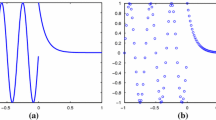
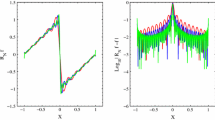
Abstract
Edge detection plays an important role in identifying regions of interest in an underlying signal or image. In some applications, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or synthetic aperture radar (SAR), data are sampled in the Fourier domain. Many algorithms have been developed to efficiently extract edges of images when uniform Fourier data are acquired. However, in cases where the data are sampled non-uniformly, such as in non-Cartesian MRI or SAR, standard inverse Fourier transformation techniques are no longer suitable. Methods exist for handling these types of sampling patterns, but are often ill-equipped for cases where data are highly non-uniform or when the data are corrupted or otherwise not usable in certain parts of the frequency domain. This investigation further develops an existing approach to discontinuity detection, and involves the use of concentration factors. Previous research shows that the concentration factor technique can successfully determine jump discontinuities in non-uniform data. However, as the distribution diverges further away from uniformity so does the efficacy of the identification. Thus we propose a method that employs the finite Fourier approximation to specifically tailor the design of concentration factors. We also adapt the algorithm to incorporate appropriate smoothness assumptions in the piecewise smooth regions of the function. Numerical results indicate that our new design method produces concentration factors which can more precisely identify jump locations than those previously developed in both one and two dimensions.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This idea was first investigated in [23].
Recall that we assume that the discontinuities occur only on grid points \(x_j\). For convenience we choose \(x_j = \frac{j}{J}\), \(-J \le j \le J\) so that the value \(x = 0\) falls on the grid point \(x_0\). The system can be designed for any chosen gridpoints, however.
References
Adcock, B., Gataric, M., Hansen, A.: On stable reconstructions from nonuniform Fourier measurements. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 7(3), 1690–1723 (2014)
Adcock, B., Gataric, M., Hansen, A.C. Stable nonuniform sampling with weighted Fourier frames and recovery in arbitrary spaces. In: 2015 International Conference on Sampling Theory and Applications (SampTA), pp. 105–109. IEEE (2015)
Adcock, B., Gataric, M., Hansen, A.C.: Weighted frames of exponentials and stable recovery of multidimensional functions from nonuniform Fourier samples. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.acha.2015.09.006
Adcock, B., Gataric, M., Romero, J.L.: Computing reconstructions from nonuniform Fourier samples: universality of stability barriers and stable sampling rates. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.07698 (2016)
Aldroubi, A., Grochenig, K.: Nonuniform sampling and reconstruction in shift-invariant spaces. SIAM Rev. 43(4), 585–620 (2001)
Archibald, R., Chen, K., Gelb, A., Renaut, R.: Improving tissue segmentation of human brain mri through preprocessing by the gegenbauer reconstruction method. NeuroImage 20(1), 489–502 (2003)
Archibald, R., Gelb, A.: A method to reduce the Gibbs ringing artifact in MRI scans while keeping tissue boundary integrity. Med. Imaging IEEE Trans. 21(4), 305–319 (2002)
Benedetto, J.: Irregular sampling and frames. In: Chui, C. (ed.) Wavelets: A Tutorial in Theory and Applications, pp. 445–507. Academic Press, Cambridge (1992)
Canny, J.: A computational approach to edge detection. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. IEEE Trans. 6, 679–698 (1986)
Chebira, A., Kovacevic, J.: Life beyond bases: the advent of frames (part I). IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24(4), 86–104 (2007)
Engelberg, S., Tadmor, E.: Recovery of edges from spectral data with noise: a new perspective. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46(5), 2620–2635 (2008)
Fessler, J.A., Sutton, B.P.: Nonuniform fast Fourier transforms using min–max interpolation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 51(2), 560–574 (2003)
Gelb, A., Cates, D.: Segmentation of images from Fourier spectral data. Commun. Comput. Phys. 5(2–4), 326–349 (2009)
Gelb, A., Hines, T.: Detection of edges from nonuniform Fourier data. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 17(11), 1152–1179 (2011)
Gelb, A., Song, G.: A frame theoretric approach to the non-uniform fast Fourier transform. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52(3), 1222–1242 (2014)
Gelb, A., Tadmor, E.: Detection of edges in spectral data. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 7(1), 101–135 (1999)
Gelb, A., Tadmor, E.: Detection of edges in spectral data. II. Nonlinear enhancement. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38(4), 1389–1408 (2000)
Gelb, A., Tadmor, E.: Adaptive edge detectors for piecewise smooth data based on the minmod limiter. J. Sci. Comput. 28(2–3), 279–306 (2006)
Han, D., Kornelson, K., Larson, D., Weber, E.: Frames for Undergraduates. In: Student Mathematical Library 40. American Mathematical Society (2007)
Jimenez, J., Medina, V., Yanez, O.: Data-driven brain MRI segmentation supported on edge confidence and a priori tissue information. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 25(1), 74–83 (2006)
Kovacevic, J., Chebira, A.: Life beyond bases: the advent of frames (part II). IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24, 115–125 (2007)
Martinez, A., Gelb, A., Gutierrez, A.: Edge detection from non-uniform Fourier data using the convolutional gridding algorithm. J. Sci. Comput. 61(3), 490–512 (2014)
Moore, R.: Designing concentration factors to detect edges from non-uniform Fourier data. Arizona State University Undergraduate Honors Thesis (2015)
Petersen, A., Gelb, A., Eubank, R.: Hypothesis testing for Fourier based edge detection methods. J. Sci. Comput. 51, 608–630 (2012)
Shattuck, D.W., Sandor-Leahy, S.R., Schaper, K.A., Rottenberg, D.A., Leahya, R.M.: Magnetic resonance image tissue classification using a partial volume model. Neuroimage 13(5), 856–876 (2001)
Song, G., Davis, J., Gelb, A.: A high-dimensional inverse frame operator approximation technique. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 54(4), 2282–2301 (2016). doi:10.1137/15M1047593
Song, G., Gelb, A.: Approximating the inverse frame operator from localized frames. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 35(1), 94–110 (2013)
Stefan, W., Viswanathan, A., Gelb, A., Renaut, R.: Sparsity enforcing edge detection method for blurred and noisy Fourier data. J. Sci. Comput. 50(3), 536–556 (2012)
Sun, W., Zhou, X.: On the stability of multivariate trigonometric systems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 235(1), 159–167 (1999)
Viswanathan, A., Gelb, A., Cochran, D.: Iterative design of concentration factors for jump dection. J. Sci. Comput. 51, 631–649 (2012)
Viswanathan, A., Gelb, A., Cochran, D., Renaut, R.: On reconstruction from non-uniform spectral data. J. Sci. Comput. 45, 487–513 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by Grants NSF-DMS 1216559 (AG), NSF-DMS 1521600 (AG), NSF-DMS 1521661 (GS), NSF 1502640 (AG), and AFOSR FA9550-15-1-0152 (AG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelb, A., Song, G. Detecting Edges from Non-uniform Fourier Data Using Fourier Frames. J Sci Comput 71, 737–758 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0320-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0320-8