Abstract
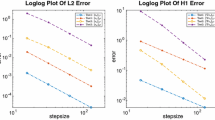
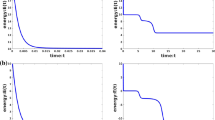
We present a linear iteration algorithm to implement a second-order energy stable numerical scheme for a model of epitaxial thin film growth without slope selection. The PDE, which is a nonlinear, fourth-order parabolic equation, is the \(L^2\) gradient flow of the energy \( \int _\Omega \left( - \frac{1}{2} \ln \left( 1 + | \nabla \phi |^2 \right) + \frac{\epsilon ^2}{2}|\Delta \phi (\mathbf{x})|^2 \right) \mathrm{d}\mathbf{x}\). The energy stability is preserved by a careful choice of the second-order temporal approximation for the nonlinear term, as reported in recent work (Shen et al. in SIAM J Numer Anal 50:105–125, 2012). The resulting scheme is highly nonlinear, and its implementation is non-trivial. In this paper, we propose a linear iteration algorithm to solve the resulting nonlinear system. To accomplish this we introduce an \(O(s^2)\) (with \(s\) the time step size) artificial diffusion term, a Douglas-Dupont-type regularization, that leads to a contraction mapping property. As a result, the highly nonlinear system can be decomposed as an iteration of purely linear solvers, which can be very efficiently implemented with the help of FFT in a collocation Fourier spectral setting. We present a careful analysis showing convergence for the numerical scheme in a discrete \(L^\infty (0, T; H^1) \cap L^2 (0,T; H^3)\) norm. Some numerical simulation results are presented to demonstrate the efficiency of the linear iteration solver and the convergence of the scheme as a whole.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, W., Conde, S., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: A linear energy stable scheme for a thin film model without slope selection. J. Sci. Comput. 52, 546–562 (2012)
Chen, W., Wang, Y.: A mixed finite element method for thin film epitaxy. Numer. Math. 122, 771–793 (2012)
Ehrlich, G., Hudda, F.G.: Atomic view of surface diffusion: tungsten on tungsten. J. Chem. Phys. 44, 1036–1099 (1966)
Evans, J.W., Thiel, P.A., Bartelt, M.C.: Morphological evolution during epitaxial thin film growth: Formation of 2D islands and 3D mounds. Surf. Sci. Rep. 61, 1–128 (2006)
Eyre, D.J.: Unconditionally gradient stable time marching the Cahn–Hilliard equation. In: Bullard, J.W., Kalia, R., Stoneham, M., Chen, L.Q. (eds). Computational and Mathematical Models of Microstructural Evolution, vol. 53, pp. 1686–1712. Materials Research Society, Warrendale, PA (1998)
Golubović, L.: Interfacial coarsening in epitaxial growth models without slope selection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 90–93 (1997)
Hu, Z., Wise, S.M., Wang, C., Lowengrub, J.S.: Stable and efficient finite-difference nonlinear-multigrid schemes for the phase field crystal equation. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 5323–5339 (2009)
Johnson, M.D., Orme, C., Hunt, A.W., Graff, D., Sudijono, J., Sander, L.M., Orr, B.G.: Stable and unstable growth in molecular beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 116–119 (1994)
Kohn, R.V.: Energy-driven pattern formation. In: Sanz-Sole, M., Soria, J., Varona, J.L., Verdera, J. (eds). Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians, vol. 1, pp. 359–384. European Mathematical Society Publishing House, Madrid (2007)
Kohn, R.V., Yan, X.: Upper bound on the coarsening rate for an epitaxial growth model. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 56, 1549–1564 (2003)
Li, B.: High-order surface relaxation versus the Ehrlich–Schwoebel effect. Nonlinearity 19, 2581–2603 (2006)
Li, B., Liu, J.-G.: Thin film epitaxy with or without slope selection. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 14, 713–743 (2003)
Li, B., Liu, J.-G.: Epitaxial growth without slope selection: energetics, coarsening, and dynamic scaling. J. Nonlinear Sci. 14, 429–451 (2004)
Moldovan, D., Golubovic, L.: Interfacial coarsening dynamics in epitaxial growth with slope selection. Phys. Rev. E 61, 6190–6214 (2000)
Qiao, Z., Sun Z., Zhang, Z.: Stability and convergence of second-order schemes for the nonlinear epitaxial growth model without slope selection. Math. Comput. (accepted)
Qiao, Z., Zhang, Z., Tang, T.: An adaptive time-stepping strategy for the molecular beam epitaxy models. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33, 1395–1414 (2011)
Qiao, Z., Sun, Z., Zhang, Z.: The stability and convergence of two linearized finite difference schemes for the nonlinear epitaxial growth model. Numer. Methods Partial Diff. Eq. 28, 1893–1915 (2012)
Schwoebel, R.L.: Step motion on crystal surfaces: II. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 614–618 (1969)
Shen, J., Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Second-order convex splitting schemes for gradient flows with Ehrlich–Schwoebel type energy: application to thin film epitaxy. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 105–125 (2012)
Trefethen, L.N.: Spectral Methods in Matlab. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA (2000)
Wise, S.M., Wang, C., Lowengrub, J.S.: An energy stable and convergent finite-difference scheme for the phase field crystal equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 2269–2288 (2009)
Wang, C., Wang, X., Wise, S.M.: Unconditionally stable schemes for equations of thin film epitaxy. Discret. Cont. Dyn. Syst. A 28, 405–423 (2010)
Xu, C., Tang, T.: Stability analysis of large time-stepping methods for epitaxial growth models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 1759–1779 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the National Science Foundation, specifically, DMS-1008852, DMS-1002618, DMS-1312701 (X. Wang), DMS-1115390 (S.M. Wise), and DMS-1115420 (C. Wang), the Ministry of Education of China and the State Administration of Foreign Experts Affairs of China under 111 project grant B08018 (W. Chen), and the Key Project National Science Foundation of China 91130004 (W. Chen). C. Wang also thanks the Key Laboratory of Mathematics for Nonlinear Sciences (EZH1411104), Fudan University, for support during his visit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Wang, C., Wang, X. et al. A Linear Iteration Algorithm for a Second-Order Energy Stable Scheme for a Thin Film Model Without Slope Selection. J Sci Comput 59, 574–601 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-013-9774-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-013-9774-0