Abstract
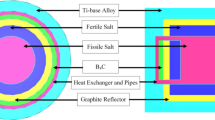
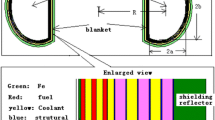
In this study, some important thermodynamic properties of the fusion reactor have been analyzed. The physical and chemical properties of molten salts have been extensively studied in the nuclear fusion program. In recent years, molten salts technology began to be used in some engineering areas, in the advanced nuclear field and especially in nuclear fusion reactor systems. Nowadays, Aries team has developed advanced designs by using the molten salts technology in order to get high thermodynamic and structural advantage on nuclear technology areas (Tillack et al. in Fusion Energ Des 65:215–261, 2003; Tillack et al. in Fusion Energ Des 49–50:689–695, 2000; El-Guebaly et al. in Fusion Energ Des 65:263–284, 2003). The Aries-St reactors are a 1000 MW fusion reactor system that based on a low aspect ratio ST plasma (Tillack et al. in Fusion Energy Des 65:215–261, 2003; Tillack et al. in Fusion Energy Des 49–50:689–695, 2000). The Aries team studies especially on liquid walls concepts and this liquid are used to increase neutronic performance of various structures of Aries-St reactors. In this research, candidate molten salts have been studied neutron effects on reactor performance which are the first wall (FW) and blanket. There are various candidate liquids that meet all the criteria such as Li17Pb83, flibe(Li2BeF4) and LiNaBeF4, LiSn that are able to breed enough tritium. In this research, we used Li17Pb83, pure lithium and flibe as candidates that are in the Aries design. Montecarlo n-particle 4b-code is used for neutronics analysis and thermodynamic features. The value of tritium breeding ratio of the Aries-St reactors must be (TBR ≥ 1.1). This can be achieved in the region of LiPb/FW blanket of reactors. Aries-St spherical reactor has high heat flux (0.8 MW/m2) and NWL (6–8 MW/m2) in this region.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- G:
-
Free energy
- E:
-
Internal energy
- S:
-
Entropy
- H:
-
Enthalpy
- Mcnp:
-
Montecarlo n-particle
- A:
-
Major radius of toroid
- a:
-
Minor radius of toroid
- β = A/a:
-
Aspect ratio of plasma
- tbr:
-
t6 + t7, Tritium breeding ratio
- mhd:
-
Magneto hydrodynamic
- Re:Ha2/N:
-
Reynolds number
- Ha:
-
Hartmann numbers
References
M.S. Tillack, X.R. Wang, J. Pulsifer, S. Malang, Fusion power core engineering for Aries-St power plant. Fusion Energ Des 65, 215–261 (2003)
Aries team, M.S. Tillack, X.R. Wang et al., Aries-St breeding blanket design and analysis. Fusion Energ Des. 49–50, 689–695 (2000)
L.A. El-Guebaly, Aries team, Aries-St nuclear analysis and shield design. Fusion Eng. Des. 65, 263–284 (2003)
M.Ü. Beyli, A. Acır, Neutronic investigation on the Aries-St fusion reactor with fissionable molten salts. Energ Convers Manag 51, 2531–2534 (2010)
T.K. Mau, S.C. Jardin, C.E. Kessel, J.E. Menard, R.L. Miller, et al., Physics basis for the aries-st power plant, www.ferp.ucsd.edu
J. Bremister, MCNP-4a general Monte Carlo code n-particle transport code, version 4a, la-12625 (1993)
R.W. Roussin, MCNP/a general Monte Carlo n-particle transport code, version 4B, Los Alamos National Laboratory Report la-12625 (1993)
A. Hançerlioğullari, M. Cini, 3D Neutronic analysis in Mhd calculations at Aries-st fusion reactors systems. J Fusion Energ (2013). doi:10.1007/s10894-013-9637-6
F. Najmabadi, The Aries Team, Spherical torus concept as power plants/the Aries-St study. Fusion Eng. Des. 65, 143–164 (2003)
A. Hançerlioğullari, M. Cini, Different mechanisms for establishing liquid walls in advanced reactor systems. J Fusion Energ 32(2), 155–163 (2013)
A. Hançerlioğullari, M. Cini, M. Güdal, Advanced power conversion efficiency in inventive plasma for hybrid toroidal reactor. J Fusion Energ (2013). doi:10.1007/s10894-013-9621-1
M. Übeyli, T. Altinok, Neutronic investigation of the Aries-St fusion reactor by using molten salt with ThF4. J Polytech. 5, 227–231 (2002)
M. Übeyli, Fissile fuel breeding in the aries-st fusion reactor by using molten salt with UF4. GÜ J Sci. 16(2), 387–394 (2003)
A. Hançerlioğullari, Montecarlo simulation method and Mcnp code system. J Kastamonu Educ 14(2), 545–556 (2006)
K. Miyamoto, Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, 2007)
O. Ozturk, M. Coskunyurek, E. Asikuzun, N. Soylu, A. Hancerliogullari, A. Varilci, C. Terzioglu, The effect of Nd2O3 addition on superconducting and structural properties and activation energy calculation of Bi-2212 superconducting system. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10854-013-1608-1
L. Bromberg, S. Pourrahimi, J.H. Schultz, P. Titus, S. Jardin, C. Kessel, W. Reiersen, The Aries Team, Superconducting poloidal field magnet engineering for the aries-st. Fusion Eng. Des. 65, 323–338 (2003)
W. Reiersen, F. Dahlgren, H.M. Fan, C. Neumeyer, I. Zatz, The toroidal field coil design for Aries-st. Fusion Eng. Des. 65, 303–322 (2003)
K. Starke, L. Buhler, S. Horanyi, Experimental mhd-flow analyses in a mock-up of a test blanket module for Iter. Fusion Energ Des 84, 1794–1798 (2009)
Tokamaks, Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion, Springer Series on Atomic, vol. 38 (2005), pp. 269–317
A. Hançerlioğullari, The use of Mcnp code in apex fusion reactor technology, Nucl Sci Technol, 1–13 ısbn:978-81-7895-546-9 (2012)
A. Hançerliogullari, Determining of energy multiplication in the apex hybrid reactor by using Thf4 and Uf4 heavy metal salts. Int J Energ Res 36, 1375–1382 (2012)
A. Hançerliogullari, Innovative fusion tokamak powerplant and basic engineering for Mhd theory. J Fusion Energ (2014). doi:10.1007/s10894-013-9659-0
O. Benes, R.J.M. Konings, Thermodynamic properties and phase diagrams of fluoride salts for nuclear applications. J Fluor Chem 130, 22–29 (2009)
T.G. Cowling, Magnetohydynamics (Adam Hilger Ltd, Bristol, 1976)
H. Bloom, The chemistry of molten sats, copyright by W.A. Benjamin (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hançerlioğulları, A. Thermodynamics Properties of Molten Salt Technology Assessment for New Generation Fusion Reactors. J Fusion Energ 33, 463–470 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-014-9694-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-014-9694-5