Abstract
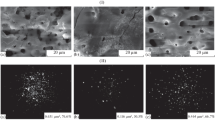
Magnesium alloys suffer from their high reactivity in common environments. Protective layers are widely created on the surface of magnesium alloys to improve their corrosion resistance. This article evaluates the influence of a calcium-phosphate layer on the electrochemical characteristics of AZ31 magnesium alloy in 0.9 % NaCl solution. The calcium phosphate (CaP) layer was electrochemically deposited in a solution containing 0.1 M Ca(NO3)2, 0.06 M NH4H2PO4 and 10 ml l−1 of H2O2. The formed surface layer was composed mainly of brushite [(dicalcium phosphate dihidrate (DCPD)] as proved by energy-dispersive X-ray analysis. The surface morphology was observed by scanning electron microscopy. Immersion test was performed in order to observe degradation of the calcium phosphatized surfaces. The influence of the phosphate layer on the electrochemical characteristics of AZ31, in 0.9 % NaCl solution, was evaluated by potentiodynamic measurements and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The obtained results were analysed by the Tafel-extrapolation method and equivalent circuits method. The results showed that the polarization resistance of the DCPD-coated surface is about 25 times higher than that of non-coated surface. The CaP electro-deposition process increased the activation energy of corrosion process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merritt K, Brown S. Release of hexavalent chromium from corrosion of stainless steel and cobalt–chromium alloys. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29:627–33.
Yang J, Merritt K. Detection of antibodies against corrosion products in patients after Co Cr total joint replacements. J Biomed Mater Res. 1994;28:1249–58.
Woodman J, Black J, Nunamaker D. Release of cobalt and nickel from a new total finger joint prosthesis made of vitallium. J Biomed Mater Res. 1983;17:655–68.
Gray-Munro JE, Seguin C, Strong M. Influence of surface modification on the in vitro corrosion rate of magnesium alloy AZ31. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2009;91A:221–30.
Almpanis G, Tsigkas G, Koutsojannis C, Mazarakis A, Kounis G, Kounis N. Nickel allergy, Kounis syndrome and intracardiac metal devices. Int J Cardiol. 2010;145:364–5.
Elias C, Lima J, Valiev R, Meyers M. Biomedical applications of titanium and its alloys. J Miner Met Mater Soc. 2008;60:46–9.
Janeček M, Nový F, Stráský J, Harcuba P, Wagner L. Fatigue endurance of Ti–6Al–4V alloy with electro-eroded surface for improved bone in-growth. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011;4:417–22.
Rho J, Ashman R, Turner C. Young’s modulus of trabecular and cortical bone material: ultrasonic and microtensile measurements. J Biomech. 1993;26:111–9.
Kitamura E, Stegaroiu R, Nomura S, Miyakawa O. Biomechanical aspects of marginal bone resorption around osseointegrated implants: considerations based on a three dimensional finite element analysis. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2004;15:401–12.
Ashman R. Elastic modulus of trabecular bone material. J Biomech. 1988;21:177–81.
Rho J, Tsui T, Pharr G. Elastic properties of human cortical and trabecular lamellar bone measured by nanoindentation. Biomaterials. 1997;18:1325–30.
Terjesen T, Apalset K. The influence of different degrees of stiffness of fixation plates on experimental bone healing. J Orthop Res. 1988;6:293–9.
Terjesen T. Bone healing after metal plate fixation and external fixation of the osteotomized rabbit tibia. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55:69–77.
Wang K. The use of titanium for medical applications in the USA. Mater Sci Eng A. 1996;213:134–7.
Karachalios T, Tsatsaronis C, Efraimis G, Papadelis P, Lyritis G, Diakoumopoulos G. The long-term clinical relevance of calcar atrophy caused by stress shielding in total hip arthroplasty: a 10-year, prospective, randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19:469–75.
Staiger MP, Pietak AM, Huadmai J, Dias G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1728–34.
Heublein B, Rohde R, Kaese V, Niemeyer M, Hartung W, Haverich A. Biocorrosion of magnesium alloys: a new principle in cardiovascular implant technology. Heart. 2003;89:651–6.
Peuster M, Beerbaum P, Bach FW, Hauser H. Are resorbable implants about to become a reality. Cardiol Young. 2006;16:107–16.
Zartner P, Buettner M, Singer H, Sigler M. First biodegradable metal stent in a child with congenital heart disease: evaluation of macro and histopathology. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007;69:443–6.
Zhang W, Li M, Chen Q, Hu W, Zhang W, Xin W. Effects of Sr on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Mg–Zr–Ca magnesium alloy for biomedical applications. Mater Des. 2012;39:379–83.
Zreiqat H, Howlett CR, Zannettino A, Evans P, Schulze-Tanzil G, Knabe C, et al. Mechanisms of magnesium- stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to commonly used orthopaedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62:175–84.
Gray-Munro JE, Strong M. The mechanisms of deposition of calcium phosphate coatings from solution onto magnesium alloy AZ31. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2009;90A:339–50.
Lindenberg M, Windhugen H, Witte F. US Patent Application 2004/0241036 A1, 2004.
Song G. Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloys. Corros Sci. 2007;49:1696–701.
Jamesh M, Kumar S, Sankara Narayanan T. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on magnesium for biomedical applications. J Coat Technol Res. 2011;9:495–502.
Gray JE, Luan B. Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys: a critical review. J Alloys Compd. 2002;336:88–113.
Chen XB, Birbilis N, Abbott TB. A simple route towards a hydroxyapatite–Mg(OH)2 conversion coating for magnesium. Corr Sci. 2011;53:2263–8.
Waterman J. Corrosion resistance of biomimetic calcium phosphate coatings on magnesium due to varying pretreatment time. Mater Sci and Eng. 2011;176:1756–60.
Shadanbaz S, Dias GJ. Calcium phosphate coatings on magnesium alloys for biomedical applications: a review. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:20–30.
Barrére F, van Blitterswijk C, de Groot K. Bone regeneration: molecular and cellular interactions with calcium phosphate ceramics. Int J Nanomed. 2006;1:317–32.
Dorozhkin S, Epple M. Biological and medical significance of calcium phosphates. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2002;41:3130–46.
Kumar M, Xie J, Chittur K, Riley C. Transformation of modified brushite to hydroxyapatite in aqueous solution: effects of potassium substitution. Biomaterials. 1999;20:1389–99.
LeGeros R, Parsons J, Daculsi G, Driessens F, Lee D, Liu S, et al. Significance of the porosity and physical chemistry of calcium phosphate ceramics biodegradation bioresorption. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1988;523:268–71.
Narayanan R, Seshadri S, Kwon T, Kim K. Calcium phosphate based coatings on titanium and its alloys. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2008;85:279–99.
Uskokovi V, Uskokovi DP. Nanosized hydroxyapatite and other calcium phosphates: chemistry of formation and application as drug and gene delivery agents. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2011;96:152–91.
Yongsheng W. Sol–gel derived hydroxyapatite coatings on metallic implants: characterization, in vitro and in vivo analysis. Biol Biomed Coat. 2011;1:1–33.
Kumar M, Dasarathy H, Riley C. Electrodeposition of brushite coatings and their transformation to hydroxyapatite in aqueous solutions. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 1999;45:302–10.
Redepenning J, Schlessinger T, Burnham S, Lippiello L, Miyano J. Characterization of electrolytically prepared brushite and hydroxyapatite coatings on orthopedic alloys. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 1996;30:287–94.
Xie J, Riley C, Chittur K. Effect of albumin on brushite transformation to hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;57:357–65.
Xie J, Riley C, Kumar M, Chittur K. FTIR/ATR study of protein adsorption and brushite transformation to hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials. 2002;23:3609–16.
Xia Z, Grover L, Huang Y, Adamopoulos I, Gbureck U, Triffitt J, et al. In vitro biodegradation of three brushite calcium phosphate cements by a macrophage cell-line. Biomaterials. 2006;27:4557–65.
Klammert U, Reuther T, Jahn C, Kraski B, Kubler A, Gbureck U. Cytocompatibility of brushite and monetite cell culture scaffolds made by three-dimensional powder printing. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:727–34.
Ji C, Ahn J. Clinical experience of the brushite calcium phosphate cement for the repair and augmentation of surgically induced cranial defects following the pterional craniotomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010;47:180–4.
Pastorek F, Hadzima B. Study of calcium phosphate (DCPD) electrodeposition process on a Mg–3Al–1Zn magnesium alloy surface. Mater Eng. 2012;19:54–63.
B. Hadzima, F. Pastorek, M. Omasta, Improve biodegradation properties of Mg–3Al–1Zn magnesium alloy by dicalcium phosphate dehydrate coating. In: Advanced manufacturing and repairing technologies in vehicle industry. 30th International Colloquium. Visegrád; 2013. ISBN 978-963-313-079-7, p. 111–115.
Wei B, Tokash JC, Zhang F, Kim Y, Logan BE. Electrochemical analysis of separators used in single-chamber, air–cathode microbial fuel cells. Electrochim Acta. 2013;89:45–51.
Han XG, Zhu F, Zhu XP, Lei MK, Xu JJ. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of modified MAO film on magnesium alloy AZ31 irradiated by high-intensity pulsed ion beam. Surf Coat Technol. 2013;228:S164–70.
Škublová L, Hadzima B, Borbás L, Vitosová M. The influence of temperature on corrosion properties of titanium and stainless steel biomaterials. Mater Eng. 2008;15:18–22.
Bukovinová L, Hadzima B. Electrochemical characteristics of magnesium alloy AZ31 in Hank’s solution. Corr Eng Sci Technol. 2012;47:352–7.
Zhou W, Shan D, Han EH, Ke W. Structure and formation mechanism of phosphate conversion coating on die-cast AZ91D magnesium alloy. Corros Sci. 2009;50:329–37.
Gu XN, Li N, Zhou WR, Zheng YF, Zhao X. Corrosion resistance and surface biocompatibility of a microarc oxidation coating on a Mg–Ca alloy. Acta Biomater. 2011;7:1880–9.
Bakhsheshi-Rad HR, Idris MH, Abdul-Kadir MR. Synthesis and in vitro degradation evaluation of the nano-HA/MgF2 and DCPD/MgF2composite coating on biodegradable Mg–Ca–Zn alloy. Surf Coat Technol. 2013;222:79–89.
Aljourani J, Raeissi K, Golozar MA. Benzimidazole and its derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution. Corr Sci. 2009;51:1836–43.
Wintermantel E, Mayer J, Blum J, Eckert K-L, Lüscher P, Mathey M. Tissue engineering scaffolds using superstructures. Biomater. 1996;17:83–91.
Xin Y, Huo K, Tao H, Tang G, Chu PK. Influence of aggressive ions on the degradation behavior of biomedical magnesium alloy in physiological environment. Acta Biomater. 2008;4:2008–15.
Song G, Atrens A, StJohn D, Wu X, Nairn J. The anodic dissolution of magnesium in chloride and sulphate solutions. Corros Sci. 1997;39:1981–2004.
Shi Y, Qi M, Chen Y, Shi P. MAO-DCPD composite coating on Mg alloy for degradable implant applications. Mater Lett. 2011;65:2201–4.
Song YW, Shan DY, Han EH. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy for biomaterial application. Mater Lett. 2008;62:3276–9.
Chun-Yan Z, Rong-Chang Z, Cheng-Long L, Jia-Cheng G. Comparison of calcium phosphate coatings on Mg–Al and Mg–Ca alloys and their corrosion behavior in Hank’s solution. Surf Coat Technol. 2010;204:3636–40.
Song Y, Zhang S, Li J, Zhao C, Zhang X. Electrodeposition of Ca–P coatings on biodegradable Mg alloy: in vitro biomineralization behavior. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:1736–42.
Acknowledgments
The research is supported by European regional development fund and Slovak state budget by the project “Research centre of the University of Žilina”, ITMS 26220220183 and “Unique equipment for evaluation of tribological properties of machines parts surfaces”, ITMS 26220220048. Authors are grateful for the support of experimental works by project VEGA No. 1/0831/13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadzima, B., Mhaede, M. & Pastorek, F. Electrochemical characteristics of calcium-phosphatized AZ31 magnesium alloy in 0.9 % NaCl solution. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 25, 1227–1237 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5161-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-014-5161-0