Abstract
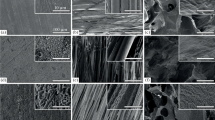
In this work, medium pressure plasma treatment of polylactic acid (PLA) is investigated. PLA is a biocompatible aliphatic polymer, which can be used for bone fixation devices and tissue engineering scaffolds. Due to inadequate surface properties, cell adhesion and proliferation are far less than optimal and a surface modification is required for most biomedical applications. By using a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) operating at medium pressure in different atmospheres, the surface properties of a PLA foil are modified. After plasma treatment, water contact angle measurements showed an increased hydrophilic character of the foil surface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) revealed an increased oxygen content. Cell culture tests showed that plasma modification of PLA films increased the initial cell attachment both quantitatively and qualitatively. After 1 day, cells on plasma-treated PLA showed a superior cell morphology in comparison with unmodified PLA samples. However, after 7 days of culture, no significant differences were observed between untreated and plasma-modified PLA samples. While plasma treatment improves the initial cell attachment, it does not seem to influence cell proliferation. It has also been observed that the difference between the 3 discharge gases is negligible when looking at the improved cell-material interactions. From economical point of view, plasma treatments in air are thus the best choice.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grandfils C, Flandroy P, Jérôme R. Control of the biodegradation rate of poly(dl-lactide) microparticles intended as chemoembolization materials. J Control Release. 1996;38:109–22.
Gogolewski S, Pineda L, Busing CM. Bone regeneration in segmental defects with resorbable polymeric membranes: IV. Does the polymer chemical composition affect the healing process? Biomaterials. 2000;21:2513–20.
Alves CM, Yang Y, Marton D, Carnes DL, Ong JL, Sylvia VL, et al. Plasma surface modification of poly(d,l-lactic acid) as a tool to enhance protein adsorption and the attachment of different cell types. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2008;87B:59–66.
Ding Z, Chen JN, Gao SY, Chang JB, Zhang JF, Kang ET. Immobilization of chitosan onto poly-l-lactic acid film surface by plasma graft polymerization to control the morphology of fibroblast and liver cells. Biomaterials. 2004;25:1059–67.
Wang SG, Cui WJ, Bei JZ. Bulk and surface modifications of polylactide. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005;381:547–56.
De Geyter N, Morent R, Gengembre L, Leys C, Payen E, Van Vlierberghe S, Schacht E. Increasing the hydrophobicity of a PP film using a helium/CF4 DBD treatment at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Chem Plasma P. 2008;28:289–98.
De Geyter N, Morent R, Leys C, Gengembre L, Payen E. Treatment of polymer films with a dielectric barrier discharge in air, helium and argon at medium pressure. Surf Coat Technol. 2007;201:7066–75.
Morent R, De Geyter N, Gengembre L, Leys C, Payen E, Van Vlierberghe S, Schacht E. Surface treatment of a polypropylene film with a nitrogen DBD at medium pressure. Eur Phys J Appl Phys. 2008;43:289–94.
Morent R, De Geyter N, Leys C, Gengembre L, Payen E. Surface modification of non-woven textiles using a dielectric barrier discharge operating in air, helium and argon at medium pressure. Text Res J. 2007;77:471–88.
De Geyter N, Morent R, Leys C. Surface characterization of plasma-modified polyethylene by contact angle experiments and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Surf Interface Anal. 2008;40:608–11.
Shi LS, Wang LY, Wang YN. The investigation of argon plasma surface modification to polyethylene: quantitative ATR-FTIR spectroscopic analysis. Eur Polym J. 2006;42:1625–33.
Sira M, Trunec D, Stahel P, Bursikova V, Navratil Z, Bursik J. Surface modification of polyethylene and polypropylene in atmospheric pressure glow discharge. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2005;38:621–7.
Morent R, De Geyter N, Leys C, Gengembre L, Payen E. Study of the ageing behaviour of polymer films treated with a dielectric barrier discharge in air, helium and argon at medium pressure. Surf Coat Technol. 2007;201:7847–54.
Morent R, De Geyter N, Leys C. Effects of operating parameters on plasma-induced PET surface treatment. Nucl Instrum Method B. 2008;266:3081–5.
Liu HZ, Cui NY, Brown NMD, Meenan BJ. Effects of DBD plasma operating parameters on the polymer surface modification. Surf Coat Technol. 2004;185:311–20.
Yang J, Bei JZ, Wang SG. Improving cell affinity of poly(d,l-lactide) film modified by anhydrous ammonia plasma treatment. Polym Adv Technol. 2002;13:220–6.
Parker JATC, Walboomers XF, Von den Hoff JW, Maltha JC, Jansen JA. Soft tissue response to microtextured silicone and poly-l-lactic acid implants: fibronectin pre-coating vs. radio-frequency glow discharge treatment. Biomaterials. 2002;23:3545–53.
Ferreira BMP, Pinheiro LMP, Nascente PAP, Ferreira MJ, Duek EAR. Plasma surface treatments of poly(l-lactic acid) (PLLA) and poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV). Mater Sci Eng C. 2009;29:806–13.
Inagaki N, Narushima K, Tsutsui Y, Ohyama Y. Surface modification and degradation of poly (lactic acid) films by Ar-plasma. J Adhesion Sci Technol. 2002;16:1041–54.
Khorasani MT, Mirzadeh H, Irani S. Plasma surface modification of poly(l-lactic acid) and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) films for improvement of nerve cells adhesion. Radiat Phys Chem. 2008;77:280–7.
Yang J, Bei JZ, Wang SG. Enhanced cell affinity of poly(d,l-lactide) by combining plasma treatment with collagen anchorage. Biomaterials. 2002;23:2607–14.
Yang J, Shi GX, Bei JZ, Wang SG, Cao YL, Shang QX, et al. Fabrication and surface modification of macroporous poly(l-lactic acid) and poly(l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) (70/30) cell scaffolds for human skin fibroblast cell culture. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62:438–46.
De Geyter N, Morent R, Desmet T, Trentesaux M, Gengembre L, Dubruel P, Leys C. Plasma modification of polylactic acid in a medium pressure DBD. Surf Coat Technol. 2010;204:3272–9.
Morent R, De Geyter N, Desmet T, Dubruel P, Leys C. Plasma surface modification of biodegradable polymers: a review. Plasma Proces Polym. 2011;8:171–90.
Borcia G, Brown NMD. Hydrophobic coatings on selected polymers in an atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2007;40:1927–36.
Heyse P, Dams R, Paulussen S, Houthofd K, Janssen K, Jacobs PA, et al. Dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure as a tool to deposit versatile organic coatings at moderate power input. Plasma Proces Polym. 2007;4:145–57.
De Geyter N, Morent R, Leys C, Gengembre L, Payen E, Van Vlierberghe S, et al. DBD treatment of polyethylene terephthalate: atmospheric versus medium pressure treatment. Surf Coat Technol. 2008;202:3000–10.
Kogelschatz U. Dielectric-barrier discharges: their history, discharge physics, and industrial applications. Plasma Chem Plasma Proces. 2003;23:1–46.
Wagner HE, Brandenburg R, Kozlov KV, Sonnenfeld A, Michel P, Behnke JF. The barrier discharge: basic properties and applications to surface treatment. Vacuum. 2003;71:417–36.
Hegemann D, Brunner H, Oerh C. Plasma treatment of polymers for surface and adhesion improvement. Nucl Instrum Method B. 2003;208:281–6.
Akishev Y, Tran MD, Descours S. Studies on cold plasma-polymer surface interaction by example of PP- and PET-films. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008;41:235203.
Akishev Yu, Grushin ME, Drachev AI, Karalnik VB, Petryakov AV, Trushkin NI. On hydrophilicity ageing of PP and PET films induced by ultraviolet radiation and hydrogen atoms. Open Plasma Physics (in press).
Briggs D. Applications of XPS in polymer technology. In: Briggs D, Seah MP, editors. Practical surface analysis—volume 1—Auger and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. West Sussex: Wiley; 1990. p. 437–83.
Briggs D. Surface analysis of polymers by XPS and static SIMS. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1998.
Acknowledgments
R. Morent acknowledges the support of the Research Foundation Flanders (FWO) for a post-doctoral research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacobs, T., Declercq, H., De Geyter, N. et al. Plasma surface modification of polylactic acid to promote interaction with fibroblasts. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 24, 469–478 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4807-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4807-z