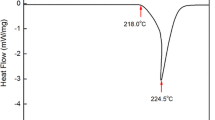
Abstract
The effects of TiO2 nanoparticles and cooling rate on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn1.5Sb0.7Cu alloy were investigated. A higher cooling rate and TiO2 nanoparticles refined the primary β-Sn dendrites, Cu6Sn5 and SbSn phase. Especially, the microstructure of the Sn1.5Sb0.7Cu composite solders under the rapid-cooled condition exhibited fine dot-like Cu6Sn5 in the eutectic regions. The improvement in strength was mostly attributed to (1) refinement of the β-Sn grain size; (2) the Orowan strengthening effect; (3) CTE mismatch between reinforcement second phase particles (Cu6Sn5 and TiO2) and the matrix; and (4) the load-bearing effect. However, the total elongation of the composite solders was observed to decrease because of micro-voids both at and along the Cu6Sn5 grain boundary regions. The fracture surfaces of all Sn1.5Sb0.7Cu composite solder were confirmed to exhibit the ductile fracture mode.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.N. Tu, K. Zeng, Tin-lead (SnPb) solder reaction in flip chip technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 34, 1–58 (2001)
L.C. Tsao, R.W. Wu, T.H. Cheng, K.H. Fan, R.S. Chen, Effects of nano-Al2O3 particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu composite solder ball grid array joints on Sn/Cu pads. Mater. Des. 50, 774–781 (2013)
H.J. Lin, T.H. Chuang, Interfacial microstructure and bonding strength of Sn–3Ag–0.5Cu and Sn–3Ag–0.5Cu–0.5Ce–XZn solder BGA packages with immersion Ag surface finish. Microelectron. Reliab. 51, 445–452 (2011)
L.C. Tsao, C.P. Chu, S.F. Peng, Study of interfacial reactions between Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu composite alloys and Cu substrate. Microelectron. Eng. 88, 2964–2969 (2011)
C.L. Chuang, L.C. Tsao, H.K. Lin, L.P. Feng, Effects of small amount of active Ti element additions on microstructure and property of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 558, 478–484 (2012)
K.S. Kim, S.H. Huh, K. Suganuma, Effects of intermetallic compounds on properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free soldered joints. J. Alloys Compd. 352, 226–236 (2003)
W.M. Xiao, Y.W. Shi, Y.P. Lei, Z.D. Xia, F. Guo, Comparative study of microstructures and properties of three valuable SnAgCuRE lead-free solder alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1095–1103 (2006)
L. Zhang, K.N. Tu, Structure and properties of lead-free solders bearing micro and nano particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 82, 1–32 (2014)
L.C. Tsao, S.Y. Chang, Effects of nano-TiO2 additions on thermal analysis, microstructure and tensile properties of Sn3.5Ag0.25Cu solder. Mater. Des. 31, 990–993 (2010)
L.C. Tsao, S.Y. Chang, C.I. Lee, W.H. Sun, C.H. Chiang, Effects of Nano-Al2O3 additions on microstructure development and hardness of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder. Mater. Des. 31, 4831–4835 (2010)
J. Shen, Y.C. Liu, D.J. Wang, H.X. Gao, Nano ZrO2 particulate-reinforced lead-free solder composite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 22, 529–532 (2006)
A.A. El-Daly, A. Fawzy, S.F. Mansour, M.J. Younis, Novel SiC nanoparticles-containing Sn–1.0Ag–0.5Cu solder with good drop impact performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 578, 62–71 (2013)
A.A. El-Daly, A. Fawzy, S.F. Mansour, M.J. Younis, Thermal analysis and mechanical properties of Sn–1.0Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy after modification with SiC nano-sized particles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 2976–2988 (2013)
Y. S. Park, Y. M. Kwon, H. Y. Son, J. T. Moon, Effect of Sb addition in Sn–Ag–Cu solder balls on the drop test reliability of BGA packages with electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG) surface finish. In: Electronic Material and Packaging, 2007
A.A. El-Daly, A.E. Hammad, A. Fawzy, D.A. Nasrall, Microstructure, mechanical properties, and deformation behavior of Sn–1.0Ag–0.5Cu solder after Ni and Sb additions. Mater. Des. 43, 40–49 (2013)
H.S. Güdera, E. Şahina, O. Şahina, H. Göçmezb, C. Duranc, Vickers and Knoop Indentation Microhardness Study of β-SiAlON Ceramic. Acta Phys. Pol. A 120, 1026–1033 (2011)
T.H. Chuang, L.C. Tsao, C.H. Chung, S.Y. Chang, Evolution of Ag3Sn compounds and microhardness of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu nano-composite solders during different cooling rate and aging. Mater. Des. 39, 475–483 (2012)
A.R. Geranmayeh, R. Mahmudi, M. Kangooie, High-temperature shear strength of lead-free Sn–Sb–Ag/Al2O3 composite solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 3967–3972 (2011)
T. Fouzder, I. Shafiq, Y.C. Chan, A. Sharif, W.K.C. Yung, Influence of SrTiO3 nano-particles on the microstructure and shear strength of Sn–Ag–Cu solder on Au/Ni metallized Cu pads. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 1885–1892 (2011)
A.A. El-Daly, T.A. Elmosalami, W.M. Desoky, M.G. El-Shaarawy, A.M. Abdraboh, Tensile deformation behavior and melting property of nano-sized ZnO particles reinforced Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu lead-free solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 17, 389–3973 (2014)
C.C. Jain, T.H. Chuang, L.P. Feng, L.C. Tsao, Effect of addition of TiO2 nanoparticles on the microstructure, microhardness and interfacial reactions of Sn3.5AgXCu solder. Mater. Des. 32, 4720–4727 (2011)
L.C. Tsao, Suppressing effect of 0.5 wt% nano-TiO2 addition into Sn–3.5Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy on the intermetallic growth with Cu substrate during isothermal aging. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 8441–8448 (2011)
L.C. Tsao, Evolution of nano-Ag3Sn particle formation on Cu–Sn intermetallic compounds of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu composite solder/Cu during soldering. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 2326–2333 (2011)
X.L. Zhong, M. Gupta, Development of lead-free Sn–0.7Cu/Al2O3 nanocomposite solders with superior strength. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 095403–095409 (2008)
J. Shen, Y.C. Chan, Effects of ZrO2 nanoparticles on the mechanical properties of Sn–Zn solder joints on Au/Ni/Cu pads. J. Alloys Compd. 477, 552–559 (2009)
E.S. Gouda, Effect of cooling rate on structure and creep behavior of Sn0.7Cu0.5Zn lead-free solder alloy. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 48, 20902–20906 (2009)
J.M. Song, J.J. Lin, C.F. Huang, H.Y. Chuang, Crystallization, morphology and distribution of Ag3Sn in Sn–Ag–Cu alloys and their influence on the vibration fracture properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 466, 9–17 (2007)
L.C. Tsao, An investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of novel Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu–XTiO2 composite solders as functions of alloy composition and cooling rate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 529, 41–48 (2011)
W.D. Callister, Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 2004), p. 252
I. Shao, P.M. Verrcken, C.L. Chien, P.C. Searson, R.C. Cammarata, Synthesis and characterization of particle-reinforced Ni/Al2O3 nanocomposite. J. Mater. Res. 17, 1412–1418 (2002)
L. Thilly, M. Veron, O. Ludwig, F. Lecourterier, Deformation mechanism in high strength Cu/Nb nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 309–310, 510–513 (2001)
G.E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, 3rd edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1986), p. 325
Q. Zhang, D.L. Chen, A model for predicting the particle size dependence of the low cycle fatigue life in discontinuously reinforced MMCs. Scr. Mater. 51, 863–867 (2004)
L.H. Dai, Z. Ling, Y.L. Bai, Size-dependent inelastic behavior of particle-reinforced metal-matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61, 1057–1063 (2001)
Z. Zhang, D.L. Chen, Contribution of Orowan strengthening effect in particulate-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 483–484, 148–152 (2008)
M. Cadek, J.N. Coleman, V. Barron, K. Hedicke, W.J. Blau, Mechanical properties and morphology of carbon nanotube reinforced semi crystalline and amorphous polymer composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 5123–5125 (2002)
S.M.L. Nai, J. Wei, M. Gupta, Improving the performance of lead-free solder reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 423, 166–169 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support of this work from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under Project No. MOST 103-2221-E-020-014. SEM was performed by the Precision Instrument Center of National Pingtung University of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C.H., Chen, CH., Chang, S.Y. et al. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticle addition and cooling rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of novel Sn1.5Sb0.7Cu solders. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 3493–3501 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2860-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2860-3