Abstract
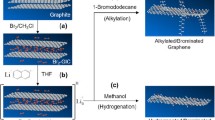
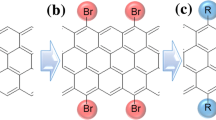
The bromination reactivity of azulene, naphthalene, and graphene with pentagonal, hexagonal zigzag and armchair, and heptagonal edges was theoretically estimated by density functional theory calculation and experimentally clarified by analyzing bromination of azulene and naphthalene using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy. The experimental and theoretical bromination reactivity of azulene with one pentagon and one heptagon was higher than that of naphthalene with two hexagons because of electron-rich carbon atoms on the pentagon. On the other hand, the tendency of theoretical bromination reactivity of pentagonal, hexagonal, and heptagonal edges on graphene was totally opposite to that on azulene and naphthalene. The order of the bromination reactivity of graphene edges was hexagonal zigzag > pentagonal > heptagonal and hexagonal armchair edges. The highest reactivity of hexagonal zigzag edges can be explained by the largest amount of electrons of carbon atoms among all of edges of graphene.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakada K, Fujita M, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus MS (1996) Edge state in graphene ribbons: nanometer size effect and edge shape dependence. Phys Rev B 54:17954–17961
Jia X, Campos-Delgado J, Terrones M, Meunier V, Dresselhaus MS (2011) Graphene edges: a review of their fabrication and characterization. Nanoscale 3:86–95
Xu Z, Zheng QS, Chen G (2007) Elementary building blocks of graphene-nanoribbon-based electronic devices. Appl Phys Lett 90:223115
Boukhvalov DW, Katsnelson MI (2008) Chemical functionalization of graphene with defects. Nano Lett 8:4373–4379
Seitsonen AP, Marco Saitta A, Wassmann T, Lazzeri M, Mauri F (2010) Structure and stability of graphene nanoribbons in oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. Phys Rev B 82:115425
Son YW, Cohen ML, Louie SG (2006) Half-metallic graphene nanoribbons. Nature 444:347–349
Son YW, Cohen ML, Louie SG (2006) Energy gaps in graphene nanoribbons. Phys Rev Lett 97:216803
Koskinen P, Malola S, Häkkinen H (2008) Self-passivating edge reconstructions of graphene. Phys Rev Lett 101:115502
Wassmann T, Seitsonen AP, Marco Saitta A, Lazzeri M, Mauri F (2008) Structure, stability, edge states, and aromaticity of graphene ribbons. Phys Rev Lett 101:096402
Castro Neto AH, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK (2009) The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys 81:109–162
Harris PJF, Liu Z, Suenaga K (2008) Imaging the atomic structure of activated carbon. J Phys 20:362201
Pumera M, Scipioni R, Iwai H, Ohno T, Miyahara Y, Boero M (2009) A mechanism of adsorption of b-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide on graphene sheets: experiment and theory. Chem Eur J 15:10851–10856
Shao Y, Wang J, Wu H, Liu J, Aksay IA, Lin Y (2010) Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: a review. Electroanal 22:1027–1036
Cervantes-Sodi F, Csányi G, Piscanec S, Ferrari AC (2008) Edge-functionalized and substitutionally doped graphene nanoribbons: electronic and spin properties. Phys Rev B 77:165427
Hod O, Barone V, Peralta JE, Scuseria GE (2007) Enhanced half-metallicity in edge-oxidized zigzag graphene nanoribbons. Nano Lett 7:2295–2299
Yan Q, Huang B, Yu J, Zheng F, Zang J, Wu J, Gu BL, Liu F, Duan W (2007) Intrinsic current-voltage characteristics of graphene nanoribbon transistors and effect of edge doping. Nano Lett 7:1469–1473
Jeon IY, Choi HJ, Choi M, Seo JM, Jung SM, Kim MJ, Zhang S, Zhang L, Xia Z, Dai L, Park N, Baek JB (2013) Facile, scalable synthesis of edge-halogenated graphene nanoplatelets as efficient metal-free eletrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Sci Rep 3:1810
Jankovský O, Šimek P, Klimová K, Sedmidubský D, Matějková S, Pumera M, Sofer Z (2014) Towards graphene bromide: bromination of graphite oxide. Nanoscale 6:6065–6074
Karlický F, Kumara Ramanatha Datta K, Otyepka M, Zbořil R (2013) Halogenated graphenes: rapidly growing family of graphene derivatives. ACS Nano 7:6434–6464
Jankovský O, Šimek P, Sedmidubský D, Matějková S, Janoušek Z, Šembera F, Pumera M, Sofer Z (2014) Water-soluble highly fluorinated graphite oxide. RSC Adv 4:1378–1387
Šimek P, Klimová K, Sedmidubský D, Jankovský O, Pumera M, Sofer Z (2015) Towards graphene iodide: iodination of graphite oxide. Nanoscale 7:261–270
Poh HL, Šimek P, Sofer Z, Pumera M (2013) Halogenation of graphene with chlorine, bromine, or iodine by exfoliation in a halogen atmosphere. Chem Eur J 19:2655–2662
Gopalakrishnan K, Subrahmanyam KS, Kumar P, Govindaraj A, Rao CNR (2012) Reversible chemical storage of halogens in few-layer graphene. RSC Adv 2:1605–1608
Tan YZ, Yang B, Parvez K, Narita A, Osella S, Beljonne D, Feng X, Müllen K (2013) Atomically precise edge chlorination of nanographenes and its application in graphene nanoribbons. Nat Commun 4:2646
Zheng J, Liu HT, Wu B, Di CA, Guo YL, Wu T, Yu G, Liu YQ, Zhu DB (2012) Production of graphite chloride and bromide using microwave sparks. Sci Rep 2:662
Sibbel F, Matsui K, Segawa Y, Studer A, Itami K (2014) Selective synthesis of [7]- and [8]cycloparaphenylenes. Chem Commun 50:954–956
Cai J, Ruffieux P, Jaafar R, Bieri M, Braun T, Blankenburg S, Muoth M, Seitsonen AP, Saleh M, Feng X, Müllen K, Fasel R (2010) Atomically precise bottom-up fabrication of graphene nanoribbons. Nature 466:470–473
Han P, Akagi K, Federici Canova F, Mutoh H, Shiraki S, Iwaya K, Weiss PS, Asao N, Hitosugi T (2014) Bottom-up graphene-nanoribbon fabrication reveals chiral edges and enantioselectivity. ACS Nano 8:9181–9187
Vo TH, Shekhirev M, Kunkel DA, Orange F, Guinel MJF, Enders A, Sinitskii A (2014) Bottom-up solution synthesis of narrow nitrogen-doped graphene nanoribbons. Chem Commun 50:4172–4174
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB et al (2009) Gaussian 09, Revision D.01. Wallingford, Gaussian Inc.
Kim K, Coh S, Kisielowski C, Crommie MF, Louie SG, Cohen ML, Zettl A (2013) Atomically perfect torn graphene edges and their reversible reconstruction. Nat Commun 4:2723
Radovic LR, Suarez A, Vallejos-Burgos F, Sofo JO (2011) Oxygen migration on the graphene surface. 2. Thermochemistry of basal-plane diffusion (hopping). Carbon 49:4226–4238
Mishra PC, Yadav A (2012) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons as finite size models of graphene and graphene nanoribbons: enhanced electron density edge effect. Chem Phys 402:56–68
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Japan Interaction in Science and Technology Forum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Yamada, Y., Fujita, R. et al. Bromination of graphene with pentagonal, hexagonal zigzag and armchair, and heptagonal edges. J Mater Sci 50, 5183–5190 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9066-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9066-1