Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the protective effect of Lithium against the toxic effect of Cadmium in the rat testes.
Methods
Twenty four adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with four different regimens: Cadmium only, Cadmium and lithium, lithium only and controls. Rats were sacrificed after 6 weeks and testicular levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine (IL-4), anti-inflammatory cytokine (TNF-α), Pro-apoptotic protein (Bax) and anti-apoptotic protein (Bcl-2) were measured by ELISA while serum levels of FSH, LH, Prolactin and Testosterone were measured using the Vidas parametric system. Antioxidant status (MDA, SOD) was also assessed in serum. Histopathological changes of testes were examined using light and electron microscopy. Immunohistochemical staining for Bax, Bcl-2 and Caspase 3 were performed.
Results
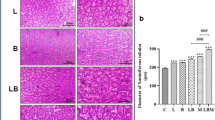
Treatment with lithium was associated with significant reduction in the toxic effects of Cadmium as shown by reduced testicular levels of TNF-α, serum levels of Malondialdehyde and testicular level of Bax, and increased levels of IL-4, Zn-Cu SOD, Bcl-2 and Testosterone. Testicular histopathology showed that Cadmium produced an extensive germ cells apoptosis and the addition of lithium in Cadmium-treated rats significantly reduced cadmium-induced testicular damage.
Conclusion(s)
Lithium has a protective effect against cadmium-induced testicular apoptosis in the rat.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoff S, Jacob A, Hurley IR. Male infertility and environmental exposure to lead and cadmium. Hum Reprod Update. 2000;6:107–21.
Laskey JW, Rehnberg GL, Laws SC, Hein JF. Reproductive effects of low acute doses of cadmium chloride in adult male rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984;73:250–5.
Laskey JW, Rehnberg GL, Laws SC, Hein JF. Age-related dose response of selected reproductive parameters to acute cadmium chloride exposure in the male Lon-Evans rat. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1986;19:393–401.
Gennart JP, Buchet JP, Roels H, Ghyselen P, Ceulemans E, Lauwerys R. Fertility of male workers exposed to cadmium, lead or manganese. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135:1208–19.
Foote RH. Cadmium affects testes and semen of rabbits exposed before and after puberty. Reprod Toxicol. 1999;13:269–77.
Benoff S, Hurley IR, Mandel FS, Paine T, Jacob A, Cooper GW, et al. Use of mannose ligands in IVF screens to mimic zona pellucida-induced acrosome reactions and predict fertilization success. Mol Hum Reprod. 1997;3(10):839–46.
Xu LC, Wang SY, Yang XF, Wang XR. Effects of cadmium on rat sperm motility evaluated with computer assisted sperm analysis. Biomed Environ Sci. 2001 Dec;14(4):312–7.
Perry DK, Smyth MJ, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Duriez P, Poirier GG, et al. Zinc is a potent inhibitor of the apoptotic protease, Caspase-3. A novel target for zinc in the inhibition of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1997;4:29–33.
Xu G, Zhou G, Jin T, Jin T, Zhou T, Hammarstrom S, et al. Apoptosis and p53 gene expression in male reproductive tissues of cadmium exposed rats. Biometals. 1999;12:131–9.
Zhou T, Zhou G, Song W, Eguchi N, Lu W, Lundin E, et al. Cadmium-induced apoptosis and changes in expression of p53, c-jun and MT-I genes in testes and ventral prostate of rats. Toxicology. 1999;142:1–13.
Chen RW, Chuang DM. Long term lithium treatment suppresses p53 and Bax expression but increases Bcl-2 expression. A prominent role in neuroprotection against excitotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:6039–42.
Hiroi T, Wei H, Hough C. Leeds, Chaung DM. Protracted lithium treatment protects against the ER stress elicited by thepsigargin in rat PC12 cells: role of intracellular calcium, GRP78 and Bcl-2. Pharmacogenomics J. 2005;5:102–11.
Omu AE, Al-Qattan F, Abdul-hadi FM, Fatinikun MT, Fernandes S. Seminal immune response in infertile men with leukocytospermia: effect on antioxidant activity. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1999;86:195–202.
Kehinde EO, Mojiminiyi OA, Mahmoud AH, Al-Awadi KA, Al-Hunayan A, Omu AE. The significance of measuring the time course of serum malondialdehyde concentration in patients with torsion of the testis. J Urol. 2003;169:2177–80.
Johnsen SG. Testicular biopsy score-count-a method for registration of spermatogenesis in human testes: normal values and result of 335 hypogonadal males. Hormones. 1970;1:2–25.
Eguchi Y, Srinivasan A, Tomaselli KJ, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y. ATP-dependent steps in Apoptotic Signal Transduction. Cancer Research. 1999;59:2174–81.
Ikediobi CO, Badisa VL, Ayuk-Takem LT, Latinwo LM, West J. Response of antioxidant enzymes and redox metabolites to cadmium-induced oxidative stress in CRL-1439 normal rat liver cells. Int J Mol Med. 2004;14:87–92.
El-Demerdash FM, Yousef MI, Kedwany FS, Baghdadi HH. Cadmium-induced changes in lipid peroxidation, blood hematology, biochemical parameters and semen quality of male rats: protective role of vitamin E and beta-carotene. Food Chem Toxicol. 2004;2:1563–71.
Yadav N, Khandelwal S. Effect of Picroliv on cadmium induced testicular damage in rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:494–501.
Siu ER, Mruk DD, Porto CS, Cheng CY. Cadmium-induced testicular injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009;238:240–9.
Chuang DM. The antiapoptotic actions of mood stabilizers: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2005;1053:195–204.
Rowe MK, Chuang DM. Lithium neuroprotection: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2004;6:1–18.
Sahebgharani M, Neijati M, Sepehrizadeh Z. Lithium chloride protects PC12 pheochromocytoma cell line from morphine-induced apoptosis. Arch Iran Med. 2008;11:639–48.
Xu J, Culman J, Blume A, Brecht S, Gohlke P. Chronic treatment with a low dose lithium protects the brain against ischemic injury by reducing apoptotic death. Stroke. 2003;34:1287–92.
Song L, Zhou T. Jope RS Lithium facilitates apoptotic signaling induced by activation of the Fas death domain-containing receptor. BMC Neurosci. 2004;5:20.
Ghosh D, Biswas NM, Ghosh PK. Effect of lithium chloride on adrenocortical activity in male rats: evidence of dose and duration dependent response. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1990;34:263–6.
Thakur SC, Thakur SS, Chaube SK, Singh SP. Subchronic supplementation of lithium carbonate induces reproductive system toxicity in male rat. Reproductive Toxicol. 2003;17:683–90.
Hockenbery DM, Oltvai ZN, Yin X-M, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 functions in an antioxidant pathway to prevent apoptosis. Cell. 1993;75:241–51.
Lenox RH, Hahn CG. Overview of the mechanism of action of lithium in the brain: fifty-year update. J Clin Psychiatry. 2000;61 Suppl 9:5–15.
Bielecka AM, Obuchowicz E. Antiapoptotic action of lithium and valproate. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60:771–82.
Disclosure information
All authors have nothing to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule
Lithium protection against toxic effect of Cadmium in rat testes suggests its potential preventive uses in male infertility among smokers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Azemi, M., Omu, F.E., Kehinde, E.O. et al. Lithium protects against toxic effects of cadmium in the rat testes. J Assist Reprod Genet 27, 469–476 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-010-9426-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-010-9426-3