Abstract
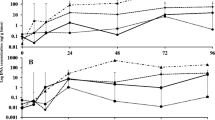
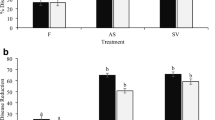
The effect of extracts of the brown algae Cystoseira myriophylloides, Laminaria digitata, and Fucus spiralis against the tomato pathogens Verticillium dahliae and Agrobacterium tumefaciens was evaluated in vitro and in the greenhouse. A significant inhibition of growth was observed only with methanolic seaweed extracts (MSE). Disease resistance was assessed in the greenhouse against Verticillium wilt using spray application of aqueous seaweed extracts (ASE) on the whole plant or using seed imbibition. Both methods significantly reduced disease severity whatever the algal species, though protection observed after seed treatments was higher than that observed after spray treatment. Spray application of ASE from C. myriophylloides and F. spiralis also resulted in significant reduction of Crown gall disease caused by the bacterial pathogen A. tumefaciens. ASE-treated plants had significantly higher levels of activity of defense enzymes polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase compared to the control. ASE did not inhibit mycelium growth of V. dahliae or development of A. tumefaciens in vitro; it is therefore suggested that induced resistance is probably the main mechanism of protection afforded by ASE.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abkhoo J, Sabbagh SK (2016) Control of Phytophthora melonis damping-off, induction of defense responses, and gene expression of cucumber treated with commercial extract from Ascophyllum nodosum. J Appl Phycol 28:1333–1342
Abouraïcha E, El Alaoui-Talibi Z, Tadlaoui-Ouafi A, El Boutachfaiti R, Petit E, Douira A, Courtois B, Courtois J, El Modafar C (2016) Glucuronan and oligoglucuronans isolated from green algae activate natural defense responses in apple fruit and reduce postharvest blue and gray mold decay. J Appl Phycol DOI. doi:10.1007/s10811-016-0926-0
Alexieva V, Sergiev I, Mapelli S, Karanov E (2001) The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 24:1337–1344
Alghazeer R, Whida F, Abduelrhman E, Gammoudi F, Azwai S (2013) Screening of antibacterial activity in marine green, red and brown macroalgae from the western coast of Libya. Natural Sci 5:7–14
Ara J, Sultana V, Qasim R, Etheshamul-Haque S, Vigar Uddin A (2005) Biological activity of Spatoglossum asperum: a brown alga. Phytother Res 19:618–623
Arunkumar K, Selvapalam N, Rengasamy R (2005) The antibacterial compound sulphoglycerolipid palmitoyl-3-0(6′-sulpho-αquinovopyranosyl)-glycerol from Sargassum wightii Greville (Phaeophyceae). Bot Mar 40:441–445
Aziz A, Poinssot B, Daire X, Adrian M, Bézier A, Lambert B, Joubert JM, Pugin A (2003) Laminarin elicits defense responses in grapevine and induces protection against Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola. Mol Plant Microbe Int 16:1118–1128
Benhissoune S, Boudoiuresque C-F, Verlaque M (2002) A checklist of the seaweeds of the Mediterranean and Atlantic coasts of Morocco. II. Phaeophyceae. Bot Mar 45:217–230
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Buzi A, Chilosi G, De Sillo D, Magro P (2004) Induction of resistance in melon to Didymella bryoniae and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by seed treatments with acibenzolar-S-methyl and jasmonate but not with salicylic acid. J Phytopathol 152:34–42
Calvo P, Nelson L, Kloepper JW (2014) Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant Soil 383:3–41
Chanthini K, Sreenath Kumar C, Jayasurya Kingsley S (2012) Antifungal activity of seaweed extracts against phytopathogen Alternaria solani. J Acad Indust Res 1:86–90
Chase AR (1989) Aliette 80WP and bacterial disease control-III. Phytotoxicity. Foliage Digest 12:4–5
Cherrab M, Bennani A, Charest PM, Serrhini MN (2002) Pathogenecity and vegetative compatibility of Verticillium dahlia Kleb. Isolates from olives in Morocco. J Phytopathol 150:703–709
Conrath U, Beckers GJM, Langenbach CJG, Jaskiewicz MR (2015) Priming for enhanced defense. Annu Rev Phytopathol 53:97–119
Cox S, Abu-Ghannam N, Gupta S (2010) An assessment of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of six species of edible Irish seawees. Int Food Res J 17:205–220
Escobar M, Dandekar MA (2003) Agrobacterium tumefaciens as an agent of disease. Trends Plant Sci 8:380–386
Faize M, Burgos L, Faize L, Petri C, Barba-Espin G, Díaz-Vivancos P, Clemente-Moreno MJ, Alburquerque HJA (2012) Modulation of tobacco bacterial disease resistance using cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase and Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase. Plant Pathol 5:858–866
Farrand SK (1990) Agrobacterium radiobacter K84: a model biocontrol system. In: Baker RR, Dunn PE (eds) New directions in biological control: alternatives for suppressing agricultural pests and diseases. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp. 679–691
Fradin EF, Thomma BPHJ (2006) Physiology and molecular aspects of Verticillium wilt diseases caused by V. dahlia and V. albo-atrum. Mol Plant Pathol 7:71–86
Hernández-Herrera RM, Virgen-Calleros G, Ruiz-Lopez M, Zañudo-Hernández J, Delano-Frier JP, Sanchez-Hernández C (2014) Extracts from green and brown seaweeds protect tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) against necrotrophic fungus Alternaria solani. J Appl Phycol 26:1607–1614
Hiraga S, Sasaki K, Ito H, Ohashi Y, Matsui H (2001) A large family of class III plant peroxidases. Plant Cell Physiol 42:462–468
Indira K, Balakrishnan S, Srinivasan M, Bragadeeswaran S, Balasubramanian T (2013) Evaluation of in vitro antimicrobial property of seaweed (Halimeda tuna) from Tuticorin coast, Tamil Nadu, southeast coast of India. Afr J Biotechnol 12:284–289
Jayaraj J, Wan A, Rahman M, Punja ZK (2008) Seaweed extract reduces foliar fungal diseases on carrot. Crop Prot 27:1360–1366
Jayaraj J, Norrie J, Punja ZK (2011) Commercial extract from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum reduces fungal diseases in greenhouse cucumber. J Appl Phycol 23:353–361
Jiménez E, Dorta F, Medina C, Ramirez A, Ramirez I, Peña-Cortés H (2011) Antiphytopathogenic activities of macro-algae extracts. Mar Drugs 9:739–756
Klarzynski O, Plesse B, Joubert JM, Yvin JC, Kopp M, Kloareg B, Fritig B (2000) Linear beta-1,3 glucans are elicitors of defense responses in tobacco. Plant Physiol 124:1027–1037
Klosterman SJ, Atallah ZK, Vallad GE, Subbarao KV (2009) Diversity, pathogenicity, and management of Verticillium species. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47:39–62
Kumar CS, Sarada DVL, Rengasamy R (2008) Seaweed extracts control the leaf spot disease of the medicinal plant Gymnema sylvestre. Indian J Sci Technol 3:1–5
Kumari R, Kaur I, Bhatnagar AK (2011) Effect of aqueous extract of Sargassum johnstonii Setchell & Gardner on growth, yield and quality of Lycopersicon esculantum Mill. J Appl Phycol 23:623–633
Lamb C, Dixon RA (1997) The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:251–275
Li B, Lu F, Wei X, Zhao R (2008) Fucoidan: structure and bioactivity. Molecules 13:1671–1695
Masia A, Ventura M, Gemma H, Sansavini S (1998) Effect of some plant growth regulator treatments on apple fruit ripening. Plant Growth Regul 25:127–134
Mattner SW, Wite D, Riches DA, Porter IJ, Arioli T (2013) The effect of kelp extract on seedling establishment of broccoli on contrasting soil types in southern Victoria, Australia. Biol Agric Hortic 29:258–270
Mattner SW, Villalta ON, Wite D, Porter IJ, Arioli T (2014) In vitro suppression of Sclerotinia minor by a seaweed extract from Durvillaea potatorum and Ascophyllum nodosum. Aust Plant Dis Notes 9:137
Mayer A (2006) Polyphenol oxidases in plants and fungi: going places? Phytochemistry 67:2318–2331
Mercier L, Lafitte C, Borderies G, Briand X, Esquerre-Tugaye MT, Fournier J (2001) The algal polysaccharide carrageenans can act as an elicitor of plant defence. New Phytol 149:43–51
Moerschbacher B, Heck B, Kogel KH, Obst O, Reisener H (1986) An elicitor of the hypersensitive lignification response in wheat leaves isolated from the rust fungus Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. II. Induction of enzymes correlated with the biosynthesis of lignin. Z Naturforsch 41c:839–844
Naseem M, Kunz M, Dandekar T (2014) Probing the unknowns in cytokinin-mediated immune defense in Arabidopsis with systems biology approaches. Bioinform Biol Insights 8:35–44
Orzali L, Forni C, Riccion L (2014) Effect of chitosan seed treatment as elicitor of resistance to Fusarium graminearum in wheat. Seed Sci Technol 42:132–149
Paudel S, Rajotte EG, Felton GW (2014) Benefits and costs of tomato seed treatment with plant defense elicitor for insect resistance. Arthropod Plant Interact 8:539–545
Paulert R, Ebbinghaus D, Urlass C, Moerschbacher B (2010) Priming of the oxidative burst in rice and wheat cell cultures by ulvan, a polysaccharide from green macroalgae, and enhanced resistance against powdery mildew in wheat and barley plants. Plant Pathol 59:634–642
Prabha V, Prakash DJ, Sudha PN (2013) Analysis of bioactive compounds and antimicrobial activity of marine algae Kappaphycus alvarezii using three solvent extracts. IJPSR 4:306–310
Raghavendra VB, Lokesh S, Prakash HS (2007) Dravya, a product of seaweed extract (Sargassum wightii), induces resistance in cotton against Xanthomonas campestris pv. malvacearum. Phytoparasitica 35:442–449
Reitz SR, Trumble SR (1996) Effects of cytokinins containing seaweed extract on Phaseolus lunatus L.: influence on nutrient availability and apex removal. Bot Mar 39:33–38
Rekanovic E, Milijasevic S, Todorovic B, Potocnik I (2007) Possibilities of biological and chemical control of Verticillium wilt in pepper. Phytoparasitica 35:436–441
Ryder MH, Jones DA (1991) Biological control of crown gall using Agrobacterium strains K84 and K1026. Aust J Plant Physiol 18:571–579
Sigee DC (1993) Bacterial plant pathology: cell and molecular aspects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Stadnik MJ, de Freitas MB (2014) Algal polysaccharides as source of plant resistance inducers. Trop Plant Pathol 39:111–118
Suleria HAR, Osborne S, Masci P, Gobe G (2015) Marine-based nutraceuticals: an innovative trend in the food and supplement industries. Mar Drugs 13:6336–6351
Talboys PW (1984) Chemical control of Verticillium wilts. Phytopathol Mediterr 23:163–175
Tian L, Wang KR, Lu JY (1998) Effect of carbendazim and tricyclazole on microsclerotia and melanin formation of Verticillium dahliae. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica 28:263–268
Varahalarao V, Chandrasekhar NK (2009) In vitro antimicrobial potentiality of some marine algae against selected phytopathogens. Biomed Pharmacol J 2:277–280
Wite D, Mattner SW, Porter IJ, Arioli T (2015) The suppressive effect of a commercial extract from Durvillaea potatorum and Ascophyllum nodosum on infection of broccoli by Plasmodiophora brassicae. J Appl Phycol 27:2157–2161
Worrall D, Holroyd GH, Moore JP, Glowacz M, Croft P, Taylor JE, Paul ND, Roberts MR (2012) Treating seeds with activators of plant defence generates longlasting priming of resistance to pests and pathogens. New Phytol 193:770–778
Zhang X, Ervin EH, Schmidt RE (2003) Physiological effects of liquid applications of seaweed extract and humic acid on creeping bentgrass. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 128:492–496
Zine H, Rifai LA, Faize M, Smaili A, Makroum K, Belfaiza M, Kabil EM, Koussa T (2016) Duality of acibenzolar-S-methyl in the inhibition of pathogen growth and induction of resistance during the interaction tomato/vertcillium dahliae. Eur J Plant Pathol 145:61–69
Zucconi F, Pera A, Forte M, De Bertoli M (1981) Evaluating toxicity in immature compost. Biocycle 22:54–57
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Moroccan CNRST (Centre National de Recherche Scientifique et Technique) within the frame work of the RS/2011/22 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 11587 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esserti, S., Smaili, A., Rifai, L.A. et al. Protective effect of three brown seaweed extracts against fungal and bacterial diseases of tomato. J Appl Phycol 29, 1081–1093 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0996-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0996-z