Abstract
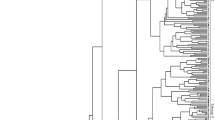
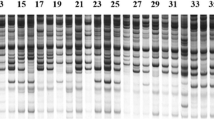
Targeted selection and continuous self-crossing were utilized to breed a new Saccharina variety. After five-generation selection breeding, the new high-yield variety “Ailunwan” with stable genetic traits was obtained. Blade length, width, thickness, and fresh weight of variety “Ailunwan” were increased by 20.2, 11.0, 49.5, and 27.3 %, respectively, and the dry matter content increased by 11.8 % compared to the control (a widely used commercial variety). Frequency distributions and coefficients of variation of blade length, width, and fresh weight are discussed, and results showed that variety “Ailunwan” had more excellent traits and lower genetic variation than the control. Grey relational analysis of fresh weight-related traits showed that each related trait was in the same correlation order both in the fourth and in the fifth generations of “Ailunwan.” On the basis of sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) analysis, the fifth generation of “Ailunwan” had the lowest gene diversity (H = 0.234) compared to the other five varieties including “Zaohoucheng” (H = 0.324), “Dongfang No. 2” (H = 0.260), “Dongfang No. 3” (H = 0.265), “Pingbancai” (H = 0.249), and the control (H = 0.270), which displayed the advantage of genetic stability. Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic Mean (UPGMA) cluster analysis based on SRAP marker also revealed that variety “Ailunwan” can be distinguished from other cultivation varieties in China and its genetic structure is relatively stable.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
Billot C, Boury S, Benet H, Kloareg B (1999) Development of RAPD markers for parentage analysis in Laminaria digitata. Bot Mar 42:307–314
Bixler HJ, Porse H (2011) A decade of change in the seaweed hydrocolloids industry. J Appl Phycol 23:321–335
Ding WD, Cao ZM, Cao LP (2010) Molecular analysis of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) by SRAP and SCAR molecular markers. Aquac Int 18:575–587
Fang TC, Wu CY, Jiang BY, Li JJ, Ren KJ (1962) The breeding of a new breed of Haidai (Laminaria japonica) and its preliminary genetic analysis. Acta Bot Sin 10:197–209 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fang TC, Ou YL, Cui JJ (1985) Breeding of hybrid Laminaria “Danza No. 10”—an application of the Laminaria haploid cell clones. J Shandong Coll Oceanol 15:64–72 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Feng FJ, Chen MM, Zhang DD, Sui X, Han SJ (2009) Application of SRAP in the genetic diversity of Pinus koraiensis of different provenances. Afr J Biotechnol 8:1000–1008
Ferriol M, Pico B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:271–282
Guillemaut P, Drouard LM (1992) Isolation of plant DNA: a fast, inexpensive, and reliable method. Plant Mol Biol Report 10:60–65
IOIMF (Institute of Oceanology, Institute of Marine Fisheries) (1976) The breeding of new varieties of Haidai (Laminaria japonica) with high production and high iodine content. Sci Sin 19:243–252 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jensen A (1993) Present and future needs for algae and algal products. Hydrobiologia 269:13–23
Ji MH (1997) Seaweed chemistry. Science, Beijing, p 777 (in Chinese)
Kain JM (1979) A view on the genus Laminaria. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 17:101–161
Lai YP, Li J, Zhang ZQ, Dong XF, Liu XC, Wei HT, Hu XR, Peng ZS, Yang WY (2009) Grey correlation analysis of morphological traits related to drought tolerance of wheat at seedling stage. J Triticeae Crops 29(6):1055–1059 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Li ZB, Shang XW (2007b) Evaluating quality of flour for Lanzhou hand-extended noodles by Grey related degree analysis. J Triticeae Crops 27(1):59–62, in Chinese with English abstract
Li XJ, Cong YZ, Yang GP, Qu SC, Li ZL, Wang GW, Zhang ZZ, Luo SJ, Dai HL, Xie JZ, Jiang JL, Wang TY (2007a) Trait evaluation and trial cultivation of Dongfang No. 2, the hybrid of a male gametophyte clone of Laminaria longissima (Laminariales, Phaeophyta) and a female one of L. japonica. J Appl Phycol 19:139–151
Lin ZX, Zhang XL, Nie YC (2004) Evaluation of application of a new molecular marker SRAP on analysis of F2 segregation population and genetic diversity in cotton. Acta Genet Sin 31:622–626
Luo YC, Yin ZC (2013) Marker-assisted breeding of Thai fragrance rice for semi-dwarf phenotype, submergence tolerance and disease resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight. Mol Breed 32:709–721
Miller MP (1997) Tools for population genetic analysis (TFPGA) 1.3: a window program for the analysis of allozyme and molecular population genetic data. Computer software distributed by author
Qiao LX, Liu HY, Guo BT, Weng ML, Dai JX, Duan DL, Wang B (2007) Molecular identification of 16 Porphyra lines using sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Aquat Bot 87:203–208
Shi YY, Yang GP, Liao MJ, Liu YJ, Shang S, Li XJ, Cong YZ (2008) Comparative study on the microsatellite DNA polymorphism of the gametophytes of L. japonica and L. longissima. Period Ocean Univ China 38(2):303–308 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Vandemark GJ, Ariss JJ, Bauchan GA, Larsen RC, Hughes TJ (2006) Estimating genetic relationships among historical sources of alfalfa germplasm and selected cultivars with sequence related amplified polymorphisms. Euphytica 152:9–16
Wang XL, Liu CL, Li XJ, Cong YZ, Duan DL (2005) Assessment of genetic diversities of selected Laminaria (Laminarales, Phaeophyta) gametophytes by inter-simple sequence repeat analysis. J Integr Plant Biol 47(6):753–758
Wang ZK, Wang C, Guan FC (2013) Comprehensive evaluation of walnuts from different growing regions. Food Sci 34(15):100–103 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (1999) POPGENE, version 1.31. Microsoft window-based freeware for population genetic analysis. Quick user guide (Francis Yeh, University of Alberta, Canada). www.ualberta.ca/-fyeh
Yin L, Lu XP, Li MN, Guo J (2006) The Grey relation analysis and evaluation of hybrid Pacesetter. J Grassl 28(3):21–25 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yotsukura N, Kawai T, Motomura T, Ichimura T (2001) Random amplified polymorphic DNA markers for three Japanese Laminaria species. Fish Sci 67:857–862
Zhang QS, Tang XX, Cong YZ, Qu SC, Luo SJ, Yang GP (2007) Breeding of an elite Laminaria variety 90-1 through interspecific gametophyte crossing. J Appl Phycol 19:303–311
Zhang QS, Shi YY, Cong YZ, Qu SC, Shang S, Yang GP (2008) AFLP analysis of the gametophyte clones derived from introduced Laminaria (Phaeophyta) and cultured varieties of China. Period Ocean Univ China 28:429–435 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang J, Liu Y, Yu D, Song HZ, Cui JJ, Liu T (2011) Study on high-temperature-resistant and high-yield Laminaria variety “Rongfu”. J Appl Phycol 23:165–171
Acknowledgments
We thank Lichao Wang, Guojun Li, Yi Li, and Lei Wang from Xunshan Group Co., Ltd for their work in Saccharina cultivation. This work was supported by Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201203063), Science and Technology Development Planning Project of Shandong Province (2014GGE29091), Agricultural Seed Project of Shandong Province, and TaiShan industrial Experts Programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Liu, T., Bian, D. et al. Breeding and genetic stability evaluation of the new Saccharina variety “Ailunwan” with high yield. J Appl Phycol 28, 3413–3421 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0810-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0810-y