Abstract
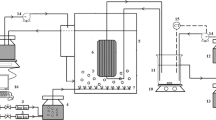
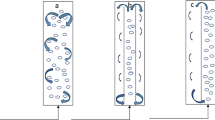
In a tubular photobioreactor, a degassing column is often used for oxygen removal and carbon dioxide addition. The column may limit growth because the conditions are optimal only right after the degassing zone. In the present study, we tested continuous oxygen removal and nutrient delivery by placing a porous membrane tube inside a photobioreactor tube. The membrane tube would simultaneously remove dissolved oxygen and release nutrients and carbon dioxide to the photobioreactor tube. We tested oxygen as a model of gas exchange; nitrate and ammonium were tested as models of macronutrients and copper as a model of micronutrients. Oxygen-poor or nutrient-rich water was flowed in a dialysis tube placed inside a glass tube containing originally air-saturated water. In 60 min, the concentration of oxygen decreased by 48 % of the initial value and the nutrients reached 55–90 % of the feed flow concentration. The results suggest that integrating a porous membrane tube into the tubular photobioreactor tube can improve oxygen removal and nutrient delivery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennan L, Owende P (2010) Biofuels from microalgae—a review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14:557–577
Cai T, Park SY, Li Y (2013) Nutrient recovery from wastewater streams by microalgae: status and prospects. Renew Sust Energ Rev 19:360–369
Camacho Rubio F, Acién Fernández FG, Sánchez Pérez JA, García Camacho F, Molina Grima E (1999) Prediction of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration profiles in tubular photobioreactors for microalgal culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:71–86
Carvalho AP, Pontes I, Gaspar H, Malcata FX (2006) Metabolic relationships between macro- and micronutrients, and the eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid contents of Pavlova lutheri. Enzyme Microb Technol 38:358–366
Chai X, Zhao X (2012) Enhanced removal of carbon dioxide and alleviation of dissolved oxygen accumulation in photobioreactor with bubble tank. Bioresour Technol 116:360–365
Cheng S (2003) Heavy metals in plants and phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:335–340
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae: research review paper. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
Dor I (1977) Process for promotion of algae growth in a sewage medium. US Patent 40443903A
Ferreira BS, Fernandes HL, Reis A, Mateus M (1998) Microporous hollow fibres for carbon dioxide absorption: mass transfer model fitting and the supplying of carbon dioxide to microalgal cultures. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 71:61–70
Kim N-J, Lee C-G (2001) A theoretical consideration on oxygen production rate in microalgal cultures. Biotechnol Bioproc Eng 6:352–358
Lee Y-K, Hing H-K (1989) Supplying CO2 to photosynthetic algal cultures by diffusion through gas-permeable membranes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:298–301
Li Y, Horsman M, Wang B, Wu N (2008) Effects of nitrogen sources on cell growth and lipid accumulation of green alga Neochloris oleoabundans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:629–636
Lide DR (ed) (2000) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 81st edition 2000–2001. CRC, Boca Raton
Molina Grima E, Acién Fernández FG, García Camacho F, Chisti Y (1999) Photobioreactors: light regime, mass transfer, and scaleup. J Biotechnol 70:231–247
Molina Grima E, Acién Fernández FG, García Camacho F, Camacho Rubio F, Chisti Y (2000) Scale-up of tubular photobioreactors. J Appl Phycol 12:355–368
Molina E, Fernández J, Acién FG, Chisti Y (2001) Tubular photobioreactor design for algal cultures. J Biotechnol 92:113–131
Pulz O (2001) Photobioreactors: production systems for phototrophic microorganisms: mini-review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:287–293
Pulz O, Gross W (2004) Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae: mini-review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:635–648
Putt R, Singh M, Chinnasamy S, Das KC (2011) An efficient system for carbonation of high-rate algae pond water to enhance CO2 mass transfer. Bioresour Technol 102:3240–3245
Raso S, van Genugten B, Vermuë M, Wijffels R (2012) Effect of oxygen concentration on the growth of Nannochloropsis sp. at low light intensity. J Appl Phycol 24:863–871
Redfield AC (1934) On the proportions of organic derivations in sea water and their relation to the composition of plankton. In: Daniel RJ (ed) James Johnstone memorial volume. University Press of Liverpool, Liverpool, pp 177–192
Sánchez Mirón A, Contreras Gómez A, García Camacho F, Molina Grima E, Chisti Y (1999) Comparative evaluation of compact photobioreactors for large-scale monoculture of microalgae. J Biotechnol 70:249–270
Seader JD, Henley EJ (2006) Separation process principles, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, p 68
Su Z, Kang R, Shi S, Cong W, Cai Z (2010) An effective device for gas–liquid oxygen removal in enclosed microalgae culture. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:428–437
Tyystjärvi E (2004) Phototoxicity. In: Noodén LD (ed) Plant cell death processes. Academic, Amsterdam, pp 271–283
Ugwu CU, Aoyagi H, Uchiyama H (2008) Photobioreactors for mass cultivation of algae: review. Bioresour Technol 99:4021–4028
Van Den Hende S, Vervaeren H, Boon N (2012) Flue gas compounds and microalgae: (bio-) chemical interactions leading to biotechnological opportunities. Biotechnol Adv 30:1405–1424
Wang B, Lan CQ, Horsman M (2012) Closed photobioreactors for production of microalgal biomasses. Biotechnol Adv 30:904–912
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the European Regional Development Fund (Bio Refine Tech project coordinated by Cursor Oy). ET was also supported by Academy of Finland. The authors are responsible for study design and collection and interpretation of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ojanen, S., Tyystjärvi, E., Holmberg, H. et al. Porous membrane as a means of gas and nutrient exchange in a tubular photobioreactor. J Appl Phycol 27, 1169–1175 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0397-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0397-0