Abstract
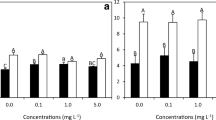
The economic red alga, Gracilaria lemaneiformis Bory, was grown at different depths in the coastal waters of the South China Sea, and its growth, pigments, ultra-violet (UV)-absorbing compounds and agar yield were investigated in order to see the impacts of depth change. Gracilaria lemaneiformis grew slower at greater depths in March, while the highest relative growth rate (RGR) was found at about 1.0 m depth in April, about 9% higher than that at surface water (0.5 m below the surface). The RGR increased with the increasing daily photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) dose received by the thalli at different depths. The contents of phycoerythrin and chlorophyll a increased, while that of UV-absorbing compounds (UVAC, absorption peak at 325 nm) decreased with increased depth. The highest levels of the UVAC in the thalli grown in surface seawater played a protective role against solar UV radiation (280–400 nm). The content of UVAC declined at deeper depths and under indoor low PAR. The agar yield of the thalli increased with the increasing depths, with the highest content found at 3.5 m depth.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armisen R (1995) World-wide use and importance of Gracilaria. J Appl Phycol 7:231–243
Beer S, Eshel A (1985) Determining phycoerythrin and phycocyanin concentrations in aqueous crude extracts of red algae. Aust J Mar Freshw Res 36:785–792
Bischof K, Kräbs G, Wiencke C, Hanelt D (2002) Solar ultraviolet radiation affects the activity of ribulose−1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase and the composition of photosynthetic and xanthophylls cycle pigments in the intertidal green alga Ulva lactuca L. Planta 215:502–509
Buma AGJ, De Boer MK, Boelen P (2001) Depth distributions of DNA damage in Antarctic marine phyto- and bacterioplankton exposed to summertime UV radiation. J Phycol 37:200–208
Dunlap WC, Rae GA, Helbling EW, Villafañe VE, Holm-Hansen O (1995) Ultraviolet-absorbing compounds in natural assemblages of Antarctic phytoplankton. Antarct J 30:323–326
Eswaran K, Mairh OP, Subbarao PV (2002) Inhibition of pigments and phycocolloid in a marine red alga Gracilaria edulis by Ultraviolet-B radiation. Biol Plantarum 45:157–159
Gao K, McKinley KR (1994) Use of macroalgae for marine biomass production and CO2 remediation: a review. J Appl Phycol 6:45–60
Franklin LA, Forster RM (1997) The changing irradiance environment: consequences for marine macrophyte physiology, productivity and ecology. Eur J Phycol 32:207–232
Flores-Moya A, Hanelt D, Figueroa F, Altamirano M, Vinegla B, Salles S (1999) Involvement of solar UV-B radiation in recovery of inhibited photosynthesis in the brown alga Dictyota dichotoma (Hudson) Lamouroux. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 49:129–135
Häder DP, Lebert M, Marangoni R, Colombetti G (1999) ELDONET-European light dosimeter network hardware and software. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 52:51–58
Häder DP, Porst M, Lebert M (2001) Photoinhibition in common Atlantic macroalgae measured on site in Gran Canaria. Helgol Mar Res 55:67–76
Han T, Han YS, Kain JM, Häder DP (2003) Thallus differentiation of photosynthesis, growth, reproduction, and UV-B sensitivity in the green alga Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 39:712–721
Hanelt D, Wiencke C, Nultsch W (1997) Influence of UV radiation on the photosynthesis of arctic macroalgae in the field. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 38:40–47
Henry BE, Van Alstyne KL (2004) Effects of UV radiation on growth and phlorotannins in Fucus gardneri (Phaeophyceae) juveniles and embryos. J Phycol 40:527–533
Karsten U, Sawall T, Wiencke C (1998) A survey of the distribution of UV-absorbing substances in tropical macroalgae. Phycol Res 46:271–279
Maegawa M, Kunieda M, Kida W (1993) Difference of the amount of UV-absorbing substance between shallow and deep water red algae. Jpn J Phycol 41:351–354
Malta M, Rijstenbil JW, Brouwer PEM, Kromkamp JC (2003) Vertical heterogeneity in physiological characteristics of Ulva spp. mats. Mar Biol 143:1029–1038
Marinho-Soriano E, Bourret E, De Casabianca ML, Maury L (1999) Agar form the reproductive and vegetative stages of Gracilaria bursa-pastoris. Bioresour Technol 67:1–5
Molloy FJ, Bolton JJ (1996) The effect of season and depth on the growth of Gracilaria gracilis at Luderitz, Namibia. Bot Mar 39:407–413
Pakker H, Beekman CAC, Breeman AM (2000a) Efficient photoreactivation of UVB-induced DNA damage in the sublittoral macroalga Rhodymenia pseudpalmata (Rhodophyta) in relation to ultraviolet-B-exposure. Eur J Phycol 35:109–114
Pakker H, Martins R, Boelen P, Buma AGJ, Nikaido O, Breeman AM (2000b) Effects of temperature in the photoreactivation of ultraviolet-B induced DNA damage in Palmaria palmate (Rhodophyta). J Phycol 36:334–341
Ramus J, Beale SI, Mauzerall D, Haward KL (1976) Changes in photosynthetic pigment concentration in seaweeds as a function of water depth. Mar Biol 37:223–229
Raven JA (1991) Responses of aquatic photosynthetic organisms to increased solar UV-B. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 9:239–244
Viñegla B, Segovia M, Figueroa FL (2006) Effect of artificial UV radiation on carbon and nitrogen metabolism in the macroalgae Fucus spiralis L. and Ulva olivascens Dangeard. Hydrobiologia 560:31–42
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total cartenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Zacher K, Roleda MY, Hanelt D, Wiencke C (2007) UV effects on photosynthesis and DNA in propagules of three Antarctic seaweeds (Adenocystis utricularis, Monostroma hariotii and Porphyra endiviifolium). Planta (In press)
Acknowledgement
This study was funded by “863” project (2006AA10A413) from Ministry of Science and Technology and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Key Project No. 90411018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Gao, K. Growth, pigments, UV-absorbing compounds and agar yield of the economic red seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta) grown at different depths in the coastal waters of the South China Sea. J Appl Phycol 20, 681–686 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-007-9247-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-007-9247-7