Abstract
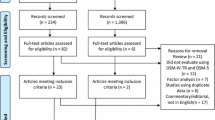
This review focuses on identifying up-to-date number of publications that compared DSM-IV/ICD-10 Asperger’s disorder (AspD) to Autistic Disorder/High-functioning Autism (AD/HFA). One hundred and twenty-eight publications were identified through an extensive search of major electronic databases and journals. Based on more than 90 clinical variables been investigated, 94 publications concluded that there were statistically significant or near significant level of quantitative and/or qualitative differences between AspD and AD/HFA groups; 4 publications found both similarities and differences between the two groups; 30 publications concluded with no differences between the two groups. Although DSM-5 ASD will eliminate Asperger’s disorder. However, it is plausible to predict that the field of ASD would run full circle during the next decade or two and that AspD will be back in the next edition of DSM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allik, H., Larsson, J. O., & Smedje, H. (2006). Sleep patterns of school-age children with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 585–595.
American Psychiatric Association. (1980). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (1987). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd edn., Revised). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: APA Press.
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental Disorders (4th edn., Text Revision). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association. (2010). Autistic disorder. Retrieved September 16, 2010, from http://www.dsm5.org/Proposed Revisions/Pages/proposedrevision.aspx?rid = 94#.
American Psychiatric Association. (2011). Proposed draft revisions to DSM disorders and criteria: A09 autism spectrum disorder. Arlington,VA: American Psychiatric Association; Available at: http://www.dsm5.org/ProposedRevisions/ Pages/proposedrevision.aspx?rid_94#. Accessed November 21, 2011.
American Psychiatric Association. (2011b). A 09 autism spectrum disorder. Retrieved November 23, 2011 from http://www.DSM-5.org/Documents/12 03%20Autism%20Spectrum %20Disorders%20-%20DSM-5.pdf.
American Psychiatric Association. (2012). DSM-5 proposed criteria for autism spectrum disorder designed to provide more accurate diagnosis and treatment. Press release. American Psychiatric Association. http://www.DSM-5.org/Documents/12-03%20Auti sm%20Spectrum%20Disorders%20-%20DSM-5.pdf. Accessed February 15, 2012.
Ariella Ritvo, R., Ritvo, E. R., Guthrie, D., & Ritvo, M. J. (2008). Clinical evidence that Asperger’s disorder is a mild form of autism. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 49, 1–5.
Asperger, H. (1944/1991). ‘‘Autistic psychopathy’’ in childhood. Translated and annotated by U. Frith. In U. Frith (Ed.), Autism and Asperger syndrome (pp. 37–92). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Barbaro, J., & Dissanayake, C. (2007). A comparative study of the use and understanding of self-presentational display rules in children with high functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 1235–1246.
Bonnel, A., McAdams, S., Smith, B., Berthiaume, C., Bertone, A., Ciocca, V., et al. (2010). Enhanced pure-tone pitch discrimination among persons with autism but not Asperger syndrome. Neuropsychologia, 48, 2465–2475.
Cederlund, M., Hagberg, B., Billstedt, E., Gillberg, I. C., & Gillberg, C. (2008). Asperger syndrome and autism: A comparative longitudinal follow-up study more than 5 years after original diagnosis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 72–85.
Craig, J., & Baron-Cohen, S. (1999). Creativity and imagination in autism and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 319–326.
Cuccaro, M. L., Nations, L., Brinkley, J., Abramson, R. K., Wright, H. H., Hall, A., Gilbert, J., & Pericak-Vance, M. A. (2007). A comparison of repetitive behaviors in Aspergers disorder and high functioning autism. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 37, 347–360.
Dahlgren, S. O., & Trillingsgaard, A. (1996). Theory of mind in non-retarded children with autism and Asperger’s syndrome: A research note. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 37, 759–763.
Dawson, S., Glasson, E. J., Dixon, G., & Bower, C. (2009). Birth defects in children with autism spectrum disorders: A population-based, nested case-control study. American Journal of Epidemiology, 169, 1296–1303.
De Bruin, E. I., Verheij, F., & Ferdinand, R. F. (2006). WISC-R subtest but no overall viq-piq difference in Dutch children with pdd-nos. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 34, 263–271.
Dissanayake, C., Bui, Q. M., Huggins, R., & Loesch, D. Z. (2006). Growth in stature and head circumference in high-functioning autism and Asperger disorder during the first 3 years of life. Developmental Psychopathology, 18, 381–393.
Dissanayake, C., Shembrey, J., & Suddendorf, T. (2010). Delayed video self-recognition in children with high functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Autism, 14, 495–508.
Dyck, M. J., Ferguson, K., & Shochet, I. M. (2001). Do autism spectrum disorders differ from each other and from non-spectrum disorders on emotion recognition tests? European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 10, 105–116.
Ehlers, S., Nydén, A., Gillberg, C., Sandberg, A. D., Dahlgren, S. O., Hjelmquist, E., et al. (1997). Asperger syndrome, autism and attention disorders: A comparative study of the cognitive profiles of 120 children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 38, 207–217.
Eisenmajer, R., Prior, M., Leekam, S., Wing, L., Gould, J., Welham, M., et al. (1996). Comparison of clinical symptoms in Autism and Asperger’s disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 1523–1531.
Endo, T., Shioiri, T., Kitamura, H., Kimura, T., Endo, S., Masuzawa, N., et al. (2007). Altered chemical metabolites in the amygdala-hippocampus region contribute to autistic symptoms of autism spectrum disorders. Biological Psychiatry, 62, 1030–1037.
Enticott, P. G., Bradshaw, J. L., Iansek, R., Tonge, B. J., & Rinehart, N. J. (2009). Electro- physiological signs of supplementary-motor-area deficits in high-functioning autism but not Asperger syndrome: An examination of internally cued movement-related potentials. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 51, 787–791.
Enticott, P. G., Rinehart, N. J., Tonge, B. J., Bradshaw, J. L., & Fitzgerald, P. B. (2010). A preliminary transcranial magnetic stimulation study of cortical inhibition and excitability in high-functioning autism and Asperger disorder. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 52, 179–183.
Fine, J., Bartolucci, G., Szatmari, P., & Ginsberg, G. (1994). Cohesive discourse in pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24, 315–329.
Foley-Nicpon, M., Assouline, S. G., & Stinson, R. D. (2012). Cognitive and academic distinctions between gifted students with autism and Asperger syndrome. Gifted Child Quarterly, 56, 77–89.
Gadow, K. D., DeVincent, C. J., Pomeroy, J., & Azizian, A. (2004). Psychiatric symptoms in preschool children with PDD and clinic and comparison samples. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34, 379–393.
Gepner, B., & Mestre, D. R. (2002). Brief report: Postural reactivity to fast visual motion differentiates autistic from children with Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32, 231–238.
Ghanizadeh, A. (2011). Can tactile sensory processing differentiate between children with autistic disorder and Asperger’s disorder? Innovations in Clinical Neuroscience, 8, 25–30.
Ghaziuddin, M. (2005). A family history study of Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35, 177–182.
Ghaziuddin, M. (2007). Defining the behavioral phenotype of Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 138–142.
Ghaziuddin, M. (2010). Brief report: Should the DSM V drop Asperger syndrome? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40, 1146–1148.
Ghaziuddin, M., & Butler, E. (1998). Clumsiness in autism and Asperger syndrome: A further report. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 1998(42), 43–48.
Ghaziuddin, M., Butler, E., Tsai, L., & Ghaziuddin, N. (1994). Is clumsiness a marker for Asperger syndrome? Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 38, 519–527.
Ghaziuddin, M., & Gerstein, L. (1996). Pedantic speaking style differentiates Asperger syndrome from high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 26, 585–595.
Ghaziuddin, M., Leininger, L., & Tsai, L. (1995a). Brief report: Thought disorder in Asperger syndrome: comparison with high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 25, 311–317.
Ghaziuddin, M., & Mountain-Kimchi, K. (2004). Defining the intellectual profile of Asperger syndrome: Comparison with high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34, 279–284.
Ghaziuddin, M., Shakal, J., & Tsai, L. (1995b). Obstetric factors in Asperger syndrome: Comparison with high-functioning autism. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 39, 538–543.
Gilchrist, A., Green, J., Cox, A., Burton, D., Rutter, M., & Le Couteur, A. (2001). Development and current functioning in adolescents with Asperger syndrome: A comparative study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 42, 227–240.
Gras-Vincendon, A., Mottron, L., Salamé, P., Bursztejn, C., & Danion, J. M. (2007). Temporal context memory in high-functioning autism. Autism, 11, 523–534.
Haglund, N. G., & Källén, K. B. (2011). Risk factors for autism and Asperger syndrome. Perinatal factors and migration. Autism, 15, 163–183.
Hallahan, B., Daly, E. M., McAlonan, G., Loth, E., Toal, F., O’Brien, F., et al. (2009). Brain morphometry volume in autistic spectrum disorder: A magnetic resonance imaging study of adults. Psychological Medicine, 39, 337–346.
Happé, F. (2011a). Why fold Asperger syndrome into autism spectrum disorder in the DSM-5? http://sfari.org/news-and-opinion/viewpoint/2011/why-fold-asperger-syndrome-into-autism-spectrum-disorder-in-the-dsm-5
Happé, F. (2011b). Editorial-criteria, categories, and continua: Autism and related disorders in DSM-5. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 6, 540–542.
Haznedar, M. M., Buchsbaum, M. S., Hazlett, E. A., LiCalzi, E. M., Cartwright, C., & Hollander, E. (2006). Volumetric analysis and three-dimensional glucose metabolic mapping of the striatum and thalamus in patients with autism spectrum disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 163, 1252–1263.
Holdnack, J., Goldstein, G., & Drozdick, L. (2011). Social perception and WAIS-IV performance in adolescents and adults diagnosed with Asperger’s syndrome and autism. Assessment, 18, 192–200.
Howlin, P. (2003). Outcome in high-functioning adults with autism with and without early language delays: Implications for the differentiation between autism and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism Developmental Disorders, 33, 3–13.
Hubbard, K., & Trauner, D. A. (2007). Intonation and emotion in autistic spectrum disorders. Journal of Psycholinguist Research, 36, 159–173.
Iwanaga, R., Kawasaki, C., & Tsuchida, R. (2000). Brief report: Comparison of sensory-motor and cognitive function between autism and Asperger syndrome in preschool children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 169–174.
Jiao, Y., Chen, R., Ke, X., Cheng, L., Chu, K., Lu, Z., et al. (2011). Predictive models for subtypes of autism spectrum disorder based on single-nucleotide polymorphisms and magnetic resonance imaging. Advances in Medical Sciences, 56, 334–342.
Jolliffe, T., & Baron-Cohen, S. (1997). Are people with autism and Asperger syndrome faster than normal on the Embedded Figures Test? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 38, 527–534.
Jolliffe, T., & Baron-Cohen, S. (1999a). The Strange Stories Test: A replication with high-functioning adults with autism or Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 395–406.
Jolliffe, T., & Baron-Cohen, S. (1999b). A test of central coherence theory: Linguistic processing in high-functioning adults with autism or Asperger syndrome: Is local coherence impaired? Cognition, 71, 149–185.
Jolliffe, T., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2000). Linguistic processing in high-functioning adults with autism or Asperger’s syndrome. Is global coherence impaired? Psychological Medicine, 30, 1169–1187.
Jou, R. J., Minshew, N. J., Keshavan, M. S., & Hardan, A. Y. (2010). Cortical gyrification in autistic and Asperger disorders: A preliminary magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Child Neurology, 25, 1462–1467.
Kaland, N. (2011). Brief report: Should Asperger syndrome be excluded from the forthcoming DSM-V? Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 5, 984–989.
Kamio, Y., & Toichi, M. (2007). Memory illusion in high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 867–876.
Kamp-Becker, I., Smidt, J., Ghahreman, M., Heinzel-Gutenbrunner, M., Becker, K., & Remschmidt, H. (2010). Categorical and dimensional structure of autism spectrum disorders: The nosologic validity of Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40, 921–929.
Kanai, C., Tani, M., Hashimoto, R., Yamada, T., Ota, H., Watanabe, H., et al. (2012). Cognitive profiles of adults with Asperger’s disorder, high-functioning autism, and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified based on the WAIS-III. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6, 58–64.
Kenworthy, L. E., Black, D. O., Wallace, G. L., Ahluvalia, T., Wagner, A. E., & Sirian, L. M. (2005). Disorganization: The forgotten executive dysfunction in high-functioning autism (HFA) spectrum disorders. Developmental Neuropsychology, 28, 809–827.
Kilpinen, H., Ylisaukko-Oja, T., Hennah, W., Palo, O. M., Varilo, T., Vanhala, R., et al. (2008). Association of DISC1 with autism and Asperger syndrome. Molecular Psychiatry, 13, 187–196.
Kim, J. A., Szatmari, P., Bryson, S. E., Streiner, D. L., & Wilson, F. J. (2000). The prevalence of anxiety and mood problems among children with autism and Asperger syndrome. Autism, 4, 117–1132.
Kjellmer, L., Hedvall, Å., Holm, A., Fernell, E., Gillberg, C., & Norrelgen, F. (2012). Language comprehension in preschoolers with autism spectrum disorders without intellectual disability: Use of the Reynell Developmental Language Scales. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6, 1119–1125.
Klin, A. (2000). Attributing social meaning to ambiguous visual stimuli in higher-functioning autism and Asperger syndrome: The Social Attribution Task. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41, 831–846.
Klin, A., Volkmar, F. R., Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., & Rourke, B. P. (1995). Validity and neuropsychological characterization of Asperger syndrome: Convergence with nonverbal learning disability syndrome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 36, 1127–1140.
Koyama, T., Tachimori, H., Osada, H., Takeda, T., & Kurita, H. (2007). Cognitive and symptom profiles in Asperger’s syndrome and high-functioning autism. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 61, 99–104.
Kugler, B. (1998). The differentiation between autism and Asperger syndrome. Autism, 2, 11–32.
Kurita, H. (1997). A comparative study of Asperger syndrome with high-functioning atypical autism. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 51, 67–70.
Kwon, H., Ow, A. W., Pedatella, K. E., Lotspeich, L. J., & Reiss, A. L. (2004). Voxel-based morphometry elucidates structural neuroanatomy of high-functioning autism and Asperger syndrome. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 46, 760–764.
Larsen, F. W., & Mouridsen, S. E. (1997). The outcome in children with childhood autism and Asperger syndrome originally diagnosed as psychotic. A 30-year follow-up study of subjects hospitalized as children. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 6, 181–190.
Latif, A., Heinz, P., & Cook, R. (2002). Iron deficiency in autism and Asperger syndrome. Autism, 6, 103–114.
Le Couteur, A., Rutter, M., Lord, G., Rios, P., Robertson, S., Holdgrater, M., et al. (1989). Autism Diagnostic Interview. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 19, 363–388.
Lewis, F. M., Murdoch, B. E., & Woodyatt, G. C. (2007). Communicative competence and metalinguistic ability: Performance by children and adults with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 1525–1538.
Lord, C., Petkova, E., Hus, V., et al. (2012). A multisite study of the clinical diagnosis of different autism spectrum disorders. Archive of General Psychiatry, 69, 306–313.
Lord, C., Risi, S., Lambrecht, L., Leventhal, B. L., DiLavore, P., Pickles, A., et al. (2000). The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30, 205–223.
Lotspeich, L. J., Kwon, H., Schumann, C. M., Fryer, S. L., Goodlin-Jones, B. L., Buonocore, M. H., et al. (2004). Investigation of neuroanatomical differences between autism and Asperger syndrome. Archive of General Psychiatry, 61, 291–298.
Macintosh, K. E., & Dissanayake, C. (2004). Annotation: The similarities and differences between autistic disorder and Asperger’s disorder: a review of the empirical evidence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45, 421–434.
Macintosh, K., & Dissanayake, C. (2006a). A comparative study of the spontaneous social interactions of children with high-functioning autism and children with Asperger’s disorder. Autism, 10, 199–220.
Macintosh, K., & Dissanayake, C. (2006b). Social skills and problem behaviours in school aged children with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 1065–1076.
Manjiviona, J., & Prior, M. (1995). Comparison of Asperger syndrome and high-functioning autistic children on a test of motor impairment. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 25, 23–39.
Manjiviona, J., & Prior, M. (1999). Neuropsychological profiles of children with Asperger syndrome and autism. Autism, 3, 327–356.
May, T., Brewer, W. J., Rinehart, N. J., Enticott, P. G., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2011). Differential olfactory identification in children with autism and Asperger’s disorder: a comparative and longitudinal study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41, 837–847.
Mazefsky, C. A., & Oswald, D. P. (2007). Emotion perception in Asperger’s syndrome and high-functioning autism: The importance of diagnostic criteria and cue intensity. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 1086–1095.
McAlonan, G. M., Cheung, C., Cheung, V., Wong, N., Suckling, J., & Chua, S. E. (2009). Differential effects on white-matter systems in high-functioning autism and Asperger’s syndrome. Psychological Medicine, 39, 1885–1893.
McAlonan, G. M., Suckling, J., Wong, N., Cheung, V., Lienenkaemper, N., Cheung, C., et al. (2008). Distinct patterns of grey matter abnormality in high-functioning autism and Asperger’s syndrome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49, 1287–1295.
McLaughlin-Cheng, E. (1998). Asperger syndrome and autism: A literature review and meta-analysis. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 13, 234–245.
Meyer, J. A., & Minshew, N. J. (2002). An update on neurocognitive profiles in Asperger syndrome and high-functioning autism. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 17, 152–160.
Miller, J. N., & Ozonoff, S. (2000). The external validity of Asperger disorder: Lack of evidence from the domain of neuropsychology. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109, 227–238.
Mori, K., Ujiie, T., Smith, A., & Howlin, P. (2009). Parental stress associated with caring for children with Asperger’s syndrome or autism. Pediatrics International, 51, 364–370.
Mukaddes, N. M., Hergüner, S., & Tanider, C. (2010). Psychiatric disorders in individuals with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder: Similarity and differences. The world Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 11, 964–971.
Muñoz-Yunta, J. A., Ortiz, T., Palau-Baduell, M., Martín-Muñoz, L., Salvadó-Salvadó, B., Valls-Santasusana, A., et al. (2008). Magnetoencephalographic pattern of epileptiform activity in children with early-onset autism spectrum disorders. Clinical Neurophysiology, 119, 626–634.
Myles, B. S., Hagiwara, T., Dunn, W., Rinner, L., Reese, M., Huggins, A., et al. (2004). Sensory issues in children with Asperger syndrome and autism. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities, 39, 283–290.
Nayate, A., Tonge, B. J., Bradshaw, J. L., McGinley, J. L., Iansek, R., & Rinehart, N. J. (2012). Differentiation of high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder based on neuromotor behaviour. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42, 707–717.
Nihei, S., & Nihei, Y. (2008). Contrasting Rorschach test results in Asperger’ s syndrome and high-functioning autism. Tohoku Psychologica Folia, 67, 6–9.
Nordahl, C. W., Dierker, D., Mostafavi, I., Schumann, C. M., Rivera, S. M., Amaral, D. G., et al. (2007). Cortical folding abnormalities in autism revealed by surface-based morphometry. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 11725–11735.
Noterdaeme, M., Wriedt, E., & Höhne, C. (2010). Asperger’s syndrome and high-functioning autism: Language, motor and cognitive profiles. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 19, 475–481.
Ozonoff, S., South, M., & Miller, J. N. (2000). DSM-IV-defined Asperger syndrome: Cognitive, behavioral and early history differentiation from high-functioning autism. Autism, 4, 29–46.
Papadopoulos, N., McGinley, J., Tonge, B. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Saunders, K., & Rinehart, N. J. (2012). An investigation of upper limb motor function in high functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder using a repetitive Fitts’ aiming task. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6, 286–292.
Paynter, J., & Peterson, C. (2010). Language and ToM development in autism versus Asperger syndrome: Contrasting influences of syntactic versus lexical/semantic maturity. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4, 377–385.
Peppé, S., Cleland, J., Gibbon, F., O’Hare, A., & Martínez Castilla, P. (2011). Expressive prosody in children with autism spectrum conditions. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 24, 41–53.
Peterson, C. C., Slaughter, V. P., & Paynter, J. (2007). Social maturity and theory of mind in typically developing children and those on the autism spectrum. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48, 1243–1250.
Pijnacker, J., Hagoort, P., Buitelaar, J., Teunisse, J. P., & Geurts, B. (2009). Pragmatic inferences in high-functioning adults with autism and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 607–618.
Planche, P., & Lemonnier, E. (2012). Children with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s syndrome: Can we differentiate their cognitive profiles? Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6, 939–948.
Ramberg, C., Ehlers, S., Nydén, A., Johansson, M., & Gillberg, C. (1996). Language and pragmatic functions in school-age children on the autism spectrum. European Journal of Disorders of Communication, 31, 387–414.
Rinehart, N. J., Bellgrove, M. A., Tonge, B. J., Brereton, A. V., Howells-Rankin, D., & Bradshaw, J. L. (2006a). An examination of movement kinematics in young people with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder: Further evidence for a motor planning deficit. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 757–767.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2001a). Movement preparation in high-functioning autism and Asperger disorder: A serial choice reaction time task involving motor reprogramming. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31, 79–88.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2002a). Lateralization in individuals with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder: A frontostriatal model. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32, 321–331.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2002b). A clinical and neurobehavioural review of high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 36, 762–770.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Moss, S. A., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2000). Atypical interference of local detail on global processing in high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41, 769–778.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Moss, S. A., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2001b). A deficit in shifting attention present in high-functioning autism but not Asperger’s disorder. Autism, 5, 67–80.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Moss, S. A., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2006b). Pseudo-random number generation in children with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder: Further evidence for a dissociation in executive functioning? Autism, 10, 70–85.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Moss, S. A., Brereton, A. V., & Tonge, B. J. (2008). Brief report: Inhibition of return in young people with autism and Asperger’s disorder. Autism, 12, 249–260.
Rinehart, N. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Tonge, B. J., Brereton, A. V., & Bellgrove, M. A. (2002c). A neurobehavioral examination of individuals with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder using a fronto-striatal model of dysfunction. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Review, 1, 164–177.
Rinehart, N. J., Tonge, B. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Iansek, R., Enticott, P. G., & Johnson, K. A. (2006c). Movement-related potentials in high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 48, 272–277.
Rinehart, N. J., Tonge, B. J., Bradshaw, J. L., Iansek, R., Enticott, P. G., & McGinley, J. (2006d). Gait function in high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder: Evidence for basal-ganglia and cerebellar involvement? European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 15, 256–264.
Rinehart, N., Tonge, B., Brereton, A., & Bradshaw, J. (2010). Attentional blink in young people with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Autism, 14, 47–66.
Ritvo, R. A., Ritvo, E. R., Guthrie, D., Yuwiler, A., Ritvo, M. J., & Weisbender, L. (2007). A scale to assist the diagnosis of autism and Asperger’s disorder in adults (RAADS): A pilot study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 213–223.
Robins, E., & Guze, S. B. (1970). Establishment of diagnostic validity in psychiatric illness: Its application to schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry, 126, 983–987.
Ropar, D., & Mitchell, P. (2001). Do individuals with autism and Asperger’s syndrome utilize prior knowledge when pairing stimuli. Developmental Science, 4, 433–441.
Rutter, M., Le Couteur, A., & Lord, C. (2003). Autism diagnostic interview-revised. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Sahyoun, C. P., Soulières, I., Belliveau, J. W., Mottron, L., & Mody, M. (2009). Cognitive differences in pictorial reasoning between high-functioning autism and Asperger’s syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 1014–1023.
Sanders, J. L. (2009). Qualitative or quantitative differences between Asperger’s disorder and autism? Historical considerations. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39, 1560–1567.
Saulnier, C. A., & Klin, A. (2007). Brief report: Social and communication abilities and disabilities in higher functioning individuals with autism and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 788–793.
Schoen, S. A., Miller, L. J., Brett-Green, B., & Hepburn, S. L. (2008). Psychophysiology of children with autism spectrum disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2, 417–429.
Schumann, C. M., Hamstra, J., Goodlin-Jones, B. L., Lotspeich, L. J., Kwon, H., Buonocore, M. H., et al. (2004). The amygdala is enlarged in children but not adolescents with autism; the hippocampus is enlarged at all ages. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 6392–6401.
Scott, J. A., Schumann, C. M., Goodlin-Jones, B. L., & Amaral, D. G. (2009). A comprehensive volumetric analysis of the cerebellum in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research, 2, 246–257.
Seung, H. K. (2007). Linguistic characteristics of individuals with high functioning autism and Asperger syndrome. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 21, 247–259.
Shriberg, L. D., Paul, R., McSweeny, J. L., Klin, A. M., Cohen, D. J., & Volkmar, F. R. (2001). Speech and prosody characteristics of adolescents and adults with high-functioning autism and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 44, 1097–1115.
South, M., Ozonoff, S., & McMahon, W. M. (2005). Repetitive behavior profiles in Asperger syndrome and high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35, 145–158.
Speirs, S., Yelland, G., Rinehart, N., & Tonge, B. (2011). Lexical processing in individuals with high-functioning autism and Asperger’s disorder. Autism, 15, 307–325.
Spek, A. A., Schatorjé, T., Scholte, E., & Van Berckelaer-Onnes, I. (2009). Verbal fluency in adults with high functioning autism or Asperger syndrome. Neuropsychologia, 47, 652–656.
Spek, A. A., Scholte, E. M., & Van Berckelaer-Onnes, I. A. (2008). Brief report: The use of WAIS-III in adults with HFA and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 782–787.
Spek, A. A., Scholte, E. M., & Van Berckelaer-Onnes, I. A. (2010). Theory of mind in adults with HFA and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40, 280–289.
Spek, A. A., Scholte, E. M., & Van Berckelaer-Onnes, I. A. (2011). Local information processing in adults with high functioning autism and asperger syndrome: the usefulness of neuropsychological tests and self-reports. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41, 859–869.
Spencer, J. V., & O’Brien, J. M. (2006). Visual form-processing deficits in autism. Perception, 35, 1047–1055.
Stanley-Cary, C., Rinehart, N., Tonge, B., White, O., & Fielding, J. (2011). Greater disruption to control of voluntary saccades in autistic disorder than Asperger’s disorder: Evidence for greater cerebellar involvement in autism? Cerebellum, 10, 70–80.
Starr, E., Szatmari, P., Bryson, S., & Zwaigenbaum, L. (2003). Stability and change among high-functioning children with pervasive developmental disorders: A 2-year outcome study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33, 15–22.
Szatmari, P., Archer, L., Fisman, S., Streiner, D. L., & Wilson, F. (1995). Asperger’s syndrome and autism: Differences in behavior, cognition, and adaptive functioning. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 34, 1662–1671.
Szatmari, P., Bryson, S. E., Boyle, M. H., Streiner, D. L., & Duku, E. (2003). Predictors of outcome among high functioning children with autism and Asperger syndrome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 44, 520–528.
Szatmari, P., Bryson, S., Duku, E., Vaccarella, L., Zwaigenbaum, L., Bennett, T., et al. (2009). Similar developmental trajectories in autism and Asperger syndrome: From early childhood to adolescence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50, 1459–1467.
Szatmari, P., Bryson, S. E., Streiner, D. L., Wilson, F., Archer, L., & Ryerse, C. (2000). Two-year outcome of preschool children with autism or Asperger’s syndrome. American Journal of Psychiatry, 157, 1980–1987.
Tamanaha, A. C., & Perissinoto, J. (2011). Comparison of the evolutional process of children with autism spectrum disorders in different language therapeutic interventions. Jornal Da Sociedade Brasileira de Fonoaudiolgia, 23, 8–12.
Tantam, D. (1991). Asperger syndrome in adulthood. In U. Frith (Ed.), Autism and Asperger syndrome (pp. 147–183). Cambidge, Great Britan: Cambridge University Press
Thede, L. L., & Coolidge, F. L. (2007). Psychological and neurobehavioral comparisons of children with Asperger’s disorder versus high-functioning autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 847–854.
Toal, F., Daly, E. M., Page, L., Deeley, Q., Hallahan, B., Bloemen, O., et al. (2009). Clinical and anatomical heterogeneity in autistic spectrum disorder: A structural MRI study. Psychological Medicine, 40, 1171–1181.
Tonge, B. J., Brereton, A. V., Gray, K. M., & Einfeld, S. L. (1999). Behavioural and emotional disturbance in high-functioning autism and Asperger syndrome. Autism, 3, 117–130.
Tsermentseli, S., O’Brien, J. M., & Spencer, J. V. (2008). Comparison of form and motion coherence processing in autistic spectrum disorders and dyslexia. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 1201–1210.
Turunen, J. A., Rehnström, K., Kilpinen, H., Kuokkanen, M., Kempas, E., & Ylisaukko-Oja, T. (2008). Mitochondrial aspartate/glutamate carrier SLC25A12 gene is associated with autism. Autism Research, 1, 189–192.
Verté, S., Geurts, H. M., Roeyers, H., Oosterlaan, J., & Sergeant, J. A. (2006a). Executive functioning in children with an Autism Spectrum Disorder: Can we differentiate within the spectrum? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 351–372.
Verté, S., Geurts, H. M., Roeyers, H., Rosseel, Y., Oosterlaan, J., & Sergeant, J. A. (2006b). Can the Children’s Communication Checklist differentiate autism spectrum subtypes? Autism, 10, 266–287.
Via, E., Radua, J., Cardoner, N., Happé, F., & Mataix-Cols, D. (2011). Meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in autism spectrum disorder: Should Asperger disorder be subsumed under a broader umbrella of autistic spectrum disorder? Archive of General Psychiatry, 68, 409–418.
Weisbrot, D. M., Gadow, K. D., DeVincent, C. J., & Pomeroy, J. (2005). The presentation of anxiety in children with pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 15, 477–496.
Wing, L. (1981). Asperger’s syndrome: A clinical account. Psychological Medicine, 11, 115–129.
Witwer, A. N., & Lecavalier, L. (2008). Examing the validity of autism spectrum disorder subtypes. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 1611–1624.
World Health Organization. (1992). The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioral disorders: Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yang, W. H., Jing, J., Xiu, L. J., Cheng, M. H., Wang, X., Bao, P., et al. (2011). Regional cerebral blood flow in children with autism spectrum disorders: A quantitative 99mTc-ECD brain SPECT study with statistical parametric mapping evaluation. Chinese Medical Journal (English), 124, 1362–1366.
Yu, K. K., Cheung, C., Chua, S. E., & McAlonan, G. M. (2011). Can Asperger syndrome be distinguished from autism? An anatomic likelihood meta-analysis of MRI studies. Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, 36, 412–421.
Zander, E., & Dahlgren, S. O. (2010). WISC-III index score profile of 520 Swedish children with pervasive developmental disorders. Psychological Assessment, 22, 213–222.
Ziatas, K., Durkin, K., & Pratt, C. (1998). Belief term development in children with autism, Asperger syndrome, specific language impairment, and normal development: links to theory of mind development. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 39, 755–763.
Ziatas, K., Durkin, K., & Pratt, C. (2003). Differences in assertive speech acts produced by children with autism, Asperger syndrome, specific language impairment, and normal development. Developmental Psychopathology, 2003(15), 73–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, L.Y. Asperger’s Disorder will be Back. J Autism Dev Disord 43, 2914–2942 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1839-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-013-1839-2