Abstract
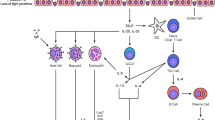
Cytokine-mediated immunity plays a dominant role in the pathogenesis of various immune diseases, including asthma. The recent identification of the family interleukin (IL)-1-related cytokine IL-18 now contributes to our understanding of the fine-tuning of cellular immunity. IL-18 can act as a cofactor for Th2 cell development and IgE production and also plays an important role in the differentiation of Th1 cells. Recent work identified an IL-18 association with the pathogenesis of asthma, wherein increased IL-18 expression was found in the serum of patients. Furthermore, IL-18 polymorphisms with susceptibility to asthma were reported, suggesting that IL-18 may be therapeutically relevant to asthma. In this review, we discuss the role of IL-18 in the pathogenesis of asthma and its therapeutic potential based on current research.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousquet, J., P.J. Bousquet, P. Godard, and J.P. Daures. 2005. The public health implications of asthma. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 83: 548–554.
Deo, S.S., K.J. Mistry, A.M. Kakade, and P.V. Niphadkar. 2010. Role played by Th2 type cytokines in IgE mediated allergy and asthma. Lung India : Official Organ of Indian Chest Society 27: 66–71.
Lund, S., H.H. Walford, and T.A. Doherty. 2013. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells in allergic disease. Current Immunology Reviews 9: 214–221.
Sims, J.E. 2002. IL-1 and IL-18 receptors, and their extended family. Current Opinion in Immunology 14: 117–122.
Okamura, H., H. Tsutsi, T. Komatsu, M. Yutsudo, A. Hakura, T. Tanimoto, et al. 1995. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-gamma production by T cells. Nature 378: 88–91.
Nakanishi, K., T. Yoshimoto, H. Tsutsui, and H. Okamura. 2001. Interleukin-18 regulates both Th1 and Th2 responses. Annual Review of Immunology 19: 423–474.
Romagnani, S. 1999. Th1/Th2 cells. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 5: 285–294.
Wild, J.S., A. Sigounas, N. Sur, M.S. Siddiqui, R. Alam, M. Kurimoto, et al. 2000. IFN-gamma-inducing factor (IL-18) increases allergic sensitization, serum IgE, Th2 cytokines, and airway eosinophilia in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Journal of Immunology 164: 2701–2710.
Rovina, N., E. Dima, P. Bakakos, E. Tseliou, K. Kontogianni, S. Papiris, et al. 2015. Low interleukin (IL)-18 levels in sputum supernatants of patients with severe refractory asthma. Respiratory Medicine 109: 580–587.
Imaoka, H., G.M. Gauvreau, R.M. Watson, S.G. Smith, B. Dua, A.J. Baatjes, et al. 2011. Interleukin-18 and interleukin-18 receptor-alpha expression in allergic asthma. The European Respiratory Journal 38: 981–983.
Imaoka, H., S. Takenaka, T. Kawayama, H. Oda, Y. Kaku, M. Matsuoka, et al. 2013. Increased serum levels of soluble IL-18 receptor complex in patients with allergic asthma. Allergology International: Official Journal of the Japanese Society of Allergology 62: 513–515.
Kawayama, T., M. Okamoto, H. Imaoka, S. Kato, H.A. Young, and T. Hoshino. 2012. Interleukin-18 in pulmonary inflammatory diseases. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research: the Official Journal of The International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research 32: 443–449.
Lu, H., X. Yang, K. Takeda, D. Zhang, Y. Fan, M. Luo, et al. 2000. Chlamydia trachomatis mouse pneumonitis lung infection in IL-18 and IL-12 knockout mice: IL-12 is dominant over IL-18 for protective immunity. Molecular Medicine 6: 604–612.
Mihm, S., S. Schweyer, and G. Ramadori. 2003. Expression of the chemokine IP-10 correlates with the accumulation of hepatic IFN-gamma and IL-18 mRNA in chronic hepatitis C but not in hepatitis B. Journal of Medical Virology 70: 562–570.
Mallat, Z., A. Corbaz, A. Scoazec, S. Besnard, G. Leseche, Y. Chvatchko, et al. 2001. Expression of interleukin-18 in human atherosclerotic plaques and relation to plaque instability. Circulation 104: 1598–1603.
Guo, H., H. Deng, H. Cui, X. Peng, J. Fang, Z. Zuo, et al. 2015. Nickel chloride (NiCl2)-caused inflammatory responses via activation of NF-kappaB pathway and reduction of anti-inflammatory mediator expression in the kidney. Oncotarget 6: 28607–28620.
Debets, R., J.C. Timans, T. Churakowa, S. Zurawski, R. de Waal Malefyt, K.W. Moore, et al. 2000. IL-18 receptors, their role in ligand binding and function: anti-IL-1RAcPL antibody, a potent antagonist of IL-18. Journal of Immunology 165: 4950–4956.
Harada, M., K. Obara, T. Hirota, T. Yoshimoto, Y. Hitomi, M. Sakashita, et al. 2009. A functional polymorphism in IL-18 is associated with severity of bronchial asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 180: 1048–1055.
Yang D.X., Li N., Zhang X.L., Wang Q. 2012. [Serum interleukin 18 and 33 levels and its clinical significance in asthma patients]. Zhonghua jie he he hu xi za zhi = Zhonghua jiehe he huxi zazhi = Chinese journal of tuberculosis and respiratory diseases 35:493–496.
Zhang, J., L. Zheng, D. Zhu, H. An, Y. Yang, Y. Liang, et al. 2014. Polymorphisms in the interleukin 18 receptor 1 gene and tuberculosis susceptibility among Chinese. PloS One 9: e110734.
Kuribayashi, K., T. Kodama, H. Okamura, M. Sugita, and T. Matsuyama. 2002. Effects of post-inhalation treatment with interleukin-12 on airway hyper-reactivity, eosinophilia and interleukin-18 receptor expression in a mouse model of asthma. Clinical and Experimental Allergy : Journal of the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology 32: 641–649.
Lunding, L., A. Schroder, and M. Wegmann. 2015. Allergic airway inflammation: unravelling the relationship between IL-37, IL-18Ralpha and Tir8/SIGIRR. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine 9: 739–750.
Hossny, E.M., S.S. El-Sayed, E.S. El-Hadidi, and S.R. Moussa. 2009. Serum interleukin-18 expression in children with bronchial asthma. The World Allergy Organization Journal 2: 63–68.
Kroeger, K.M., B.M. Sullivan, and R.M. Locksley. 2009. IL-18 and IL-33 elicit Th2 cytokines from basophils via a MyD88- and p38alpha-dependent pathway. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 86: 769–778.
Oda H., Kawayama T., Imaoka H., Sakazaki Y., Kaku Y., Okamoto M., et al. 2014. Interleukin-18 expression, CD8(+) T cells, and eosinophils in lungs of nonsmokers with fatal asthma. Annals of allergy, asthma & immunology: official publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology 112:23–28 e21.
Sawada, M., T. Kawayama, H. Imaoka, Y. Sakazaki, H. Oda, S. Takenaka, et al. 2013. IL-18 induces airway hyperresponsiveness and pulmonary inflammation via CD4+ T cell and IL-13. PloS One 8: e54623.
Murai, H., H. Qi, B. Choudhury, J. Wild, N. Dharajiya, S. Vaidya, et al. 2012. Alternaria-induced release of IL-18 from damaged airway epithelial cells: an NF-kappaB dependent mechanism of Th2 differentiation? PloS One 7: e30280.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81270011; 81472125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.