Abstract
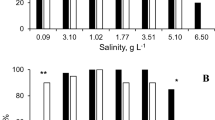
An increasing number of studies demonstrate the critical role of the host–parasite relationship for the persistence and distribution of freshwater mussels. Laboratory experiments are a powerful tool for quantifying the physiological compatibility between parasitic mussel larvae and fish hosts and are clearly applicable to species conservation. Recent findings, however, indicate potential need to control for biases caused by infection intensity and host stress responses. We tested glochidia metamorphosis success and host plasma cortisol response using Lampsilis siliquoidea glochidia on Lepomis macrochirus. The main aims were to (1) compare metamorphosis success in response to infection intensity (number of attached glochidia per fish) and (2) compare metamorphosis success between typical and reduced-stress approaches to the handling and infection of host fish. We found no effect of the glochidia bath density used to infect the fish (1000–4000–8000 glochidia l−1) or the resulting infection intensity on metamorphosis success, although host plasma cortisol was correlated with infection intensity at 24 h post infection. Small but statistically significant differences in metamorphosis success were observed between the typical and reduced-stress approaches. Overall, typical host compatibility testing methods appear to be robust to these variables, but more emphasis on standardizing laboratory protocols may provide more repeatable data.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnhart, M. C., W. R. Haag & W. N. Roston, 2008. Adaptations to host infection and larval parasitism in the Unionoida. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 27: 370–394.
Barton, B. A., R. E. Peter & C. R. Paulencu, 1980. Plasma cortisol levels of fingerling rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) at rest, and subjected to handling, confinement, transport, and stocking. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 805–811.
Bauer, G., 1987a. The parasitic stage of the freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera L.) I. Host response to glochidiosis. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 76: 393–402.
Bauer, G., 1987b. The parasitic stage of the freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera L.) III. Host relationship. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 76: 413–423.
Blažek, R. & M. Gelnar, 2006. Temporal and spatial distribution of glochidial larval stages of European unionid mussels (Mollusca: Unionidae) on host fishes. Folia Parasitologica 53: 98–106.
Bly, J. E., S. M. Quiniou & L. W. Clem, 1997. Environmental effects on fish immune mechanisms. Developments in Biological Standardization 90: 33–43.
Dodd, B. J., M. C. Barnhart, C. L. Rogers-Lowery, T. B. Fobian & R. V. Dimock, 2005. Cross-resistance of largemouth bass to glochidia of unionid mussels. Journal of Parasitology 91: 1064–1072.
Dodd, B. J., M. C. Barnhart, C. L. Rogers-Lowery, T. B. Fobian & R. V. Dimock Jr., 2006. Persistence of acquired immunity of largemouth bass to glochidia of unionid mussels. Journal of Fish and Shellfish Immunity 21: 473–484.
Douda, K., 2015. Host-dependent vitality of juvenile freshwater mussels: implications for breeding programs and host evaluation. Aquaculture 445: 5–10.
Douda, K., P. Horký & M. Bílý, 2012. Host limitation of the thick-shelled river mussel: identifying the threats to declining affiliate species. Animal Conservation 15: 536–544.
Douda, K., J. Sell, L. Kubíková-Peláková, P. Horký, A. Kaczmarczyk & M. Mioduchowska, 2014. Host compatibility as a critical factor in management unit recognition: population-level differences in mussel-fish relationships. Journal of Applied Ecology 51: 1085–1095.
Dubansky, B., B. Whitaker & F. Galvez, 2011. Influence of cortisol on the attachment and metamorphosis of larval Utterbackia imbecillis on bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus). The Biological Bulletin 220: 97–106.
Ford, D. F. & A. M. Oliver, 2015. The known and potential hosts of texas mussels: implications for future research and conservation efforts. Freshwater Mollusk Biology and Conservation 18: 1–14.
Fritts, A., M. Fritts, D. Peterson, D. Fox & R. Bringolf, 2012. Critical linkage of imperiled species: gulf sturgeon as hosts for purple bankclimber mussels. Freshwater Science 31: 1223–1232.
Geist, J., 2010. Strategies for the conservation of endangered freshwater pearl mussels (Margaritifera margaritifera L.): a synthesis of conservation genetics and ecology. Hydrobiologia 644: 69–88.
Haag, W. R. & J. A. Stoeckel, 2015. The role of host abundance in regulating populations of freshwater mussels with parasitic larvae. Oecologia 178: 1159–1168.
Haag, W. R. & J. D. Williams, 2014. Biodiversity on the brink: an assessment of conservation strategies for North American freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 735: 45–60.
Jansen, W., G. Bauer & E. Zahner-Meike, 2001. Glochidial mortality in freshwater mussels. In Bauer, G. & K. Wachtler (eds.), Ecology and Evolution of the Freshwater Mussels Unionoida. Springer, Berlin.
Kat, P. W., 1984. Parasitism and the Unionacea (Bivalvia). Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 59: 189–207.
Keller, A. E. & D. S. Ruessler, 1997. Determination or verification of host fish for nine species of unionid mussels. American Midland Naturalist 138: 402–407.
Kirk, S. G. & J. B. Layzer, 1997. Induced metamorphosis of freshwater mussel glochidia on nonhost fish. Nautilus 110: 102–106.
Levine, T. D., B. K. Lang & D. J. Berg, 2012. Physiological and ecological hosts of Popenaias popeii (Bivalvia: Unionidae): laboratory studies identify more hosts than field studies. Freshwater Biology 57: 1854–1864.
Meyers, T. R., R. E. Millemann & C. A. Fustish, 1980. Glochidiosis of salmonid fishes. IV. Humoral and tissue responses of coho and chinook salmon to experimental infection with Margaritifera margaritifera (L) (Pelecypoda, Margaritanidae). Journal of Parasitology 66: 274–281.
Österling, M. E., 2011. Test and application of a non-destructive photo-method investigating the parasitic stage of the threatened mussel Margaritifera margaritifera on its host fish Salmo trutta. Biological Conservation 144: 2984–2990.
Paling, J. E., 1968. A method of estimating the relative volumes of water flowing over the different gills of a freshwater fish. Journal of Experimental Biology 48: 533–544.
Pickering, A. D. & T. G. Pottinger, 1989. Stress responses and disease resistance in salmonid fish: effects of chronic elevation of plasma cortisol. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 7: 253–258.
R Development Core Team, 2013. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Viena.
Roberts, A. D. & M. C. Barnhart, 1999. Effects of temperature, pH, and CO2 on transformation of the glochidia of Anodonta suborbiculata on fish hosts and in vitro. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 18: 477–487.
Rogers, C. L. & R. V. Dimock, 2003. Acquired resistance of bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus to glochidia larvae of the freshwater mussel Utterbackia imbecillis (Bivalvia : Unionidae) after multiple infections. Journal of Parasitology 89: 51–56.
Rogers-Lowery, C. L., R. V. Dimock Jr. & R. E. Kuhn, 2007. Antibody response of bluegill sunfish during development of acquired resistance against the larvae of the freshwater mussel Utterbackia imbecillis. Developmental and Comparative Immunology 31: 143–155.
Rohlenová, K., S. Morand, P. Hyršl, S. Tolarová, M. Flajšhans & A. Šimková, 2011. Are fish immune systems really affected by parasites? An immunoecological study of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Parasites & Vectors 4: 120.
Schwalb, A. N., M. S. Poos & J. D. Ackerman, 2011. Movement of logperch-the obligate host fish for endangered snuffbox mussels: implications for mussel dispersal. Aquatic Sciences 73: 223–231.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Laszlo Kovacs, Evan Clark, and Paul Durham for their valuable comments and help with experimental procedures. The research was funded by the Czech Science Foundation (13-05872S) and Missouri State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Manuel P. M. Lopes-Lima, Ronaldo G. Sousa, Lyuba E. Burlakova, Alexander Y. Karatayev & Knut Mehler / Ecology and Conservation of Freshwater Bivalves
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douda, K., Martin, M., Glidewell, E. et al. Stress-induced variation in host susceptibility to parasitic freshwater mussel larvae. Hydrobiologia 810, 265–272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2895-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2895-3