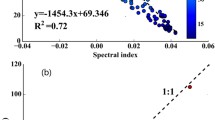
Abstract
Global warming is predicted to increase the intensity and frequency of short-term temperature fluctuation. However, the effect of temperature fluctuation on phytoplankton is rarely considered. We analyzed the effect of fluctuating temperature on cyanobacterial dominance and blooms in spring (March–May) with long-term data analyses, laboratory simulation, and field observation. Our results showed that the magnitude of air temperature fluctuation in spring has increased in Lake Taihu over the past 58 years (1956–2013) and was negatively correlated with cyanobacterial blooms onset time (1987–2013). Air temperature fluctuation was one of the predictors of the best model for the variability in the bloom size in spring (2000–2011). The results from the field observation (2009–2013) also indicated that there was a positive correlation between diel air temperature difference and the ratio of cyanobacteria to total algae. Laboratory experiments suggested that water temperature fluctuation slowed the growth rates of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Cyclotella meneghiniana but not Microcystis aeruginosa, which confirmed our findings of field observation and long-term data analysis. Therefore, the increased temperature fluctuation under global warming may promote cyanobacterial dominance. Our findings provide further understanding of inter-annual difference of cyanobacterial blooms onset time in the warming world.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalde, J., L. Betancourt, E. Torres, A. Cid & C. Barwell, 1998. Purification and characterization of phycocyanin from the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. IO9201. Plant Science 136: 109–120.
Amano, Y., Y. Sakai, T. Sekiya, K. Takeya, K. Taki & M. Machida, 2010. Effect of phosphorus fluctuation caused by river water dilution in eutrophic lake on competition between blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa and diatom Cyclotella sp. Journal of Environmental Sciences 22: 1666–1673.
APHA, 1985. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. APHA-AWWA-WPCF, Washington, U. S. A.
Bäuerle, E., D. Ollinger & J. Ilmberger, 1998. Some meteorological hydrological and hydrodynamical aspects of upper Lake Constance. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Special Issues Advanced Limnology 53: 31–83.
Benincà, E., V. Dakos, E. H. Van Nes, J. Huisman & M. Scheffer, 2011. Resonance of plankton communities with temperature fluctuations. The American Naturalist 178: E85–E95.
Cao, H., Y. Tao, F. Kong & Z. Yang, 2008. Relationship between temperature and cyanobacterial recruitment from sediments in laboratory and field studies. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 23: 405–412.
Carpenter, S. R., S. G. Fisher, N. B. Grimm & J. F. Kitchell, 1992. Global change and freshwater ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 23: 119–139.
Chen, Y. W., B. Q. Qin, K. Teubner & M. T. Dokulil, 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 445–453.
Deng, J., B. Qin, H. W. Paerl, Y. Zhang, J. Ma & Y. Chen, 2014a. Earlier and warmer springs increase cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in subtropical Lake Taihu, China. Freshwater Biology 59: 1076–1085.
Deng, J., B. Qin, H. W. Paerl, Y. Zhang, P. Wu, J. Ma & Y. Chen, 2014b. Effects of nutrients, temperature and their interactions on spring phytoplankton community succession in Lake Taihu, China. PLoS One 9: e113960. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113960.
Dokulil, M. T. & K. Teubner, 2000. Cyanobacterial dominance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 438: 1–12.
Duan, H., R. Ma, X. Xu, F. Kong, S. Zhang, W. Kong, J. Hao & L. Shang, 2009. Two-decade reconstruction of algal blooms in China’s Lake Taihu. Environmental Science & Technology 43: 3522–3528.
Elliott, J. A. & L. May, 2008. The sensitivity of phytoplankton in Loch Leven (UK) to changes in nutrient load and water temperature. Freshwater Biology 53: 32–41.
Falkowski, P. G. & J. A. Raven, 1997. Aquatic Photosynthesis. Blackwell Science, Malden, MA.
Fotheringham, A. S., C. Brunsdon & M. Charlton, 2002. Geographically Weighted Regression: the Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships. Wiley, Chichester.
Gao, Y., J. C. Cornwell, D. K. Stoecker & M. S. Owens, 2012. Effects of cyanobacterial-driven pH increases on sediment nutrient fluxes and coupled nitrification-denitrification in a shallow fresh water estuary. Biogeosciences 9: 2697–2710.
Geller, W., R. Berberovic, U. Gaedke, H. Muller & H. R. Pauli, 1991. Relations among the components of autotrophic and heterotrophic plankton during the seasonal cycle 1987 in Lake Constance. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie 24: 831–836.
Houghton, J., 2005. Global warming. Reports on Progress in Physics 68: 1343–1403.
Hu, C. M., Z. Lee, R. H. Ma, K. Yu, D. Li & S. L. Shang, 2010. Moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake, China. Journal of Geophysical Research 115: C04002.
Huber, V., C. Wagner, D. Gerten & R. Adrian, 2012. To bloom or not to bloom: contrasting responses of cyanobacteria to recent heat waves explained by critical thresholds of abiotic drivers. Oecologia 169: 245–256.
Jeppesen, E., M. Meerhoff, B. Jacobsen, R. Hansen, M. Søndergaard, J. Jensen, T. Lauridsen, N. Mazzeo & C. Branco, 2007. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulation – the successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia 581: 269–285.
Jöhnk, K. D., J. Huisman, J. Sharples, B. Sommeijer, P. M. Visser & J. M. Stroom, 2008. Summer heatwaves promote blooms of harmful cyanobacteria. Global Change Biology 14: 495–512.
Ke, Z. X., P. Xie & L. G. Guo, 2008. Controlling factors of spring–summer phytoplankton succession in Lake Taihu (Meiliang Bay, China). Hydrobiologia 607: 41–49.
Latour, D., O. Sabido, M. J. Salencon & H. Giraudet, 2004. Dynamics and metabolic activity of the benthic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa in the Grangent reservoir (France). Journal of Plankton Research 26: 719–726.
Lürling, M., 2006. Effects of a surfactant (FFD-6) on Scenedesmus morphology and growth under different nutrient conditions. Chemosphere 62: 1351–1358.
Lürling, M., F. Eshetu, E. J. Faassen, S. Kosten & V. L. M. Huszar, 2012. Comparison of cyanobacterial and green algal growth rates at different temperatures. Freshwater Biology 58: 552–559.
McKee, D., D. Atkinson, S. E. Collings, J. W. Eaton, A. Gill, I. Harvey, K. Hatton, T. Heyes, D. Wilson & B. Moss, 2003. Response of freshwater microcosm communities to nutrients, fish, and elevated temperature during winter and summer. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 707–722.
McQueen, D. J. & D. R. S. Lean, 1987. Influence of water temperature and nitrogen to phosphorus ratios on the dominance of blue-green algae in Lake St. George, Ontario. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 44: 598–604.
Meis, S., S. J. Thackeray & I. D. Jones, 2009. Effects of recent climate change on phytoplankton phenology in a temperate lake. Freshwater Biology 54: 1888–1898.
Montagnes, D. & T. Weisse, 2000. Fluctuating temperatures affect growth and production rates of planktonic ciliates. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21: 97–102.
Mooij, W., S. Hülsmann, L. De Senerpont Domis, B. Nolet, P. Bodelier, P. Boers, L. Pires, H. Gons, B. Ibelings, R. Noordhuis, R. Portielje, K. Wolfstein & E. Lammens, 2005. The impact of climate change on lakes in the Netherlands: a review. Aquatic Ecology 39: 381–400.
Myers, R. H., 1990. Classical and Modern Regression with Applications. PWS and Kent Publishing Company, Boston.
Norusis, M., 2008. SPSS 16.0 Statistical Procedures Companion. Prentice Hall Press.
O’Neil, J., T. W. Davis, M. A. Burford & C. Gobler, 2012. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14: 313–334.
Paerl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2008. Climate: blooms like it hot. Science 320: 57–58.
Paerl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2009. Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environmental Microbiology Reports 1: 27–37.
Paul, V. J., 2008. Global warming and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. In Hudnell, H. K. (ed) Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs, Vol. 619. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Springer, New York: 239–257.
Qin, B. Q., W. P. Hu & W. M. Chen, 2004. Process and Mechanism of Environmental Changes of the Taihu Lake. Science Press, Beijing (In Chinese).
Qin, B., P. Xu, Q. Wu, L. Luo & Y. Zhang, 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. In Qin, B., Z. Liu & K. Havens (eds) Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes with Special Reference to Lake Taihu, China. Developments in Hydrobiology, Vol. 194. Springer, Dordrecht: 3–14.
Rangel, T. F., J. A. F. Diniz-Filho & L. M. Bini, 2010. SAM: a comprehensive application for Spatial Analysis in Macroecology. Ecography 33: 46–50.
Recknagel, F., J. Bobbin, P. Whigham & H. Wilson, 2002. Comparative application of artificial neural networks and genetic algorithms for multivariate time-series modelling of algal blooms in freshwater lakes. Journal of Hydroinformatics 4: 125–133.
Reynolds, C. S., 1984. Phytoplankton periodicity: the interactions of form, function and environmental variability. Freshwater Biology 14: 111–142.
Reynolds, C. S., 2006. Ecology of Phytoplankton (Ecology, Biodiversity and Conservation). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Rippka, R., J. Deruelles, J. B. Waterbury, M. Herdman & R. Y. Stanier, 1979. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Journal of General Microbiology 111: 1–61.
Robarts, R. D. & T. Zohary, 1987. Temperature effects on photosynthetic capacity, respiration, and growth rates of bloom-forming cyanobacteria. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 21: 391–399.
Stanier, R., R. Kunisawa, M. Mandel & G. Cohen-Bazire, 1971. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriological Reviews 35: 171.
Valderrama, J., 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Marine Chemistry 10: 109–122.
Wagner, C. & R. Adrian, 2009. Cyanobacteria dominance: quantifying the effects of climate change. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 2460–2468.
Yan, R., F. Kong & X. Han, 2004. Analysis of the recruitment of the winter survival algae on the sediments of Lake Taihu by fluorometry. Journal of Lake Science 16: 163–168. (In Chinese).
Zhang, M., X. Shi, Y. Yu & F. Kong, 2011. The acclimative changes in photochemistry after colony formation of the cyanobacterial Microcystis aeruginosa. Journal of Phycology 47: 524–532.
Zhang, M., H. Duan, X. Shi, Y. Yu & F. Kong, 2012a. Contributions of meteorology to the phenology of cyanobacterial blooms: implications for future climate change. Water Research 46: 442–452.
Zhang, M., Y. Yu, Z. Yang & F. Kong, 2012b. Photochemical responses of phytoplankton to rapid increasing-temperature process. Phycological Research 60: 199–207.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Hongtao Duan for the assistance in achieving the data sets of cyanobacterial blooms onset time and area. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31200353, 31470520, 31200296, 310702420), the project of water pollution control and treatment in Lake Taihu (JSZC-G2013-257), and the frontier project of Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, CAS (NIGLAS2012135010). We also thank the two anonymous reviewers for their useful comments and constructive suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling editor: Zhengwen Liu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Qin, B., Yu, Y. et al. Effects of temperature fluctuation on the development of cyanobacterial dominance in spring: implication of future climate change. Hydrobiologia 763, 135–146 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2368-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2368-0