Abstract
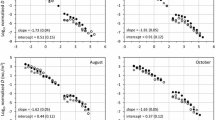
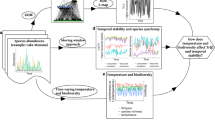
Food-chain length (FCL) is commonly used in ecological investigations to gain insight into how ecosystems function. Several studies have investigated the mechanisms underlying FCL patterns, but none has specifically examined the effect of temperature variability. In river ecosystems, water temperature variability can modify community structure, individuals’ activity, and individuals’ physiological rates, among other things. As such, we expected that it would negatively influence FCL. To test this prediction, we took advantage of a dataset comprising five streams, which mainly differ according to their temperature variability. At each stream, we (i) studied the species composition of macroinvertebrates and fish, and using nitrogen and carbon stable isotopes, (ii) estimated realized FCL, and (iii) examined food web structure. For macroinvertebrates, but not for fish, species composition differed among sites displaying low and high temperature variability. FCL was negatively influenced by temperature variability. Confirming this trend, we found a highly significant linear relationship between FCL and temperature variability using data from the literature. As for food web structure, the trophic position of filter-feeders/shredders may explain the FCL differences among sites. Our study gives additional support to the “dynamic stability” hypothesis and advances a step further by suggesting that temperature variability alone may reduce FCL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdoli, A., D. Pont & P. Sagnes, 2005. Influence of female age, body size and environmental conditions on annual egg production of the bullhead. Journal of Fish Biology 67: 1327–1341.
Abdoli, A., D. Pont & P. Sagnes, 2007. Intrabasin variations in age and growth of bullhead: the effects of temperature. Journal of Fish Biology 70: 1224–1238.
Anderson, C. & G. Cabana, 2007. Estimating the trophic position of aquatic consumers in river food webs using stable nitrogen isotopes. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 26: 273–285.
Borderelle, A. L., D. Gerdeaux, P. Giraudoux & V. Verneaux, 2009. Influence of watershed′s anthropogenic activities on fish nitrogen and carbon stable isotope ratios in nine French lakes. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 392: 1–13.
Cabana, G. & J. B. Rasmussen, 1996. Comparison of aquatic food chains using nitrogen isotopes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93: 10844–10847.
Carpenter, S. R. & J. F. Kitchell, 1993. The Trophic Cascade in Lakes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
De Angelis, D. L., S. M. Bartell & A. L. Brenkert, 1989. Effects of Nutrient Recycling and Food-Chain Length on Resilience. The American Naturalist 134: 778–805.
Death, R. G., 2008. The effect of flood on aquatic invertebrate communities. In Lancaster, J. & R. A. Briers (eds), Aquatic Insects: Challenges to Populations. CABI, Oxford: 103–121.
Duffy, J. E., J. P. Richardson & K. E. France, 2005. Ecosystem consequences of diversity depend on food chain length in estuarine vegetation. Ecology Letters 8: 301–309.
Finlay, J., 2004. Patterns and controls of lotic algal stable carbon isotope ratios. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 850–861.
Finlay, J. & C. Kendall, 2007. Stable isotope tracing of temporal and spatial variability in organic matter sources to freshwater ecosystems. In Michener, R. & K. Lajtha (eds), Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford: 283–333.
Fischer, S. & H. Kummer, 2000. Effects of residual flow and habitat fragmentation on distribution and movement of bullhead (Cottus gobio L.) in an alpine stream. Hydrobiologia 422–423: 305–317.
Garrott, R. A., L. L. Eberhardt, J. K. Otton, P. J. White & M. A. Chaffee, 2002. A geochemical trophic cascade in Yellowstone’s geothermal environments. Ecosystems 5: 659–666.
Hairston Jr., N. G. & N. G. Hairston Sr., 1993. Cause-effect relationships in energy flow, trophic structure, and interspecific interactions. The American Naturalist 142: 379–411.
Hairston, N. G., F. E. Smith & L. B. Slobodkin, 1960. Community structure, population control, and competition. The American Naturalist 94: 421–425.
Jardine, T. D., M. Gray, S. MacWilliam & R. Cunjak, 2005. Stable isotope variability in tissues of temperate stream fishes. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 134: 1103–1110.
Jenkins, G., G. Woodward & A. Hildrew, 2013. Long-term amelioration of acidity accelerates decomposition in headwater streams. Global Change Biology 19: 4, 1100–1106.
Kondolf, G. M., D. R. Montgomery, H. Piégay & L. Schmitt, 2005. Geomorphic classification of rivers and streams. In Kondolf, G. M. & H. Piégay (eds), Tools in Fluvial Geomorphology. Wiley, Chichester: 171–204.
Layman, C. A., D. A. Arrington, C. G. Montaña & D. M. Post, 2007. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 88: 42–48.
Lindeman, R. L., 1942. The trophic-dynamic aspect of ecology. Ecology 23: 399–417.
McHugh, P. A., A. R. McIntosh & P. G. Jellyman, 2010. Dual influences of ecosystem size and disturbance on food chain length in streams. Ecology Letters 13: 881–890.
Pauly, D., V. Christensen, J. Dalsgaard, R. Froese & F. Torres, 1998. Fishing down marine food webs. Science 279: 860–863.
Persat, H. & G. H. Copp, 1990. Electric fishing and point abundance sampling for the ichthyology of large rivers. In Cowx, I. G. (ed.), Developments in Electric Fishing. Kluwer, Amsterdam: 197–209.
Pimm, S. L. & J. H. Lawton, 1977. Number of trophic levels in ecological communities. Nature 268: 329–331.
Post, D. M., 2002a. The long and short of food-chain length. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 17: 269–277.
Post, D. M., 2002b. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 83: 703–718.
Post, D. M., 2007. Testing the productive-space hypothesis: rational and power. Oecologia 153: 973–984.
Post, D. M. & G. Takimoto, 2007. Proximate structural mechanisms for variation in food-chain length. Oikos 116: 775–782.
Post, D. M., M. L. Pace & N. G. Hairston, 2000. Ecosystem size determines food-chain length in lakes. Nature 405: 1047–1049.
Power, M., K. R. R. A. Guiguer & D. R. Barton, 2003. Effects of temperature on isotopic enrichment in Daphnia magna: implications for aquatic food-web studies. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 17: 1619–1625.
Reyjol, Y., J. P. Léna, F. Hervant & D. Pont, 2009. Effects of temperature on biological and biochemical indicators of the life-history strategy of bullhead Cottus gobio. Journal of Fish Biology 75: 1427–1445.
Rutherford, J., S. Blackett, C. Blackett, L. Saito & R. Davies-Colley, 1997. Predicting the effects of shade on water temperature in small streams. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 31: 707–721.
Sabo, J. L. & D. M. Post, 2008. Quantifying periodic, stochastic, and catastrophic environmental variation. Ecological Monographs 78: 19–40.
Sabo, J. L., J. C. Finlay & D. M. Post, 2009. Food chains in freshwaters. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1162: 187–220.
Sabo, J. L., J. C. Finlay, T. Kennedy & D. M. Post, 2010. The role of discharge variation in scaling of drainage area and food chain length in rivers. Science 330: 965–967.
Smyntek, P., S. Maberly & J. Grey, 2012. Dissolved carbon dioxide concentration controls baseline stable carbon isotope signatures of a lake food web. Limnology and Oceanography 57: 1292–1302.
Sterner, R., A. Bajpai & T. Adams, 1997. The enigma of food chain length: absence of theoretical evidence for dynamic constraints. Ecology 78: 2258–2262.
Tachet, H., P. Richoux, M. Bournaud & P. Usseglio-Polatera, 2010. Invertébrés d’eau douce: Systématique, biologie, écologie, 2nd ed. CNRS Editions, Paris.
Takimoto, G. & D. M. Post, 2012. Environmental determinants of food-chain length: a meta-analysis. Ecological Research. doi:10.1007/s11284-012-0943-7.
Thorp, J. H. & M. D. Delong, 2002. Dominance of autochthonous autotrophic carbon in food webs of heterotrophic rivers. Oikos 96: 543–550.
Townsend, C. R., R. M. Thompson, A. R. McIntosh, C. Kilroy, E. Edwards & M. R. Scarsbrook, 1998. Disturbance, resource supply, and food-web architecture in streams. Ecology Letters 1: 200–209.
Usseglio-Polatera, P., M. Bournaud, P. Richoux & H. Tachet, 2000. Biomonitoring through biological traits of benthic macroinvertebrates: how to use species trait databases? Hydrobiologia 422–423: 153–162.
Vander Zanden, M. J. & J. B. Rasmussen, 1999. Primary consumer δ13C and δ15N and the trophic position of aquatic consumers. Ecology 80: 1395–1404.
Vander Zanden, M. J. & J. B. Rasmussen, 2001. Variation in δ15N and δ13C trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 2061–2066.
Vanderklift, M. A. & S. Ponsard, 2003. Sources of variation in consumer-diet δ15N enrichment: a meta-analysis. Oecologia 136: 169–182.
Wallace, R. K., 1981. An assessment of diet-overlap indexes. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 110: 72–76.
Walters, A. W. & D. M. Post, 2008. An experimental disturbance alters fish size structure but not food chain length in streams. Ecology 89: 3261–3267.
Werner, R. A. & W. A. Brand, 2001. Referencing strategies and techniques in stable isotope ratio analysis. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 15: 501–519.
Whittaker, R. H. & C. W. Fairbanks, 1958. A study of plankton copepod communities in the Columbia Basin, Southeastern Washington. Ecology 39: 46–65.
Woodland, R., M. Rodríguez, P. Magnan, H. Glémet & G. Cabana, 2012. Incorporating temporally dynamic baselines in isotopic mixing models. Ecology 93: 131–144.
Woodward, G., J. P. Benstead, O. S. Beveridge, J. Blanchard, T. Brey, L. E. Brown, W. F. Cross, N. Friberg, T. C. Ings, U. Jacob, S. Jennings, M. E. Ledger, A. M. Milner, J. M. Montoya, E. O’Gorman, J. M. Olesen, O. L. Petchey, D. E. Pichler, D. C. Reuman, M. S. A. Thompson, F. J. F. Van Veen & G. Yvon-Durocher, 2010a. Ecological networks in a changing climate. Advances in Ecological Research 42: 71–138.
Woodward, G., J. B. Dybkjaer, J. S. Òlafsson, G. M. Gìslason, E. R. Hannesdòttir & N. Friberg, 2010b. Sentinel systems on the razor’s edge: effects of warming on Arctic geothermal stream ecosystems. Global Change Biology 16: 1979–1991.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Virginie Raymond for assistance in the field and sample preparation. Stable isotope analyses were carried out with EA-IRMS at Cemagref/Irstea Antony, Research Unit HBAN with the patient support of Jonathan Epissard. Bernard Hugueny and Olivier Delaigue gave helpful recommendations for statistical analyses. We also thank Michel Sanchez for kindly allowing us to work on his properties and for his welcome. We express our gratitude to Julien Peschard, who created the site map. We thank Deborah Slawson for copyediting the initial manuscript. This work was funded by the French Ministry of Ecology and Sustainable Development (MEDDAD) under a “Global Change and demographic strategies of fish populations” contract (APR Biodiversity and Climate Change 2005), 2007–2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: M. Power
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hette-Tronquart, N., Roussel, JM., Dumont, B. et al. Variability of water temperature may influence food-chain length in temperate streams. Hydrobiologia 718, 159–172 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1613-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1613-7