Abstract
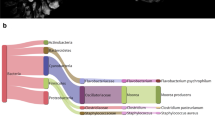
Among Neotropical fish fauna, the South American killifish genus Austrolebias (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae) constitutes an excellent model to study the genomic evolutionary processes underlying speciation events. Recently, unusually large genome size has been described in 16 species of this genus, with an average DNA content of about 5.95 ± 0.45 pg per diploid cell (mean C-value of about 2.98 pg). In the present paper we explore the possible origin of this unparallel genomic increase by means of comparative analysis of the repetitive components using NGS (454-Roche) technology in the lowest and highest Rivulidae genomes. Here, we provide the first annotated Rivulidae-repeated sequences composition and their relative repetitive fraction in both genomes. Remarkably, the genomic proportion of the moderately repetitive DNA in Austrolebias charrua genome represents approximately twice (45 %) of the repetitive components of the highly related rivulinae taxon Cynopoecilus melanotaenia (25 %). Present work provides evidence about the impact of the repeat families that could be distinctly proliferated among sublineages within Rivulidae fish group, explaining the great genome size differences encompassing the differentiation and speciation events in this family.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Aparicio S, Chapman J, Stupka E, Putnam N, Chia JM, Dehal P et al (2002) Whole genome shotgun assembly and analysis of the genome of Fugu rubripes. Science 297:1301–1310
Balzer S, Malde K, Lanzén A, Sharma A, Jonassen I (2010) Characteristics of 454 pyrosequencing data—enabling realistic simulation with flowsim. Bioinformatics 26:i420–i425
Ferreira DC, Porto-Foresti F, Oliveira C, Foresti F (2011) Transposable elements as a potential source for understanding the fish genome. MGSs 1:112–117
García G (2006) Multiple simultaneous speciation in killifishes of the Cynolebias adloffi species complex (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae) from phylogeography and chromosome data. J Zool Syst Evol Res 44:75–87. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0469.2005.00346.x
García G, Scvortzoff E, Máspoli MC, Vaz-ferreira R (1993) Analysis of karyotypic evolution in natural populations of Cynolebias (Pisces, Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae) using banding techniques. Cytologia 58:85–94
García G, Scvortzoff E, Hernández A (1995) Karyotypic heterogeneity in South American annual killifishes of the genus Cynolebias (Pisces, Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Cytologia 60:103–110
García G, Lalanne A, Aguirre G, Cappetta M (2001) Chromosome evolution in the annual killifish genus Cynolebias and mitochondrial phylogenetic analysis. Chromosome Res 9:437–448
García G, Alvarez-Valin F, Gómez N (2002) Mitochondrial genes: Signals and Noise in phylogenetic reconstruction within killifish genus Cynolebias (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Biol J Linn Soc Lond 76:49–59
García G, Gutiérrez V, Ríos N, Turner B, Santiñaque F, López-Carro B, Folle G (2014) Burst speciation processes and genomic expansion in the neotropical annual killifish genus Austrolebias (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Genetica 142:87–98
Gordon A, Hannon GJ (2010) FASTX-toolkit. FASTQ/A short-reads preprocessing tools. (unpublished) http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Lande R (1984) The expected fixation rate of chromosomal inversions. Evolution 38:743–752
Loureiro M, de Sá RO (1998) Osteological analysis of the killifish genus Cynolebias (Cyprinodontiformes: Rivulidae). J Morphol 238:109–262
Mable BK, Alexandrou MA, Taylor MI (2011) Genome duplication in amphibians and fish: an extended synthesis. J Zool 284:151–182. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2011.00829.x
Medrano JF, Aasen E, Sharrow L (1990) DNA extraction from nucleated red blood cells. Biotechniques 8:43
Nikaido M, Noguchi H, Nishihara H, Toyoda A, Suzuki Y, Kajitani R, Suzuki H, Okuno M, Aibara M, Ngatunga BP et al (2013) Coelacanth genomes reveal signatures for evolutionary transition from water to land. Genome Res 23:1740–1748. doi:10.1101/gr.158105.113
Novák P, Neumann P, Macas J (2010) Graph-based clustering and characterization of repetitive sequences in next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinformatics 11:378
Novák P, Neumann P, Pech J, Steinhais J, Macas J (2013) RepeatExplorer: a Galaxy-based web server for genome-wide characterization of eukaryotic repetitive elements from next-generation sequence reads. Bioinformatics 29:792–793. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btt054
Piednoël M, Aberer AJ, Schneeweiss GM, Macas J, Novak P, Gundlach H, Temsch EM, Renner S (2012) Next-generation sequencing reveals the impact of repetitive DNA across phylogenetically closely related genomes of orobanchaceae. Mol Biol Evol 29:3601–3611. doi:10.1093/molbev/mss168
Poulter R, Butler M (1998) A retrotransposon family from the pufferfish (fugu) Fugu rubripes. Gene 215:241–249
Rebollo R, Horard B, Hubert B, Vieira C (2010) Jumping genes and epigenetics: towards new species. Gene 454:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2010.01.003
Reichwald K, Lauber C, Nanda I, Kirschner J, Hartmann N, Schories S, Gausmann U, Taudien S, Schilhabel MB, Szafranski K et al (2009) High tandem repeat content in the genome of the short-lived annual fish Nothobranchius furzeri: a new vertebrate model for aging research. Genome Biol 10:R16.1–R16.17. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-2-r16
Schartl M, Walter RB, Shen Y, Garcia T, Catchen J, Amore A, Braasch I, Chalopin D, Volff JN, Lesch KP et al (2013) The genome of the platyfish, Xiphophorus maculatus, provides insights into evolutionary adaptation and several complex traits. Nat Genet 45:567. doi:10.1038/ng.2604
Spaink HP, Jansen HJ, Dirks RP (2014) Advances in genomics of bony fish. Brief Funct Genomic 13:144–156
Volff JN (2005) Genome evolution and biodiversity in teleost fish. Heredity 94:280–294
Volff JN, Korting C, Altschmied J, Duschl J, Sweeney K, Wichert K et al (2001) Jule from the fish Xiphophorus is the first complete vertebrate Ty3/Gypsy retrotransposon from the Mag family. Mol Biol Evol 18:101–111
Volff JF, Bouneau L, Ozouf-Costaz C, Fischer C (2003) Diversity of retrotransposable elements in compact pufferfish genomes. Trends Genet 19:674–678
Wang W, Yi Q, Ma L, Zhou X, Zhao H, Wang X, Qi J, Yu H, Wang Z, Zhang Q (2014) Sequencing and characterization of the transcriptome of half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). BMC Genom 15:470. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-470
Wourms JP (1967) Annual fishes. In: Wilt FH, Wessels N (eds) Methods in developmental biology. Thomas and Crowell Company, New York, pp 123–137
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by Dedicación Total_ Project (UdelaR, Uruguay) and Fondo Clemente Estable_1_2011_1_6784 (Agencia Nacional Investigación e Innovación, Uruguay) Project to G.G. We thank M. Vaio for your assistance in the RepeatExplorer processing data. G.G. and V.G. acknowledge the support of Sistema Nacional de Investigadores (ANII, Uruguay). The present paper version was improved incorporating the valuables suggestions furnished by two anonymous Reviewers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10709_2015_9834_MOESM2_ESM.docx
Electronic Supplementary Material 2. Major moderately cluster Repeats detected in D. rerio in the RepeatExplorer analysis. (DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García, G., Ríos, N. & Gutiérrez, V. Next-generation sequencing detects repetitive elements expansion in giant genomes of annual killifish genus Austrolebias (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae). Genetica 143, 353–360 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-015-9834-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-015-9834-5