Abstract
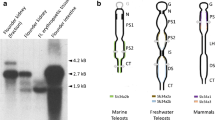
A sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter gene, NaPi-IIb (slc34a2), was isolated from yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) intestine through homology cloning and the rapid amplification of cDNA ends. The full-length cDNA of slc34a2 consisted of 2326 bp with an open reading frame encoding 621 amino acids, a 160-bp 5′ untranslated region, and a 300-bp 3′ untranslated region. The deduced amino acid sequence showed 79.0 and 70.9 % sequence identity to Astyanax mexicanus and Pundamilia nyererei, respectively. The membrane-spanning domains based on the hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties of the deduced amino acids were predicted, and results showed that the putative protein had eight transmembrane domains, with the intracellular NH2 and COOH termini. Two functional regions including first intracellular loop and third extracellular loop as well as the six N-glycosylation sites in second extracellular loop were found. The slc34a2 mRNA in the tested tissues was examined through semiquantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and quantitative real-time PCR, with the highest level found in the anterior intestine, followed by the posterior and middle intestines. The slc34a2 mRNA expression in the whole intestine under different dietary phosphorus (P) treatments was detected using qPCR. The results showed that the slc34a2 expression levels in the low-P groups (0.33 and 0.56 %) were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than levels in the sufficient-P (0.81 %) and high-P (1.15, 1.31, and 1.57 %) groups. High expression of slc34a2 mRNA in low-P groups stimulated P utilization efficiency, indicating the close relationship between genotype and phenotype in yellow catfish. In contrast with conventional strategies (formula and feeding strategies), this study provided another possible approach by using molecular techniques to increase the P utilization in yellow catfish.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arima K, Collins JF, Hines ER, Bai L, Ghishan FK (2000) Molecular cloning of murine sodium–phosphate cotransporter Type IIb (Na/P(i)-IIb) gene promoter and characterization of gene structure. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Struct Expr 1494:149–154
Arima K, Hines ER, Kiela PR, Drees JB, Collins JF, Chishan FK (2002) Glucocorticoid regulation and glycosylation of mouse intestinal Type IIb Na-Pi cotransporter during ontogeny. Am J Physiol-Gastr Liver Physiol 283:426–434
Avila EM, Tu H, Basantes S, Ferraris RP (2000) Dietary phosphorus regulates intestinal transport and plasma concentrations of phosphate in rainbow trout. J Comp Physiol (B) 170:201–209
Brazy PC, Gullans SR, Mandel LJ, Dennis VW (1982) Metabolic requirement for inorganic phosphate by the rabbit proximal tubule. J Clin Invest 70:53–62
Brichon G (1973) Phosphorus absorption by the intestine of the eel (Anguilla anguilla L). Demonstration and characteristics of in vitro phosphate ion transport in the fresh water eel. Soc Biol Fil 167:1142–1145
Cho CY, Bureau DP (2001) A review of diet formulation strategies and feeding systems to reduce excretory and feed wastes in aquaculture. Aquac Res 32(s1):349–360
Coloso RM, Basantes SP, King K, Hendrix MA, Fletcher JW, Weis P, Ferraris RP (2001) Effect of dietary P and vitamin D3 on phosphorus levels in effluent from the experimental culture of rainbow trout. Aquaculture 202:145–161
Coloso RM, King K, Fletcher JW, Weis P, Werner A, Ferraris RP (2003) Dietary P regulates phosphate transporter expression, phosphatase activity, and effluent P partitioning in trout culture. J Comp Physiol 173B:519–530
Corut A, Senyigit A, Ugur SA, Altin S, Ozcelik U, Calisir H, Yildirim Z, Gocmen A, Tolun A (2006) Mutations in SLC34A2 cause pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis and are possibly associated with testicular microlithiasis. Am J Hum Genet 79:650–656
Cross HS, Debiec H, Peterlik M (1990) Mechanism and regulation of intestinal phosphate absorption. Miner Electrol Metab 16:115–124
Deer DM, Lampel KA, González-Escalona N (2010) A versatile internal control for use as DNA in real-time PCR and as RNA in real-time reverse transcription PCR assays. Lett Appl Microbiol 50:366–372
Fanning AS, Anderson JM (1996) Protein–protein interactions: PDZ domain Networks. Curr Biol 6:1385–1388
Feild JA, Zhang L, Brun KA, Brooks DP, Edwards RM (1999) Cloning and functional characterization of a sodium-dependent phosphate transporter expressed in human lung and small intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 258:578–582
Gisler SM, Stagljar I, Traebert M, Bacic D, Biber J, Murer H (2001) Interaction of the Type IIa Na/Pi cotransporter with PDZ proteins. J Biol Chem 276:9206–9213
Gowen RJ, Weston DP, Ervik A (1991) Aquaculture and the benthic environment. In: Cowey CB, Cho CY (eds) Nutritional strategies and aquaculture waste. Univ. of Guelph, Ontario, pp 187–206
Graham C, Nalbant P, Scholermann B, Hentschel H, Kinne RK, Werner A (2003) Characterization of a Type IIb sodium–phosphate cotransporter from zebra fish (Danio rerio) kidney. Am J Physiol-Renal 284:727–736
Green JA, Brannon EL, Hardy RW (2002) Effects of dietary Phosphorus and lipid levels on utilization and excretion of phosphorus and nitrogen by rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). 2. Production-scale study. Aquac Nutr 8:291–298
Hashimoto M, Wang DY, Kamo T, Zhu Y, Tsujiuchi T, Konishi Y, Tanaka M, Sugimura H (2000) Isolation and localization of Type IIb Na/Pi cotransporter in the developing rat lung. Am J Pathol 157:21–27
Hayes G, Busch A, Lötscher M, Waldegger S, Lang F, Verrey F, Biber J, Murer H (1994) Role of N-linked glycosylation in rat renal Na/Pi cotransport. J Biol Chem 269:24143–24149
Hernando N, Karim-Jimenez Z, Biber J (2001) Molecular determinants for apical expression and regulatory membrane retrieval of the Type IIa Na/Pi cotransporter. Kidney Int 60:431–435
Hilfiker H, Hattenhauer O, Traebert M, Forster I, Murer H, Biber J (1998) Characterization of a murine type II sodium–phosphate cotransporter expressed in mammalian small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14564–14569
Huqun IS, Miyazawa H, Ishii K, Uchiyama B, Ishida T, Tanaka S, Tazawa R, Fukuyama S, Tanaka T et al (2007) Mutations in the SLC34A2 gene are associated with pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175:263–268
Katai K, Miyamoto K, Kishida S, Segawa H, Nii T, Tanaka H, Tani Y, Arai H, Tatsumi S, Morita K, Taketani Y et al (1999) Regulation of intestinal Na+-dependent phosphate co-transporters by a low-phosphate diet and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Biochem J 343:705–712
Ketola HG, Richmond ME (1994) Requirement of rainbow trout for dietary phosphorus and its relationship to the amount discharged in hatchery effluents. Trans Am Fish Soc 123:587–594
Kohl B, Herter P, Hulseweh B, Elger M, Hentschel H, Kinne RK, Werner A (1996) Na-Pi cotransport in flounder: same transport system in kidney and intestine. Am J Physiol-Renal 270:937–944
Köhler K, Forster IC, Stange G, Biber J, Murer H (2002) Identification of functionally important sites in the first intracellular loop of the NaPi-IIa cotransporter. Am J Physiol-Renal 282:687–696
Lall SP (1991) Digestibility, metabolism and excretion of dietary phosphorus in fish. In: Cowey CB, Cho CY (eds) Nutritional strategies and aquaculture waste. University of Guelph, Ontario, p 2136
Møbjerg N, Werner A, Hansen SM, Novak I (2007) Physiological and molecular mechanisms of inorganic phosphate handling in the toad (Bufo bufo). Eur J Physiol 454:101–113
Morita K, Haga H, Tanaka H, Fujioka A, Segawa H, Katai K, Tatsumi S, Koda T, Taketani Y, Hisano S et al (1998) Efffect of dietary phosphate on Na+-dependent phosphate cotransporters function and expression in the rat kidney. Clin Exp Nephrol 2:109–116
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2000) Proximal tubular phosphate reabsorption: molecular mechanisms. Physiol Rev 80:1373–1409
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2001) Molecular mechanisms in proximal tubular and small intestinal phosphate reabsorption (plenary lecture). Mol Membr Biol 18:3–11
Nakamura Y (1985) Sodium-dependent absorption of inorganic phosphate by the carp intestine. Comp Biochem Physiol 80A:437–439
Nalbant P, Böhmer C, Dehmelt L, Wehner F, Werner A (1999) Functional characterization of a Na/Pi cotransporter (NaPi-II) from zebra fish and identification of related transcripts. J Physiol 520:79–89
NRC (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. The National Academies Press Washington, DC
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:45
Radanovic T, Wagner CA, Murer H, Biber J (2005) Regulation of Intestinal Phosphate Transport I. Segmental expression and adaptation to low-Pi diet of the Type IIb Na+-Pi cotransporter in mouse small intestine. Am J Physiol-Gastr Liver Physiol 288:496–500
Radanovic T, Gisler SM, Biber J, Murer H (2006) Topology of the Type IIa Na+/Pi cotransporter. J Membr Biol 212:41–49
Reining SC, Liesegang A, Betz H, Biber J, Murer H, Hernando N (2010) Expression of renal and intestinal Na/Pi cotransporters in the absence of GABARAP. Pflugers Arch 460:207–217
Rodehutscord M (1996) Response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) growing from 50 to 200 g to supplements of dibasic sodium phosphate in a semi-purified diet. J Nutr 126:324–331
Roy PK, Lall SP (2003) Dietary phosphorus requirement of juvenile haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus L.). Aquaculture 221:451–468
Schröder B, Breves G, Rodehutscord M (1996) Mechanisms of intestinal phosphorus absorption and availability of dietary phosphorus in pigs. Deutsche Tieraerztliche Wochenschrift 103:209–214
Sugiura SH (2009) Identification of intestinal phosphate transporters in fishes and shellfishes. Fish Sci 75:99–108
Sugiura SH, Ferraris RP (2004a) Dietary phosphorus-responsive genes in the intestine, pyloric ceca, and kidney of rainbow trout. Am J Physiol-Regul 287:541–550
Sugiura SH, Ferraris RP (2004b) Contributions of different NaPi cotransporter isoforms to dietary regulation of P transport in the pyloric caeca and intestine of rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 207:2055–2064
Sugiura SH, McDaniel NK, Ferraris RP (2003) In vivo fractional P(i) absorption and NaPi-II mRNA expression in rainbow trout are up-regulated by dietary P restriction. Am J Physiol-Regul 285:770–781
Sugiura SH, Marchant D, Kelsey K, Wiggins T, Ferraris RP (2006) Effluent profile of commercially used low-phosphorus fish feeds. Environ Pollut 140:95–101
Sugiura SH, Kelsey K, Ferraris RP (2007) Molecular and con-ventional responses of large rainbow trout to dietary phosphorus restriction. J Comp Physiol 177:461–472
Talbot C, Hole R (1994) Fish diets and the control of eutrophication resulting from aquaculture. J Appl Ichthyol 10:258–270
Tang Q, Wang C, Xie C, Jin J, Huang Y (2012) Dietary available phosphorus affected growth performance, body composition, and hepatic antioxidant property of Juvenile Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Sci World J 2012:1–9
Traebert M, Hattenhauer O, Murer H, Kaissling B, Biber J (1999) Expression of Type II Na-Pi cotransporter in alveolar Type II cells. Am J Physiol Lung C 277:868–873
Wagner CA, Hernando N, Forster IC, Biber J (2014) The SLC34 family of sodium-dependent phosphate transporters. Pflügers Archiv-Eur J Physiol 466:139–153
Walton J, Gray TK (1979) Absorption of inorganic phosphate in the human small intestine. Clin Sci Mol Med 56:407–412
Werner A, Kinne RK (2001) Evolution of the Na-P(i) cotransport systems. Am J Physiol-Regul 280:301–312
Werner A, Murer H, Kinne RK (1994) Cloning and expression of a renal Na-Pi cotransport system from flounder. Am J Physiol 267:311–317
Wiesmann D, Scheid H, Pfeffer E (1988) Water pollution with phosphorus of dietary origin by intensively fed rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Rich.). Aquaculture 69:263–270
Yan F, Angel R, Ashwell CM (2007) Characterization of the chicken small Intestine Type IIb sodium phosphate cotransporter. Poult Sci 86:67–76
Zhao Y, Gul Y, Li S, Wang W (2011) Cloning, identification and accurate normalization expression analysis of PPARα gene by GeNorm in Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:462–468
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 31172421), Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (Project No. 201203083), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013PY076). Thanks were given to Dr. Xiaolei Wang from University of Pittsburgh for his valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Tang, Q. & Wang, C. Characterizing and evaluating the expression of the type IIb sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter (slc34a2) gene and its potential influence on phosphorus utilization efficiency in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fish Physiol Biochem 42, 51–64 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0116-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0116-z