Abstract
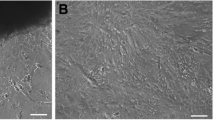
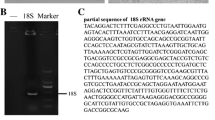
A new marine fish cell line, TK, derived from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) kidney, was established by the method of trypsin digestion and subcultured for more than 50 passages over a period of 300 days. The TK cells were maintained in Minimum Essential Medium Eagle (MEM) supplemented with HEPES, antibiotics, fetal bovine serum (FBS), 2-Mercaptoethanol (2-Me), and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). The suitable growth temperature for TK cells was 24°C, and microscopically, TK cells were composed of fibroblast-like cells. Chromosome analysis revealed that the TK cell line has a normal diploid karyotype with 2n = 44. Two fish viruses LCDV-C (lymphocystis disease virus from China) and TRBIV (turbot reddish body iridovirus) were used to determine the virus susceptibility of TK cell line. The TK cell line was found to be susceptible to TRBIV, and the infection was confirmed by cytopathic effect (CPE) and transmission electron microscopy, which detected the viral particles in the cytoplasm of virus-infected cells. Finally, significant green fluorescent signals were observed when the TK cells were transfected with pEGFP-N3 vector, indicating its potential utility for fish virus study and genetic manipulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloch B, Larsen JL (1993) An iridovirus-like agent associated with systemic infection in cultured turbot Scophthalmus maximus fry in Denmark. Dis Aquat Organ 15:235–240
Bonewald LF (1999) Establishment and characterization of an osteocyte-like cell line, MLO-Y4. J Bone Miner Metab 17:61–65
Bouza C, Sanchez L, Martnez P (1994) Karotypic characterization of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) with conventional, fluorochrome and restriction endonuclease-banding techniques. Mar Biol 120:609–613
Chang SF, Ngoh GH, Kuch LFS, Qin QW, Chen CL, Lam TJ, Sin YM (2001) Development of a tropical marine fish cell line from Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) for virus isolation. Aquaculture 192:133–145
Chen SL, Sha ZX, Ye HQ (2003a) Establishment of a pluripotent embryonic cell line from sea perch blastula embryo. Aquaculture 218:141–151
Chen SL, Ye HQ, Sha ZX, Hong Y (2003b) Derivation of a pluripotent embryonic cell line from red sea bream blastulas. J Fish Biol 63:795–805
Chen SL, Ren GC, Sha ZX, Hong Y (2005) Development and characterization of a continuous embryonic cell line from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquaculture 249:63–68
Dash PK, Tiwari M, Santhosh SR, Parida M, Lakshmana Rao PV (2008) RNA interference mediated inhibition of Chikungunya virus replication in mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:718–722
Donato MT, Lahoz A, Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ (2008) Cell lines: a tool for in vitro drug metabolism studies. Curr Drug Metab 9:1–11
Earley EM (1975) Chromosome preparations from monolayer cell culture. TCA Man 1:31–35
Fan TJ, Geng XF, Cong RS, Jiang GJ, Yu QT, Fu YF, Wang J, Yu MM, Yang XX, Wu JD (2007) Establishment of a novel fin cell line from turbot, Scophthalmus maximus. Period Ocean Univ China 37(5):759–766
Fernández RD, Yoshimizu M, Kimura T, Ezura Y, Inouye K, Takami I (1993) Characterization of three continuous cell lines from marine fish. J Aquat Anim Health 5:127–136
Fernández-Puentes C, Novoa B, Figueras A (1993) Initiation of a cell line from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 29A(12):899–900
Fryer JL, Lannon CN (1994) Three decades of fish cell culture: a current listing of cell lines derived from fish. J Tissue Cult Methods 16:87–94
Hellberg H, Koppang EO, Tørud B, Bjerkås I (2002) Subclinical herpesvirus infection in farmed turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Dis Aqua Org 49:27–31
Hightower LH, Renfro JL (1988) Recent applications of fish cell culture to biomedical research. J Exp Zool 248:290–302
Hong Y, Chen SL, Gui JF, Schartl M (2004) Retention of the developmental pluripotency in medaka embryonic stem cells after gene transfer and long-term drug selection towards for gene targeting in fish. Transgen Res 13:41–50
Iwamotoa R, Hasegawab O, LaPatrac S, Yoshimizud M (2002) Isolation and characterization of the Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) lymphocystis disease virus. J Aquat Anim Health 14:114–123
Johansen R, Sommerset I, Tørud B, Korsnes K, Hjortaas MJ, Nilsen F, Nerland AH, Dannevig BH (2004) Characterization of nodavirus and viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in farmed turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.). J Fish Dis 27:591–601
Ledermann B (2000) Embryonic stem cells and gene targeting. Exp Physiol 85:603–613
Levan A (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220
Meng L, Chen SL, Liu Y (2008) Construction of a cDNA library from spleen of Scophthalmus maximus and identification of immune-related genes by EST sequencing. J Fish China 33:713–718
Nishizawa T, Savas H, Isidan H, Ustündağ C, Iwamoto H, Yoshimizu M (2006) Genotyping and pathogenicity of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus from free-living turbot (Psetta maxima) in a Turkish coastal area of the Black Sea. Appl Environ Microb 72:2373–2378
Novoa B, Figueras A, Puentes CF, Ledo A, Toranzo AE (1993) Characterization of a birnavirus isolated from diseased turbot cultured in Spain. Dis Aqua Org 15:163–169
Parameswaran V, Ishaq Ahmed VP, Shukla R, Bhonde RR, Sahul Hameed AS (2007) Development and characterization of two new cell lines from milkfish (Chanos chanos) and grouper (Epinephelus coioides) for virus isolation. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 9:281–291
Pardo BG, Fernández C, Millán A, Bouza C, Vázquez-López A, Vera M, Alvarez-Dios JA, Calaza M, Gómez-Tato A, Vázquez M, Cabaleiro S, Magariños B, Lemos ML, Leiro JM, Martínez P (2008) Expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from immune tissues of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) challenged with pathogens. BMC Vet Res 4:37
Park KC, Osborne JA, Montes A, Dios S, Nerland AH, Novoa B, Figueras A, Brown LL, Johnson SC (2009) Immunological responses of turbot (Psetta maxima) to nodavirus infection or polyriboinosinic polyribocytidylic acid (pIC) stimulation, using expressed sequence tags (ESTs) analysis and cDNA microarrays. Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:91–108
Petersen OW, Gudjonsson T, Villadsen R, Bissell MJ, Rønnov-Jessen L (2003) Epithelial progenitor cell lines as models of normal breast morphogenesis and neoplasia. Cell Prolif 36:33–44
Shi CY, Wang YG, Yang SL, Huang J, Wang QY (2004) The first report of an iridovirus-like agent infection in farmed turbot Scophthalmus maximus in China. Aquaculture 236:11–25
Shi CY, Huang J, Yang B, Liu L (2008) PCR method for detection of turbot reddish body iridovirus (TRBIV): development and application. J Fish Sci China 15:830–836
Sun XQ, Qu LY, Zhang JX (2000) Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of lymphocystis virus of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). High Technol Lett (9):19–21
Tocher D, Carr J, Sargent JR (1989) Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in fish cells: differential metabolism of (n_3) and (n_6) series acids by cultured cells originating from fresh water teleost fish and from marine teleost fish. Comp Biochem Physiol B 94:367–374
Xu HT, Piao CA, Jiang ZL, Wang WX (2000) Study on the causative agent of lymphocystic disease in cultured flounder Paralichthys olivaceus, in China. China J Virol (16):223–226
Zhang QY, Ruan HM, Li ZQ, Yuan XP, Gui JF (2003) Infection and propagation of lymphocystis virus isolated from the cultured flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in grass carp cell lines. Dis Aquat Org (57):27–34
Zhao XJ, Chen SL, Wang N, Wang XL, Xing SC (2010) Cloning, recombinant expression and purification of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) mature IGF-1. J Fish China 34:1–7
Zhou GZ, Li ZQ, Yuan XP, Zhang QY (2007) Establishment, characterization, and virus susceptibility of a new marine cell line from red spotted grouper (Epinephelus akaara). Mar Biotechnol (NY) 9:370–376
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Y. Y. Hou and J. S. Tan in the College of Medical Science, Qingdao University for their kind assistance in the electron microscopic preparation. This study was supported by grants from the National 863 High Technology Research Foundation of China (2006AA09Z406, 2006AA10A401), Taishan Scholar Project Fund and the Basic Scientific Research Fund of YSFRI (2008-ts-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
N. Wang and X. L. Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Wang, X.L., Sha, Z.X. et al. Development and characterization of a new marine fish cell line from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Physiol Biochem 36, 1227–1234 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-010-9402-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-010-9402-y