Abstract
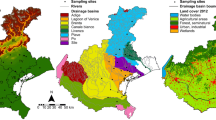
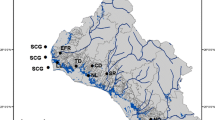
The Paraná River, the sixth largest in the world, is the receptor of pollution loads from tributaries traversing urban and industrialized areas plus agricultural expanses, particularly so in the river’s middle and lower reaches along the Argentine sector. In the present study, we analyzed and discussed the main water quality parameters, sediment compositions, and content of the herbicide glyphosate plus its metabolite aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in water and sediments. Samples were obtained from distal positions in the principal tributaries of the Paraná and the main watercourse during surveys conducted in 2011 and 2012 to monitor the basin. Only 15 % of the water samples contained detectable concentrations of glyphosate at an average concentration of 0.60 μg/L, while no detectable levels of AMPA were observed. The herbicide and metabolite were primarily present in sediments of the middle and lower stretch’s tributaries, there occurring at a respective average of 37 and 17 % in samples. The mean detectable concentrations measured were 742 and 521 μg/kg at mean, maximum, and minimum glyphosate/AMPA ratios of 2.76, 7.80, and 0.06, respectively. The detection of both compounds was correlated with the presence of sulfides and copper in the sediment matrix.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, J. (1976). An ignition method for determination of total phosphorus in lake sediment. Water Research, 10, 329–331.
Aparicio, V. C., De Gerónimo, E., Marino, D., Primost, J., Carriquiriborde, P., & Costa, J. L. (2013). Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere, 93, 1866–1873.
APHA (1998). In L. S. Clesceri, A. E. Greenberg, & A. D. Eaton (Eds.), Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Bindraban, P. S., Franke, A. C., Ferrar, D. O., Ghersa, C. M., Lotz, L. A. P., Nepomuceno, A., Smulders, M. J. M., & van de Wiel, C. C. M. (2009). GM-related sustainability: agro-ecological impacts, risks and opportunities of soy production in Argentina and Brazil. Wageningen: Plant Research International B.V..
Campodonico, V. A., García, M. G., & Pasquini, A. I. (2015). The dissolved chemical and isotopic signature down flow the confluence of two large rivers: the case of the Paraná and Paraguay rivers. Journal of Hydrology, 528, 161–176.
CONABIO, 2013. Consejo Argentino para la información y el desarrollo de la biotecnología, www.argenbio.org
Day, P. (1965). Particle fractionation and particle size analysis methods of soil analysis. In C. Black (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, part I (pp. 545–566). Wisconsin: American Society of Agronomy.
Degenhardt, D., Humphries, D., Cessna, A. J., Messing, P., Badiou, P. H., Raina, R., Farenhorst, A., & Pennock, D. J. (2012). Dissipation of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water and sediment of two Canadian prairie wetlands. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 47, 631–639.
Faircloth, W. H., Dale Monks, C., Patterson, M. G., Wehtje, G. R., Delaney, D. P., & Sanders, J. C. (2004). Cotton and weed response to glyphosate applied with sulfur-containing additives. Weed Technology, 18, 404–411.
Heinemann, J. A., Agapito-Tenfen, S. Z., & Carman, J. A. (2013). A comparative evaluation of the regulation of GM crops or products containing dsRNA and suggested improvements to risk assessments. Environment International, 55, 43–55.
Heiri, O., Lotter, A. F., & Lemcke, G. (2001). Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content insediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology, 25, 101–110.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernández, J., & Fernández, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34, 807–816.
Ibáñez, M., Pozo, O. J., Sancho, J. V., López, F. J., & Hernández, F. (2005). Residue determination of glyphosate, glufosinate and aminomethylphosphonicacid in water and soil samples by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1081, 145–155.
ICH, 2005. International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use guidelines. Expert Working Group, Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1), London.
Iriondo, M. (1988). A comparison between the Amazon and the Paraná River systems, in: E. Degens, S. Kempe, S. Naidu (Eds.), Transport of carbon and minerals in major world rivers, lakes and estuaries. Pt. 5. Mitteilungen des Geologish-Paläeontologischen Instituts der Universität Hamburg. SCOPE/UNEP, Sonderband, 66, 77–92.
Konta, J. (1985). Crystalline materials and chemical maturity of suspended solids of some major world rivers. Mineralogica et Petrographica Acta, 29, 121–133.
Leguizamón, A. (2014). Modifying Argentina: GM soy and socio-environmental change. Geoforum, 53, 149–160.
Manassero, M., Camilión, C., Poiré, D., Da Silva, M., & Ronco, A. (2008). Grain size analysis and clay mineral association in bottom sediments from Paraná River basin. Latin American Journal Sedimentology and Basin Analysis, 15, 125–137.
Marino, D., & Ronco, A. (2005). Cypermethrin and chlorpiryfos concentration levels in surface water bodies of the Pampa Ondulada, Argentina. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 75, 820–826.
Meyer, M.T., Loftin, K.A., Lee, E.A., Hinshaw, G.H., Dietze, J.E., Scribner, E.A., 2009. Determination of glyphosate, its degradation product aminomethylphosphonic acid, and glufosinate, in water by isotope dilution and on line solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods, book 5, chap. A10, 32p.
Miles, C. J., & Moye, H. A. (1988). Extraction of glyphosate herbicide from soil and clay minerals and determination of residues in soils. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 36, 486–491.
Morillo, E., Undabeytia, T., Maqueda, C., & Ramos, A. (2000). Glyphosate adsorption on soils of different characteristics. Influence of copper addition. Chemosphere, 40, 103–107.
Nalewaja, J. D., & Matysiak, R. (1993). Influence of diammonium sulfate and other salts on glyphosate phytotoxicity. Pesticide Science, 38, 77–84.
Orfeo, O., & Stevaux, J. (2002). Hydraulic and morphological characteristics of middle and upper reaches of the Paraná River (Argentina and Brazil). Geomorphology, 44, 309–332.
Peluso, M. L., Abelando, M., Apartín, C. D., Almada, P., & Ronco, A. E. (2013a). Integrated quality assessment of bottom sediments from the Paraná basin. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 98, 179–186.
Peluso, L., BulusRossini, G., Salibián, A., & Ronco, A. (2013b). Physicochemical and ecotoxicological based assessment of bottom sediments from the Luján River basin, Buenos Aires Argentina. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 5993–6002.
Peruzzo, P. J., Porta, A. A., & Ronco, A. E. (2008). Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in North Pampasic region of Argentina. Environmental Pollution, 156, 61–66.
Lupi, L., Miglioranza, K. S. B., Aparicio, V. C., Marino, D., Bedmar, F., & Wunderlin, D. A. (2015). Occurrence of glyphosate and AMPA in an agricultural watershed from the southeastern region of Argentina. Science of the Total Environment, 536, 687–694.
Primost, J. E. (2013). Estudio de niveles ambientales de glifosato y AMPA en una zona modelo de intensa actividad agrícola en los alrededores de Urdinarrain (80 pp). Entre Ríos. Graduate Thesis: Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Argentina.
Quinn, G. P., & Keough, M. J. (2002). Experimental design and data for biologists. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Ronco, A., Carriquiriborde, P., Natale, G. S., Martin, M., Mugni, H., & Bonetto, C. (2008). Integrated approach for the assessment of biotech soybean pesticides impact on low order stream ecosystems of the Pampasic Region. In Ecosystem ecology research (pp. 209–239). New York: Nova Science.
Ronco, A., Almada, P., Apartin, C., Marino, D., Abelando, M., Bernasconi, C., Primost, J., Santillán, J.M., Amoedo, P. and Bulus Rossini, G., 2011. Monitoreo ambiental de los principales afluentes de los Ríos Paraná y Paraguay. Proceedings of the III Congreso Internacional sobre cambio climático y desarrollo sustentable, 08-11 August, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, La Plata, Argentina.
Sancho, J. V., Hernández, F., López, F. J., Hogendoorn, E. A., Dijkman, E., & van Zoonen, P. (1996). Rapid determination of glufosinate, glyphosate and AMPA in environmental water samples using precolumn fluorogenic labeling and coupled-column liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 737, 75–83.
SAyDS- OPS- PNA- UNLP, 2007. Caracterización Sanitaria y Ambiental de las Aguas en Tramos Específicos de los Ríos Paraná, Paraguay. Uruguay y sus Afluentes (Tres campañas). Technical Report. Secretaria de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sustentable; Organización Panamericana de la Salud; Prefectura Naval Argentina; Universidad Nacional de La Plata, 90 pp.
Taylor, P. J. (2005). Matrix effects: the Achilles heel of quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray–tandem mass spectrometry. Clinical Biochemistry, 38, 328–334.
USEPA, 1996. Method 9030 (acid-soluble and acid-insoluble sulfides: distillation) 3050 (acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soils), test methods for evaluating solid waste, vol. 1B: laboratory manual, physical/chemical methods (SW-846), United States Environmental Protection Agency, 3rd ed. US Government Printing Office, Washington (Update 3).
USEPA, 2008. Risks of glyphosate use to ederally threatened California Red-legged Frog (Rana aurora draytonii), United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Fate and Effects Division, Office of Pesticide Programs, Washington, D.C. 20460
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from UNLP PITAP-2010 and ANPCyT, PICT 2010-0891/PICT2012-3031. The authors wish to thank the Federico Leloir crew of the Prefectura Naval Argentina and the CIMA-UNLP laboratory team for their assistance, collaboration, and technical support. Dr. Donald F. Haggerty, a retired academic career investigator and native English speaker, edited the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
A. E. Ronco, D. J. G. Marino and C. D. Apartin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronco, A.E., Marino, D.J.G., Abelando, M. et al. Water quality of the main tributaries of the Paraná Basin: glyphosate and AMPA in surface water and bottom sediments. Environ Monit Assess 188, 458 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5467-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5467-0