Abstract
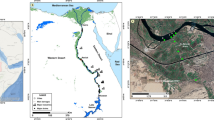
The state of Sinaloa in Mexico is an industrialized agricultural region with a documented pesticide usage of 700 t year−1; which at least 17 of the pesticides are classified as moderately to highly toxic. Pollutants in the water column of rivers and drains are of great concern because the water flows into coastal lagoons and nearshore waters and thereby affects aquatic organisms. This study was done in four municipalities in the state of Sinaloa that produce food intensively. To investigate the link between pollution in the lagoons and their proximity to agricultural sites, water was sampled in three coastal lagoons and in the rivers and drains that flow into them. Seawater from the Gulf of California, 10 km from the coast, was also analyzed. Concentrations of nutrients, organochlorines, and organophosphorus pesticides were determined. Nutrient determination showed an unhealthy environment with N/P ratios of <16, thus favoring nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. The organochlorine pesticides showed a clear accumulation in the coastal lagoons from the drains and rivers, with ΣHCH showing the highest concentrations. In the southern part of the region studied, pollution of the coastal lagoon of Pabellones could be traced mainly to the drains from the agricultural sites. Accumulation of OC pesticides was also observed in the Gulf of California. Tests for 22 organophosphates revealed only five (diazinon, disulfoton, methyl parathion, chlorpyrifos, and mevinphos); diazinon was detected at all the sites, although methyl parathion was present at some sites at concentrations one order of magnitude higher than diazinon.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arellano-Aguilar, O., & Macías-Garcia, C. (2008). Effects of methyl parathion exposure on development and reproduction in the viviparous fish Girardinichthys multiradiatus. Environmental Toxicology, 24(2), 178–186.
Band-Schmidt, C., Bustillos-Guzmán, J. J., López-Cortés, J. D., Garate-Lizarraga, I., Nunez-Vazquez, E. J., & Hernandez-Sandoval, F. E. (2010). Ecological and physiological studies of Gymnoinium catenatum in the Mexican Pacific: a review. Marine Drugs, 8(6), 1935–1961.
Berger, M., Loffler, D., Ternes, T., Heininger, P., Ricking, M., & Schwarzbauer, J. (2016). The effect of distribution processes on the isomeric composition of hexachlorocyclohexane in a contaminated riverine system. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13(4), 995–1008.
Burt, T. P., Matchett, L. S., Goulding, K. W. T., Webster, C. P., & Haycock, N. E. (1999). Denitrification in riparian buffer zones: the role of floodplain hydrology. Hydrological Processes, 13(10), 1451–1463.
Carvalho, F. P., Gonzalez-Farias, F., Villeneuve, J. P., Cattini, C., Hernandez-Garza, M., Mee, L. D., et al. (2002). Distribution, fate and effects of pesticide residues in tropical coastal lagoons of Northwestern Mexico. Environmental Toxicology, 23(11), 1257–1270.
CEC Commission for the Environmental Cooperation (2009). Compilación y clasificación de información inédita sobre sustancias tóxicas persistentes y bioacumulables. Montreal, Canada: CEC CCA CCE Three countries working together to protect our shared environment.
CICLOPAFEST (2002). Acuerdo que establece la clasificación y codificación de mercancías cuya importación está sujeta a regulación por parte de las dependencias que integran la CICOPLAFEST. In Diario Oficial de la Federación (Ed.), (pp. March 29th). Mexico.
Correll, D. L. (1998). The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. Journal of Enviornmental Quality, 27(2), 261–266.
Garcia-de la Parra, L. González-Valdivia, C. Cernates-Mojica, J. Aguilar Zárate, G. Bastidas-Bastidas, P. & Betancourt-Lozano, M. (Eds.). (2014). Plaguicidas y PCB en sedimentos de granjas camaronícolas en un sistema costero de Sinaloa. (Pacífico Mexicano. Contaminación e impacto ambiental: diagnóstico y tendencias). Mexico City, Mexico: UAC, UNAM-ICMYL, CIAD-Mazatlán, CIBNOR, CICESE.
Dìaz, J. R., Rosenberg, R., Rabalais, N. N., & Levin, A. L. (2009). Dead zone dilema. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(12), 1767–1768.
Downing, J. A. (1992). The nitrogen:phosphorous relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 37(5), 936–945.
European Commission (2013). Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/ 105/EC as regards priority substances in the field of water policy, Off. J. Eur. Union L226/1 (24.08.2013) 1.
FAO (2016). http://faostat3.fao.org. Accessed January 2016.
Galindo, R. J. G., Medina, J. M. A., Villagrana, L. C., & Ibarra, C. L. (1997). Environmental and pollution condition of the Huizache-Caimanero Lagoon, in the north-west of Mexico. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34(12), 1072–1077.
Gonzales-Farias, F., Cisneros-Estrada, X., Fuentes-Ruiz, C., Díaz-Gonzales, G., & Botello, A. V. (2002). Pesticide distribution in sediments of a tropical coastal lagoon adjacent to an irrigation district in northwest Mexico. Environmental Technology, 23(11), 1247–1256.
González-Farias, F. A., Cisneros Estrada, X., Escobedo Urías, D., & López Hernández, M. (Eds.). (2014). Impacto socioeconómico del uso de agroquímicos en distritos de riesgo (DR 063 Guasave, Sinaloa, y DR de temporal tecnificado 009 El Bejuco, Nayarit). (Pacífico mexicano. Contaminación e impacto ambiental: disgnóstico y tendencias.). Mexico: UAC, UNAM-ICYML, CIAD-Mazatlán, CIBNOR, CICESE.
Granados-Galván, I. A., Rodríguez-Meza, D. G., Luna-González, A., & González-Ocampo, H. A. (2015). Human health risk assessment of pesticide residues in snappers (Lutjanus) fish from the Navachiste Lagoon complex, Mexico. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 97(1–2), 178–187.
Guerrero Galván, R. (1998). Estudio biogeoquímico de los procesos de mezclado estuarino en la Laguna Costera Subtropical de México., PhD Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City.
Heisler, J., Glibert, P., Burkholder, J., Anderson, D., Cochlan, W., Dennison, W., et al. (2008). Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: a scientific consensus. Harmful Algae, 8, 3e13.
Hernández-Antonio, A., & Hansen, M. A. (2011). Use of pesticides in two agricultural areas of Mexico and evaluation of water and sediment pollution. Revista Internacional de Contaminaciòn Ambiental, 27(2), 115–127.
Khan, F., Naushin, F., Rehman, F., Masoodi, A., Irfan, M., Hashmi, F., et al. (2014). Eutrophication: global scenario and local threat to dynamics of aquatic ecosystems. In A. A. Ansari, & S. S. Gill (Eds.), Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences and Control. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer Science + Business Media. pp. 17–26.
Lewitus, A. J., Horner, R. A., Caron, D. A., Garcia-Mendoza, E., Hickey, B. M., Hunter, M., et al. (2012). Harmful algal blooms along the North American west coast region: history, trends, causes, and impacts. Harmful Algae, 19, 133–159.
Ley Federal de Derechos (2016). Disposiciones aplicables en materia de aguas nacionales. Mexico: Comisión Nacional de Agua.
Leyva Morales, J., García De La Parra, L. M., Bastidas Bastidas, J. E., Astorga Rodríguez, J. E., Bejarano Trujillo, J., Cruz Hernández, A., et al. (2014). Pesticide use in a technified agricultural valley in Northwest Mexico. Revista Internacional de Contaminaciòn Ambiental, 30(2), 247–261.
Loomis, D., Mattpck, H., Straif, K., & Zavadil, A. (2015). Carcinogenicity of lindane, DDT, and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. The Lancet Oncology, 16(8), 891–892.
McCarty, L. S., & Mackay, D. (1993). Enhancing ecotoxicological modeling and assessment. Body residues and modes of toxic action. Environmental Science and Technology, 27(9), 1718–1728.
Montes, A. M., González-Farias, F. A., & Botello, A. V. (2012). Pollution by organochlorine pesticides in Navachiste-Macapule, Sinaloa, Mexico. Enviornmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(3), 1359–1369.
O’Neill, K., Schreider, M., McArthur, L., & Schreider, S. (2015). Changes in the water quality characteristics during a macroalgal bloom in a coastal lagoon. Ocean & Coastal Management, 118(SI), 32–36.
Osuna-Flores, I., & Riva, M. C. (2002). Organochlorine pesticide residue concentrations in shrimps, sediments, and surface water from Bay of Ohuira, Topolobampo, Sinaloa, Mexico. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 68(4), 532–539.
Piñón-Gimate, A., Soto-Jiménez, M. F., Ochoa-Izaguirre, M. J., García-Pagés, E., & Páez-Osuna, F. (2009). Macroalgae blooms and d15N in subtropical coastal lagoons from the Southeastern Gulf of California: discrimination among agricultural, shrimp farm and sewage effluents. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(8), 1144–1151.
Ranalli, A. J., & Macalady, D. L. (2010). The importance of the riparian zone and in-stream processes in nitrate attenuation in undisturbed and agricultural watersheds—a review of the scientific literature. Journal of Hydrology, 389(3–4), 406–415.
SANCO 2009. Method validation and quality control procedures for pesticide residues analysis. Brussels: European Commission, DG-SANCO.
SIAP, & SAGARPA (2015). Anuario Estadistico de la Producción Agricola. http://www.siap.gob.mx/cierre-de-la-produccion-agricola-por-estado/. Accessed January 2016.
Vàrgas-Gonzàlez, H. H., Mèndez-Rodrìguez, L. C., Garcìa-Hernàndez, J., Mendoza-Salgado, R. A., Zenteno-Savın, T., & Arreola-Lizàrraga, J. A. (2016). Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in populations of the clam Chione californiensis in coastal lagoons of the Gulf of California. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 51(7), 435–445.
Vittozzi, L., Fabrizi, L., Di Consiglio, E., & Testai, E. (2001). Mechanism aspects of organophosphorothionate toxicity in fish and humans. Enviornmental International, 26(3), 125–129.
WHO (2009). The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard and guidelines to classification. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press.
Yard, E. E., Murphy, M. W., Schneeberger, C., Narayanan, J., Hoo, E., Freiman, A., et al. (2014). Microbial and chemical contamination during and after flooding in the Ohio River-Kentucky, 2011. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, 49(11), 1236–1243.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Greenpeace Mexico for their support with the land samples and the National Network on Algal Blooms from CICESE with the sea samples. We also thank Jessica Zamora for the map design and M. Hernánez Quiroz for his logistic support throughout the study. We thank Ann Grant for the English editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arellano-Aguilar, O., Betancourt-Lozano, M., Aguilar-Zárate, G. et al. Agrochemical loading in drains and rivers and its connection with pollution in coastal lagoons of the Mexican Pacific. Environ Monit Assess 189, 270 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5981-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5981-8