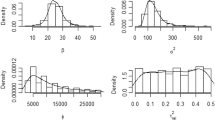
Abstract
Groundwater nitrate contamination from agriculture is of paramount environmental interest. A continuous consumption of polluted water as drinking water or for culinary purposes is by no means a minor hazard for people’s health that must be studied. This research presents a new methodology for the spatial analysis of health risk rate from intake of nitrate-polluted groundwater. The method is illustrated through its application to a water quality sampling campaign performed in the south of Spain in 2003. The probability risk model used by the US Environmental Protection Agency has been applied, considering a residential intake framework and three representative population age groups (10, 40 and 65 years).The method was based upon coupling Monte Carlo simulations and geostatistics, which allowed mapping of the health risk coefficient (RC). The maps obtained were interpreted in the framework of water resources management and user’s health protection (municipalities). The results showed waterborne health risk caused by nitrate-polluted water is moderately low for the region. The observed risk was larger for the elderly and children, although no significant differences were found among the three age groups (RC average values of 95th percentile for age of 0.37, 0.33 and 0.37, respectively). Significant risk values of RC > 1 were obtained for 10 % of the surface in the NW site of the study area, where the municipalities with the highest contamination thresholds are located (agricultural activity). Nitrate concentration and intake rate stood out as the main explanatory variables of the RC.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
91/676/EC. (1991). Directive 91/676/EC: Council directive of 12 December 1991 concerning the protection of waters against pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources. Official Journal of the European Communities, L375, 1–13.
2000/60/EC. (2000). Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23.10.2000: A framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Communities, L327, 0001–0073.
Ako, A. A., Shimada, J., Hosono, T., Ichiyanagi, K., Nkeng, G. E., Fantong, W. Y., et al. (2011). Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking, domestic, and agricultural uses in the Banana Plain (Mbanga, Njombe, Penja) of the Cameroon Volcanic Line. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(6), 559–575.
Al Kuisi, M., Al-Qinna, M., Margane, A., & Aljazzar, T. (2009). Spatial assessment of salinity and nitrate pollution in Amman Zarqa Basin: A case study. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59(1), 117–129.
Antunes, I. M. H. R., & Albuquerque, M. T. D. (2013). Using indicator kriging for the evaluation of arsenic potential contamination in an abandoned mining area (Portugal). Science of the Total Environment, 442, 545–552.
Aquilina, L., Vergnaud-Ayraud, V., Labasque, T., Bour, O., Molénat, J., Ruiz, L., et al. (2012). Nitrate dynamics in agricultural catchments deduced from groundwater dating and long-term nitrate monitoring in surface- and groundwaters. Science of the Total Environment, 435–436, 167–178.
Barnes, D. G., Dourson, M., Dourson, M., Preuss, P., Barnes, D. G., Bellin, J., et al. (1988). Reference dose (RfD): Description and use in health risk assessments. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 8(4), 471–486.
Benes, V., Pekny, V., Skorepa, J., & Vrba, J. (1989). Impact of diffuse nitrate pollution sources on groundwater quality: Some examples from Czechoslovakia. Environmental Health Perspectives, 83, 5–24.
Castillo, A. (2005). El acuífero de la Vega de Granada: Ayer y hoy (1966–2004). In J. A. Lopez-Geta, A. Pulido Bosch, & J. C. Baquero Ubeda (Eds.), Agua, Minería y Medio Ambiente. Libro Homenaje al Profesor Rafael Fernández Rubio. Madrid: IGME.
Castillo, A., Sánchez-Díaz, L., Chica-Olmo, M., & Luque-Espinar, J. A. (2004). Distribución espacial de nitratos en el acuífero de la Vega de Granada: análisis de las situaciones en 1983 y 2003. Geogaceta, 36, 111–114.
Chica-Olmo, M., Luque-Espinar, J. A., Rodriguez-Galiano, V., Pardo-Igúzquiza, E., & Chica-Rivas, L. (2014). Categorical Indicator Kriging for assessing the risk of groundwater nitrate pollution: The case of Vega de Granada aquifer (SE Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 470–471, 229–239.
Chilès, J. P., & Delfiner, P. (1999). Geostatistics: Modeling spatial uncertainty. New York: Wiley.
De Roos, A. J., Ward, M. H., Lynch, C. F., & Cantor, K. P. (2003). Nitrate in public water supplies and the risk of colon and rectum cancers. Epidemiology, 14(6), 640–649.
Decisioneering. (2007). Crystal ball (7.1st ed.). CO, USA: Denver.
Deutsch, C. V., & Journel, A. G. (1998). GSLIB: geostatistical software library and user’s guide. New York: Oxford University Press.
Downs, T. J., Cifuentes-Garcia, E., & Suffet, I. M. (1999). Risk screening for exposure to groundwater pollution in a wastewater irrigation district of the Mexico City region. Environmental Health Perspectives, 107(7), 553–561.
Enwright, N., & Hudak, P. F. (2009). Spatial distribution of nitrate and related factors in the high plains aquifer, Texas. Environmental Geology, 58(7), 1541–1548.
Fewtrell, L. (2004). Drinking-water nitrate, methemoglobinemia, and global burden of disease: A discussion. Environmental Health Perspectives, 112(14), 1371–1374.
Fryer, M., Collins, C. D., Ferrier, H., Colvile, R. N., & Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J. (2006). Human exposure modelling for chemical risk assessment: A review of current approaches and research and policy implications. Environmental Science and Policy, 9(3), 261–274.
Garcia-Soldado, M. J. (2008). Metodología basada en SIG para el desarrollo de un Sistema Soporte de Decisión en la gestión de la calidad de los recursos hídricos subterráneos de la Vega de Granada. Granada: University of Granada.
Hinsby, K., Condesso de Melo, M. T., & Dahl, M. (2008). European case studies supporting the derivation of natural background levels and groundwater threshold values for the protection of dependent ecosystems and human health. Science of the Total Environment, 401(1–3), 1–20.
Hosono, T., Tokunaga, T., Kagabu, M., Nakata, H., Orishikida, T., Lin, I.-T., et al. (2013). The use of delta N-15 and delta O-18 tracers with an understanding of groundwater flow dynamics for evaluating the origins and attenuation mechanisms of nitrate pollution. Water Research, 47(8), 2661–2675.
IGME. (1972). Utilización de las aguas subterráneas para la mejora del regadío en la Vega de Granada. In A. Bouton (Ed.), Proyecto piloto de utilizacion de aguas subterraneas para el desarrollo agricola de la cuenca del Guadalquivir (p. 204). Madrid: FAO.
IGME (1990). Atlas Hidrogeológico de la Provincia de Granada: Instituto Tecnológico Geominero de España.
INE (2013). Spanish statistical office. http://www.ine.es. Accessed 14/08/2013 2013.
Journel, A. G. (1986). Geostatistics: Models and tools for the Earth sciences. Mathematical Geology, 18(1), 119–140.
Katz, B. G., Griffin, D. W., & Davis, J. H. (2009). Groundwater quality impacts from the land application of treated municipal wastewater in a large karstic spring basin: Chemical and microbiological indicators. Science of the Total Environment, 407(8), 2872–2886.
Knobeloch, L., Salna, B., Hogan, A., Postle, J., & Anderson, H. (2000). Blue babies and nitrate-contaminated well water. Environmental Health Perspectives, 108(7), 675–678.
Kohfahl, C., Sprenger, C., Herrera, J. B., Meyer, H., Chacon, F. F., & Pekdeger, A. (2008). Recharge sources and hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in semiarid and karstic environments: A field study in the Granada Basin (Southern Spain). Applied Geochemistry, 23(4), 846–862.
Li, P., Li, X., Meng, X., Li, M., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of northwest China. Exposure and Health, 1–19.
Li, P., Wu, J., Qian, H., Lyu, X., & Liu, H. (2014). Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: A case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(4), 693–712.
Liu, C. W., Lin, C. N., Jang, C. S., Ling, M. P., & Tsai, J. W. (2011). Assessing nitrate contamination and its potential health risk to Kinmen residents. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(5), 503–514.
Liu, C.-W., Wang, Y.-B., & Jang, C.-S. (2013). Probability-based nitrate contamination map of groundwater in Kinmen. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(12), 10147–10156.
Luque-Espinar, J. A., Chica-Olmo, M., Pardo-Igúzquiza, E., & García-Soldado, M. J. (2008). Influence of climatological cycles on hydraulic heads across a Spanish aquifer. Journal of Hydrology, 354(1–4), 33–52.
MAGRAMA (2012). Propuesta de Proyecto de Plan Hidrológico de la Demarcación Hidrográfica del Guadalquivir (p. 466).
Majumdar, D. (2003). The blue baby syndrome. Resonance, 8(10), 20–30.
Rodriguez-Fernandez, J., & Sanz de Galdeano, C. (2006). Late orogenic intramontane basin development: The Granada basin, Betics (southern Spain). Basin Research, 18(1), 85–102.
Rodriguez-Galiano, V., & Chica-Olmo, M. (2012). Land cover change analysis of a Mediterranean area in Spain using different sources of data: Multi-seasonal Landsat images, land Surface temperature, digital terrain models and texture. Applied Geography, 35, 208–218.
Rodriguez-Galiano, V., Mendes, M. P., Garcia-Soldado, M. J., Chica-Olmo, M., & Ribeiro, L. (2014). Predictive modeling of groundwater nitrate pollution using random forest and multisource variables related to intrinsic and specific vulnerability: A case study in an agricultural setting (Southern Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 476, 189–206.
USEPA (1989). Risk assessment guidance for superfund. Volume 1: Human health evaluation manual. Washington, USA: Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA (1992). Guidelines for exposure assessment. (Vol. Fed. Reg. 57:22888-22938). Washington, USA: Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA. (2011). Exposure factors handbook. Washington, USA: Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA (2015). IRIS Integrated risk information system database. http://www.epa.gov/iris.
Wakida, F. T., & Lerner, D. N. (2005). Non-agricultural sources of groundwater nitrate: A review and case study. Water Research, 39(1), 3–16.
Ward, M. H., Kilfoy, B. A., Weyer, P. J., Anderson, K. E., Folsom, A. R., & Cerhan, J. R. (2010). Nitrate intake and the risk of thyroid cancer and thyroid disease. Epidemiology, 21(3), 389–395.
Wu, J., & Sun, Z. (2015). Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Exposure and Health, 1–19.
Yang, C. Y., Cheng, M. F., Tsai, S. S., & Hsieh, Y. L. (1998). Calcium, magnesium, and nitrate in drinking water and gastric cancer mortality. Japanese Journal of Cancer Research, 89(2), 124–130.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support given by the Spanish MINECO (project BIA2013-43462-P) and Junta de Andalucía (Group RNM122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chica-Olmo, M., Peluso, F., Luque-Espinar, J.A. et al. A methodology for assessing public health risk associated with groundwater nitrate contamination: a case study in an agricultural setting (southern Spain). Environ Geochem Health 39, 1117–1132 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9880-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9880-7