Abstract
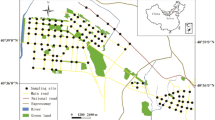
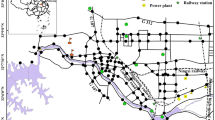
Due to rapid urbanization and the scarcity of land, most of the urban parks and squares in cities are built close to major roads or industrial areas, where they are subject to many potential pollution sources, including vehicle exhaust and industrial emissions. The aims of this study were to determine the concentrations of selected metals (Pb, Cr, Cu, Ni, Zn, and Cd) in road dusts collected in urban parks and squares in Changchun, China, on June 1, 2013 (International Children’s Day) and to estimate the pollution sources. The mean Pb, Cr, Cu, Ni, Zn, and Cd contents (70.89, 60.30, 43.56, 23.16, 170.80, and 0.3111 mg kg−1 dry weight, respectively) in urban dusts were higher than their corresponding natural background values, particularly Pb, Cu, Zn, and Cd, which had about 2.5, 1.4, 1.9, and 2.6-fold higher levels, respectively. The results of principal component analysis indicated that Cr and Ni concentrations were mainly of natural origin, while Pb, Cu and Zn were derived from anthropogenic activities, and Cd tended to be from both sources. The geoaccumulation index (I geo) of these metals in the urban dusts under study indicates that they are uncontaminated with Cr and Ni; uncontaminated to moderately contaminated with Cu and Zn; and moderately contaminated with Pb and Cd. In addition, five particle sizes were analyzed separately for heavy metal concentrations. In all studied areas, there are large differences in the metal-loading percentage of different particle-size fractions among the samples, and the particles in 250–2,000-μm fraction are dominant in the total metal loading.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams, P. W. (2002). Soils: Their implications to human health. The Science of the Total Environment, 291, 1–32.
Adachi, K., & Tainosho, Y. (2004). Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environment International, 30(8), 1009–1017. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.04.004.
Adgate, J. L., Willis, R. D., Buckley, T. J., Chow, J. C., Watson, J. G., Rhoads, G. G., et al. (1998). Chemical mass balance source apportionment of lead in house dust. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(1), 108–114. doi:10.1021/es970052x.
Ahmed, F., Bibi, M. H., & Ishiga, H. (2007). Environmental assessment of Dhaka City (Bangladesh) based on trace metal contents in road dusts. Environmental Geology, 51(6), 975–985. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0367-1.
Ahmed, F., & Ishiga, H. (2006). Trace metal concentrations in street dusts of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Atmospheric Environment, 40(21), 3835–3844. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.03.004.
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2007). Determination of metal accumulation in deposited street dusts in Amman, Jordan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29(1), 1–10. doi:10.1007/s10653-006-9067-8.
Al-Shayeb, S. M., & Seaward, M. R. D. (2001). Heavy metal content of roadside soils along ring road in Riyadh (Saudi Arabia). Asian Journal of Chemistry, 13(2), 407–423.
Amato, F., Pandolfi, M., Viana, M., Querol, X., Alastuey, A., & Moreno, T. (2009). Spatial and chemical patterns of PM10 in road dust deposited in urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 43(9), 1650–1659. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.12.009.
Artaxo, P., Oyola, P., & Martinez, R. (1999). Aerosol composition and source apportionment in Santiago de Chile. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B-Beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms, 150(1–4), 409–416. doi:10.1016/s0168-583x(98)01078-7.
Banerjee, A. D. K. (2003). Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environmental Pollution, 123(1), 95–105. doi:10.1016/s0269-7491(02)00337-8.
Barlow, P. L. (1999). The lead ban, lead replacement petrol, and the potential for engine damage. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 46(6), 439–449. doi:10.1108/00035599910299405.
Bosco, M. L., Varrica, D., & Dongarra, G. (2005). Case study: inorganic pollutants associated with particulate matter from an area near a petrochemical plant. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t]. Environmental Research, 99(1), 18–30. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2004.09.011.
Charlesworth, S., Everett, M., McCarthy, R., Ordonez, A., & de Miguel, E. (2003). A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environment International, 29(5), 563–573. doi:10.1016/s0160-4120(03)00015-1.
Chen, T. B., Wong, J. W. C., Zhou, H. Y., & Wong, M. H. (1997). Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong. Environmental Pollution, 96(1), 61–68. doi:10.1016/s0269-7491(97)00003-1.
Chen, X., Xia, X. H., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, P. (2010). Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181(1–3), 640–646. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.060.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Lei, M., Huang, Z. C., Wu, H. T., Chen, H., et al. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 60(4), 542–551. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.072.
Dach, J., & Starmans, D. (2005). Heavy metals balance in Polish and Dutch agronomy: Actual state and previsions for the future. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 107(4), 309–316. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2005.02.017.
Du, Y., Gao, B., Zhou, H., Ju, X., Hao, H., & Yin, S. (2013). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dusts in urban parks of Beijing, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 18, 299–309. doi:10.1016/j.proenv.2013.04.039.
Duong, T. T. T., & Lee, B.-K. (2009). Partitioning and mobility behavior of metals in road dusts from national-scale industrial areas in Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 3502–3509. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.04.036.
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Li, X. D., & Wong, S. C. (2004). Lead contamination and isotope signatures in the urban environment of Hong Kong. Environment International, 30(2), 209–217. doi:10.1016/s0160-4120(03)00175-2.
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Wong, C. S. C., Aydin, A., Song, Z., You, M., & Li, X. D. (2006). Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the urban environment of Guangzhou, SE China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28(4), 375–391. doi:10.1007/s10653-005-9036-7.
EPA (2011). Exposure factors handbook, 2011 edition (final). Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: EPA/600/R-09/052F.
EPAC (1997a). Soil quality, determination of copper, zinc—flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry (GB/T 17138-1997). <http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/trhj/trjcgfffbz/199805/t19980501_82031.htm>.
EPAC (1997b). Soil quality, determination of lead, cadmium—graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry (GB/T 17141-1997). http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/trhj/trjcgfffbz/199805/t19980501_82029.htm.
Ferreira-Baptista, L., & De Miguel, E. (2005). Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 39(25), 4501–4512. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.026.
Folk, R. L. (1974). Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Austin, TX: Hemphill.
Goyer, R. A. (1997). Toxic and essential metal interactions. Annual Review of Nutrition, 17(1), 37–50.
Gray, C., McLaren, R., & Roberts, A. (2003). Atmospheric accessions of heavy metals to some New Zealand pastoral soils. The Science of the Total Environment, 305(1–3), 105–115. doi:10.1016/s0048-9697(02)00404-7.
Guo, P. (2005). Study on heavy metal contamination mechanism and countermeasure in urban soil of Changchun. Jilin University, Changchun. (In Chinese).
Han, Y. M., Cao, J. J., Posmentier, E. S., Fung, K., Tian, H., & An, Z. S. (2008). Particulate-associated potentially harmful elements in urban road dusts in Xi’an, China. Applied Geochemistry, 23(4), 835–845. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.09.008.
Han, Y. M., Du, P. X., Cao, J. J., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355(1–3), 176–186. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.02.026.
Hunt, A., Johnson, D. L., & Griffith, D. A. (2006). Mass transfer of soil indoors by track-in on footwear. Science of the Total Environment, 370(2–3), 360–371. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.07.013.
Johansson, L., & Westerlund, L. (2001). Energy savings in indoor swimming-pools: Comparison between different heat-recovery systems. Applied Energy, 70(4), 281–303. doi:10.1016/s0306-2619(01)00043-5.
Laidlaw, M. A. S., & Filippelli, G. M. (2008). Resuspension of urban soils as a persistent source of lead poisoning in children: A review and new directions. Applied Geochemistry, 23(8), 2021–2039. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.05.009.
Li, X. D., Poon, C. S., & Liu, P. S. (2001). Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Applied Geochemistry, 16(11–12), 1361–1368. doi:10.1016/s0883-2927(01)00045-2.
Lu, X. W., Wang, L. J., Lei, K., Huang, J., & Zhai, Y. X. (2009). Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 1058–1062. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.052.
Lu, X. W., Wang, L. J., Li, L. Y., Lei, K., Huang, L., & Kang, D. (2010). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173(1–3), 744–749. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.001.
Mang, T., & Dresel, W. (2007). Lubricants and lubrication (2nd ed.). Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH.
Martin, A. C., Rivero, V. C., & Marin, M. T. L. (1998). Contamination by heavy metals in soils in the neighbourhood of a scrapyard of discarded vehicles. Science of the Total Environment, 212(2–3), 145–152.
Meng, X. X., & Li, S. Z. (1995). Study on background value of soil environment of the Jilin Province. Beijing: Science.
Mico, C., Recatala, L., Peris, A., & Sanchez, J. (2006). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65(5), 863–872. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.016.
Miguel, E. D., Llamas, J. F., Chacon, E., Berg, T., Larssen, S., Royset, O., et al. (1997). Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: Unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmospheric Environment, 31(17), 2733–2740.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geochemical Journal, 2, 108–118.
Ndiokwere, C. L. (1984). A study of heavy-metal pollution from motor-vehicle emissions and its effect on roadside soil, vegetation and crops in Nigeria. Environmental Pollution Series B-Chemical and Physical, 7(1), 35–42. doi:10.1016/0143-148x(84)90035-1.
Papanikolaou, N. C., Hatzidaki, E. G., Belivanis, S., Tzanakakis, G. N., & Tsatsakis, A. M. (2005). Lead toxicity update. A brief review. Medical science monitor, 11(10), RA329.
Ritter, C. J., & Rinefierd, S. M. (1983). Natural background and pollution levels of some heavy-metals in soils from the area of Dayton, Ohio. Environmental Geology, 5(2), 73–78.
Schwar, M. J. R., Moorcroft, J. S., Laxen, D. P. H., Thompson, M., & Armorgie, C. (1988). Baseline metal-in-dust concentrations in greater London. Science of the Total Environment, 68, 25–43. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(88)90359-2.
Sezgin, N., Ozcan, H. K., Demir, G., Nemlioglu, S., & Bayat, C. (2004). Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environment International, 29(7), 979–985. doi:10.1016/s0160-4120(03)00075-8.
Shi, X. M., Chen, L. X., & Wang, J. H. (2013). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal pollution in street dusts of Xianyang city, NW China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69(6), 1973–1979. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2032-1.
Shi, G. T., Chen, Z. L., Xu, S. Y., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Bi, C. J., et al. (2008). Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environmental Pollution, 156(2), 251–260. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.02.027.
Siciliano, S. D., James, K., Zhang, G. Y., Schafer, A. N., & Peak, J. D. (2009). Adhesion and enrichment of metals on human hands from contaminated soil at an arctic urban Brownfield. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(16), 6385–6390. doi:10.1021/es901090w.
Smolders, E., & Degryse, F. (2002). Fate and effect of zinc from tire debris in soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(17), 3706–3710. doi:10.1021/es025567p.
Soto-Jimenez, M. F., & Flegal, A. R. (2011). Childhood lead poisoning from the smelter in Torreon, Mexico. Environmental Research, 111(4), 590–596. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2011.01.020.
Stone, M., & Marsalek, J. (1996). Trace metal composition and speciation in street sediment: Sault Ste Marie, Canada. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 87(1–4), 149–169. doi:10.1007/bf00696834.
Sutherland, R. A. (2003). Lead in grain size fractions of road-deposited sediment. Environmental Pollution, 121(2), 229–237. doi:10.1016/s0269-7491(02)00219-1.
Sutherland, R. A., & Tolosa, C. A. (2000). Multi-element analysis of road-deposited sediment in an urban drainage basin, Honolulu, Hawaii. Environmental Pollution, 110(3), 483–495. doi:10.1016/s0269-7491(99)00311-5.
Weckwerth, G. (2001). Verification of traffic emitted aerosol components in the ambient air of Cologne (Germany). Atmospheric Environment, 35(32), 5525–5536. doi:10.1016/s1352-2310(01)00234-5.
Wei, B. G., Jiang, F. Q., Li, X. M., & Mu, S. Y. (2009). Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban road dusts from Urumqi, NW China. Microchemical Journal, 93(2), 147–152. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2009.06.001.
Yamamoto, N., Takahashi, Y., Yoshinaga, J., Tanaka, A., & Shibata, Y. (2006). Size distributions of soil particles adhered to children’s hands. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 51(2), 157–163. doi:10.1007/s00244-005-7012-y.
Yang, Z. P., Lu, W. X., Long, Y. Q., Bao, X. H., & Yang, Q. C. (2011a). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 108(1), 27–38. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.09.006.
Yang, T., Zeng, Q. L., Liu, Z. F., & Liu, Q. S. (2011b). Magnetic properties of the road dusts from two parks in Wuhan city, China: Implications for mapping urban environment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 177(1–4), 637–648. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1662-6.
Zhang, M. K., & Wang, H. (2009). Concentrations and chemical forms of potentially toxic metals in road-deposited sediments from different zones of Hangzhou, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 21(5), 625–631. doi:10.1016/s1001-0742(08)62317-7.
Zheng, N., Liu, J. H., Wang, Q. C., & Liang, Z. Z. (2010). Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, northeast of China. Science of the Total Environment, 408(4), 726–733. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.075.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the Knowledge Innovative Program of The Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-YW-N-077), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41071056), and Strategic Priority Research Program of Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiang, L., Yang, W., Jingshuang, L. et al. Grain-size distribution and heavy metal contamination of road dusts in urban parks and squares in Changchun, China. Environ Geochem Health 37, 71–82 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9631-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9631-6