Abstract
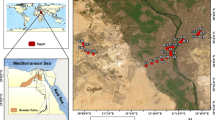
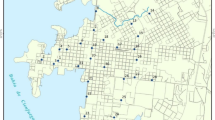
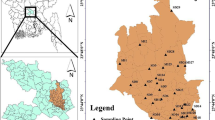
Geochemical analysis of street dusts was conducted to evaluate the environment of Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Dust samples were collected from different areas (industrial, commercial, and residential) of Dhaka City, and their major, trace and rare earth elements (REE) were determined. Samples from the commercial area had Pb concentrations double those of the industrial and residential areas. Contents of Zn, Cu, Ni, and Cr in the industrial areas were greater than those in the commercial and residential areas. The REE patterns of all dusts in Dhaka are similar and are comparable to the average upper continental crust. The condition of the Dhaka environment was compared to that in Japan and other baseline sediments using Zn–Fe2O3 and Pb–Fe2O3 diagrams. Zn–Fe2O3 trends for the dusts show steep inclination compared to the baseline sediment and the Japanese urban sediment trends. Dhaka lake data show enrichment of Zn over the dusts, suggestive of Zn pollution from poorly controlled industrial sources. In contrast, on the Pb–Fe2O3 diagram, Dhaka dusts have greater Pb contents than lake sediments, probably due to the higher traffic density in the commercial area compared to the residential area including the area around the lake. The results suggest that higher levels of Pb and Zn in street dusts in Dhaka can most likely be attributed to the anthropogenic sources like vehicle emissions to the atmosphere and a rapid development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham J (1998) Spatial distribution of major and trace elements in shallow reservoir sediments: an example from Lake Waco, Texas. Environ Geol 36(3–4):349–363
Adriano DC (2001) Trace elements in terrestrial environments: biogeochemistry, bioavailability, and risks of metals, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 867
Ahmed F, Bibi MH, Sattar MA, Rahman MM, Ishiga H (2002) Trace metal contamination in agricultural land of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Environ Sci 8:154–159
Ahmed F, Bibi MH, Monsur MH, Ishiga H (2005) Present environment and historic changes from the record of lake sediments, Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Environ Geol 48(1):25–36
Ali MM, Ishiga H, Wakatsuki T (2003) Distribution and changes in heavy metal contents of paddy soils in different physiographic units of Bangladesh. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 49(4):527–538
Banerjee ADK (2003) Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environ Pollut 123:95–105
Bibi MH, Ahmed F, Ishiga H (2006) Distribution of arsenic and other trace elements in the Holocene sediments of the Meghna River Delta, Bangladesh. Environ Geol (in press)
BRTA (Bangladesh Road Transport Authority) (2002) Air pollution in Bangladesh. BRTA associated with Greater Dhaka Metropolitan Area Integrated Transport Study. Working paper no. 23
Chandrajith RLR, Okumura M, Hashitani H (1995) Human influence on the Hg pollution in Lake Jinzai, Japan. Appl Geochem 10:229–235
Chen TB, Wong JWC, Zhou HY, Wong MH (1997) Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong. Environ Pollut 96(1):61–68
Chowdhury QI, Rahman G, Majumder MK, Rana B (2000) Smoke and haze in Dhaka’s concrete jungle. Air pollution in Asian cities. Forum of Environmental Journalists of Bangladesh (FEJB), Dhaka, pp 1–14
Condie KC (1993) Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust: contrasting results from surface samples and shales. Chem Geol 104:1–37
De Miguel E, Llamas JF, Chacón E, Berg T, Larssen S, Røyset O, Vadset M (1997) Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmos Environ 31(17):2733–2740
Dolgopolova A, Weiss DJ, Seltmann R, Dulski P (2006) Dust dispersal and Pb enrichment at the rare-metal Orlovka-Spokoinoe mining and ore processing site: Insights from REE patterns and elemental ratios. J Hazard Mater 132:90–97
Domingo LE, Kyuma K (1983) Trace elements in tropical Asian paddy soils. I. Total trace element status. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 29(4):439–452
Fabis W (1987) Schadstoftbelastung von Böden-Auswirkurgen auf Böden-und wasserqalitat Allg Farstzeitsehr. BLV Verlaggesellshaft, Munich, pp 128–131
Fakayode SO, Olu-Owolabi BI (2003) Heavy metal contamination of roadside topsoil in Osogbo, Nigeria: its relationship to traffic density and proximity to highways. Environ Geol 44:150–157
Gao S, Wedepohl KH (1995) The negative Eu anomaly in Archean sedimentary rocks: implications for decomposition, age and importance of their granitic sources. Earth Planet Sci Lett 133:81–94
Hossen M (2002) Air pollution. Bangladesh environment facing the 21st century, 2nd edn. Society for Environment and Human Development (SEHD), Dhaka, pp 207–216
ICT (International Consultants, Technocrats Pvt. Ltd., India) (2001) Urban transport and environment improvement study. ICT associated with Balloffet-Entranco, USA and others. Final Report, ADB TA 3297-Ban
Imperato M, Adamo P, Naimo D, Arienzo M, Stanzione D, Violante P (2003) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ Pollut 124:247–256
Ishiga H, Dozen K, Ahmed F, Bibi MH, Kaita M (2003) Evaluation of sedimentary environment using a Zn–Fe2O3 diagram. Geosci Rep Shimane Univ Japan 22:15–20
Jahn B-M, Gallet S, Han J (2001) Geochemistry of the Xining, Xifeng and Jixian sections, Loess Plateau of China: eolian dust provenance and paleosol evolution during the last 140 ka. Chem Geol 178:71–94
Karim MM, Islam M, Hoque MS (2000) Current status, comprehensive management tool, and state-of-art solution for air quality in Bangladesh. Bangladesh environment 2000 (an outcome of ICBEN-2000). Bangladesh Poribesh Andolon (BAPA), Dhaka, pp 1–28
Khuda ZRMM (2001) Environmental degradation, challenges of the 21st century. Environmental Survey and Research Unit, Dhaka, pp 247
Li X, Chi-sun P, Liu PS (2001) Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Appl Geochem 16:1361–1368
Li X, Siu-lan L, Sze-chung W, Shi W, Thornton I (2004) The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environ Pollut 129:113–124
McLennan SM, Taylor SR, McCulloch MT, Maynard JB (1990) Geochemical and Zd-Sr isotopic composition of deep-sea turbidites: crustal evolution and plate tectonic associations. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 54:2015–2050
McLennan SM, Hemming S, McDaniel DK, Hanson GN (1993) Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance and tectonics. Geol Soc Am Spec Paper 284:21–40
Mondol MN, Bhuyian MAR, Noor S, Chamon AS, Rahman M, Faiz SMA (2002) Growth, yield and mineral nutrition of rice, wheat and lettuce grown on heavy metal polluted soil. Bangladesh J Environ Sci 8:60–64
Musashino M (1990) The Panthalassa- a cerium-rich Atlantic-type ocean: sedimentary environments of the Tamba Group, Southwest Japan. Tectonophysics 181:165–177
Ogasawara M (1987) Trace element analysis of rock samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, using Rh anode tube. Bull Geol Surv Japan 38(2):57–68
Plank T, Langmuir CH (1998) The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chem Geol 145:325–394
Potts PJ, Tindle AG, Webb PC (1992) Geochemical reference material compositions. Whittles, Caithness, pp 313
Preda M, Cox ME (2002) Trace metal occurrence and distribution in sediments and mangroves, Pumicestone region, southeast Queensland, Australia. Environ Int 28:433–449
Rahman G, Majumder MK, Rana B (1999) State of air pollution in Bangladesh. Bangladesh state of environment report 1999. Forum of Environmental Journalists of Bangladesh (FEJB), Dhaka, pp 71–84
Roser BP (2000) Whole-rock geochemical studies of clastic sedimentary suites. Mem Geol Soc Jpn 57:73–89
Sezgin N, Ozcan HK, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2003) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ Int 29:979–985
Singh M, Sharma M, Tobschall HJ (2005) Weathering of the Ganga alluvial plain, northern India: implications from fluvial geochemistry of the Gomati River. Appl Geochem 20:1–21
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 312
Wang WH, Wong MH, Leharne S, Fisher B (1998) Fractionation and biotoxicity of heavy metals in urban dusts collected from Hong Kong and London. Environ Geoch Health 20:185–198
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Yoshihiro Sawada of Shimane University, Japan for access to the XRF facilities, to Manabu Kaita of Shimane University for the REE analysis, and to Md. Mostafizur Rahman of Rajshahi University, Bangladesh for his cooperation in sampling. Part of the investigation was carried out under the Visiting Researchers Program of the Research Reactor Institute, Kyoto University, Japan. We thank the Dhaka City Corporation Authority for the valuable support in sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, F., Bibi, M.H. & Ishiga, H. Environmental assessment of Dhaka City (Bangladesh) based on trace metal contents in road dusts. Environ Geol 51, 975–985 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0367-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0367-1