Abstract
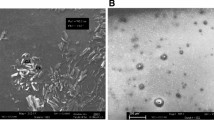
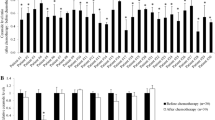
Acid ceramidases are enzymes with a vital role in metabolizing ceramide to sphingosine-1-phosphate that is an antiproliferative metabolite in the ceramide pathway. Inhibition of exogenous ceramides with ceramidase inhibitors lead to augmented ceramide levels in cells and in turn lead to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Our study aimed at targeting ceramide metabolic pathway to induce apoptosis in human breast cancer cell line (MCF7) and we examined the antiproliferative and apoptotic activities of ceranib-2, an inhibitor of human ceramidase, on this cell line as well ultrastructural and mophological changes. Methods used for our examinations in this study were the colorimetric MTT assay, Annexin V/Propidium iodide and JC-1 staining, transmission electron microscopy and confocal microscopy. Ceranib-2 effectively inhibited the viability of MCF7 cells in 24 h in a dose dependent manner leading to apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway by reducing the potential of mitochondrial membrane. Additionally, significant changes on cell morphology and ultrastructure were observed on MCF7 cells exposed to ceranib-2 indicating apoptotic cell death. Collectively, our data demonstrate that ceranib-2 exerts a great potential to be an antineoplastic compound and that the mechanism of its action rely on its apoptosis inducing ability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akalin Ciftci G, Iscan A, Kutlu M (2015) Escin reduces cell proliferation and induces apoptosis on glioma and lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cytotechnology. doi:10.1007/s10616-015-9877-6
Bansode RR, Ahmedna M, Svoboda KR, Losso JN (2011) Coupling in vitro and in vivo paradigm reveals a dose dependent inhibition of angiogenesis followed by initiation of autophagy by C6-ceramide. Int J Biol Sci 7:629–644
Beckham TH, Lu P, Cheng JC, Zhao D, Turner LS, Zhang X, Hoffman S, Armeson KE, Liu A, Marrison T, Hannun YA, Liu X (2012) Acid ceramidase-mediated production of sphingosine-1 phosphate promotes prostate cancer invasion through upregulation of cathepsin B. Int J Cancer 131:2034–2043
Beckham TH, Cheng JC, Lu P, Marrison ST, Norris JS, Liu X (2013) Acid ceramidase promotes nuclear export of PTEN through sphingosine 1-phosphate mediated Akt signaling. PlosOne 8:765–793
Bhabak KP, Kleuser B, Huwiler A, Arenz C (2013) Effective inhibition of acid and neutral ceramidases by novel B-13 and LCL-464 analogues. Bioorg Med Chem 21:874–882
Bold RJ, Termuhlen PM, McConkey DJ (1997) Apoptosis cancer and cancer therapy. Surg Oncol 6:133–142
Brizuela L, Martin C, Jeannot P, Ader I, Gstalder C, Andrieu G, Bocquet M, Laffosse JM, Gomez-Brouchet A, Malavaud B, Sabbadini RA, Cuvillier O (2014) Osteoblast-derived sphingosine 1-phosphate to induce proliferation and confer resistance to therapeutics to bone metastasis-derived prostate cancer cells. Mol Oncol 8:1181–1195
Cai Z, Bettaieb A, Mahdani NE, Legres LG, Stancou R, Masliah J, Chouaib S (1997) Alteration of the sphingomyelin/ceramide pathway is associated with the resistance of human breast carcinoma MCF7 cells to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 272:6918–6926
Draper JM, Xia Z, Smith RA, Zhung Y, Wang W, Smith CD (2011) Discovery and evaluation of inhibitors of human ceramidase. Mol Cancer Ther 10:2052–2261
Eranshaw WC (1995) Nuclear changes in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:337–343
Fox TE, Finnegan CM, Blumenthal R, Kester M (2006) The clinical potential of sphingolipid based therapeutics. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1017–1023
Futerman AH, Hannun YA (2004) The complex life of simple sphingolipids. EMBO Rep 5:777–782
Garcia-Ruiz C, Colell A, Mari M, Morales A, Fernandez-Checa JC (1997) Direct effect of ceramide on the mitochondrial electron transport chain leads to generation of reactive oxygen species. Role of mitochondrial glutathione. J Biol Chem 272:11369–11377
Ghafourifar P, Klein SD, Schucht O, Schenk U, Pruschy M, Rocha S, Richter C (1999) Mitochondrial nitric-oxide synthase stimulation causes cytochrome c release from isolated mitochondria. Evidence for intramitochondrial peroxynitrite formation. J Biol Chem 274:6080–6084
Kabadere S, Kuş G, Uyar R, Oztopcu-Vatan P (2014) Licofelone abolishes survival of carcinogenic fibroblasts by inducing apoptosis. Drug Chem Toxicol 37:1–7
Kamesaki H (1998) Mechanisms involved in chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and their implications in cancer chemotherapy. Int J Hematol 68:29–43
Kolesnick R (2002) The therapeutic potential of modulating the ceramide/sphingomyelin pathway. J Clin Invest 110:3–8
Kus G, Oztopcu-Vatan P, Uyar R, Kabadere S (2013) Cytotoxic and apoptotic functions of licofelone on rat glioma cells. Acta Biol Hungarica 64:438–452
Kus G, Kabadere S, Uyar R, Kutlu HM (2015) Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by the novel ceramidase inhibitor ceranib-2. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 51:1056–1063. doi:10.1007/s11626-015-9932-9
Liu T, Hannafon B, Gill L, Kelly W, Benbrook D (2007a) Flex-Hets differentially induce apoptosis in cancer over normal cells by directly targeting mitochondria. Mol Cancer Ther 6:1814–1822
Liu X, Elojeimy S, Turner LS, Mahdy AEM, Zeidan YH, Bielawski J, Dong JY, El-Zawahry AM, Guo GW, Hannun YA, Holman DH, Rubinchik S, Szulc Z, Keane TE, Tavassoli M, Norris JS (2007b) Acid ceramidase inhibition: a novel target for cancer therapy. Front Biosci 13:2293–2298
Ogretmen B (2006) Minireview: sphingolipids in cancer: regulation of pathogenesis and therapy. FEBS Lett 580:5467–5476
Ogretmen B, Hannun YA (2004) Biologically active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 4:604–616
Radin NS (2003) Killing tumours by ceramide-induced apoptosis: a critique of available drugs. Biochem J 371:243–256
Reynolds CP, Maurer BJ, Kolesnik RN (2004) Ceramide synthesis and metabolism as a target for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 206:169–180
Rivzi F, Heimann T, Herrneiter A, O’brien WJ (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction links ceramide activated HRK expression and cell death. PlosOne 6:e18137
Sanger N, Ruckhäberle E, Györffy B, Engels K, Heinrich T, Fehm T, Graf A, Holtrich U, Becker S, Karn T (2015) Acid ceramidase is associated with an improved prognosis in both DCIS and invasive breast cancer. Mol Oncol 9:58–67
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Ahmedin J (2014) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29
Sleiman RH, Esmerian MO, Kobeissy H, Dbaibo G (2013) P53 and ceramide as collaborators in the stress response. Int J Mol Sci 14:4982–5012
Struckhoff AP, Bittman R, Burow ME, Clean S, Elliott S, Hammond T, Tang Y, Beckman BS (2004) Novel ceramide analogs as a potential chemotherapeutic agents in breast cancer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:523–531
Sun MG, Williams J, Munoz-Pinedo C, Perkins GA, Brown JM, Ellisman MH, Green DR, Frey TG (2007) Correlated three-dimensional light and electron microscopy reveals transformation of mitochondria during apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 9:1057–1065
Vejselova D, Kutlu HM, Kus G, Kabadere S, Uyar R (2014) Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of ceranib-2 offering potential for a new antineoplastic agent in the treatment of cancer cells. Turk J Biol 38:916–921
Vethakanraj HS, Babu TA, Sudarsanan GB, Duraisamy PK, Kumar SA (2015) Targeting ceramide metabolic pathway induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 464:833–839
von Haefen C, Wieder T, Gillissen B, Stärck L, Graupner V, Dörken B, Daniel PT (2002) Ceramide induces mitochondrial activation and apoptosis via a Bax-dependent pathway in human carcinoma cells. Oncogene 21:4009–4019
Yang HL, Chen CS, Chang WH, Lu FJ, Lai YC, Chan CC et al (2006) Growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in MCF7 breast cancer cells by Antrodia camphorata. Cancer Lett 231:215–227
Acknowledgments
We kindly thanks the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for the financial support that was provided for Djanan Vejselova and the Anadolu University Scientific Research Project Unit (Project No: 1505F234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors claim no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vejselova, D., Kutlu, H.M. & Kuş, G. Examining impacts of ceranib-2 on the proliferation, morphology and ultrastructure of human breast cancer cells. Cytotechnology 68, 2721–2728 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9997-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9997-7