Abstract
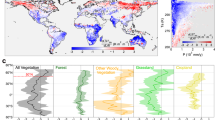
Geoengineering such as solar radiation management (SRM) can be an emergent option to avoid devastating climatic warming, but its ramifications are barely understood. The perturbation of the Earth’s energy balance, atmospheric dynamics, and hydrological cycling may exert unexpected influences on natural and human systems. In this study, I evaluate the impacts of SRM deployment on terrestrial ecosystem functions using a process-based ecosystem model (the Vegetation Integrative Simulator for Trace gases, VISIT) driven by the climate projections by multiple climate models. In the SRM-oriented climate projections, massive injection of sulphate aerosols into the stratosphere lead to increased scattering of solar radiation and delayed anthropogenic climate warming. The VISIT simulations show that canopy light absorption and gross primary production are enhanced in subtropics in spite of the slight decrease of total incident solar radiation. The retarded temperature rise during the deployment period leads to lower respiration, and consequently, an additional net terrestrial ecosystem carbon uptake by about 20%. After the SRM termination, however, along with the temperature rise, this carbon is released rapidly to the atmosphere. As a result of altered precipitation and radiation budget, simulated runoff discharge is suppressed mainly in the tropics. These SRM-induced influences on terrestrial ecosystems occurr heterogeneously over the land surface and differed among the ecosystem functions. These responses of terrestrial functions should be taken into account when discussing the costs and benefits of geoengineering.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applegate PJ, Keller K (2015) How effective is albedo modification (solar radiation management geoengineering) in preventing sea-level rise from Greenland Ice Sheet? Env Res Lett 10:084018. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/1010/1088/084018
Aquila V, Garfinkel CI, Newman PA, Oman LD, Waugh DW (2014) Modifications of the quasi-biennial oscillation by a geoengineering perturbation of the stratospheric aerosol layer. Geophys Res Lett 41:1738–1744. doi:10.1002/2013GL058818
Bahn O, Chesney M, Gheyssens J, Knutti R, Pana AC (2015) Is there room for geoengineering in the optimal climate policy mix? Env Sci Policy 48:67–76
Bala G, Duffy PB, Taylor KE (2008) Impact of geoengineering schemes on the global hydrological cycle. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 105:7664–7669
Barrett S, Lenton TM, Millner A, Tavoni A, Carpenter S, Anderies JM, Chapin FSI, Crépin A-S, Daily G, Ehrlich P, Folke C, Galaz V, Hughes T, Kautsky N, Lambin EF, Naylor R, Nyborg K, Polasky S, Scheffer M, Wilen J, Xepapadeas A, de Zeeuw A (2014) Climate engineering reconsidered. Nat Clim Change 4:527–529
Berdahl M, Robock A, Ji D, Moore JC, Jones A, Kravitz B, Watanabe S (2014) Arctic cryosphere response in the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project G3 and G4 scenarios. J Geophys Res 119:1308–1321
Caldeira K, Bala G, Cao L (2013) The science of geoengineering. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 41:231–256
Canadell JG, Le Quéré C, Raupach MR, Field CB, Buitenhuis ET, Ciais P, Conway TJ, Gillett NP, Marland G (2007) Contributions to accelerating atmospheric CO2 growth from economic activity, carbon intensity, and efficiency of natural sinks. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:18866–18870
Crutzen PJ (2006) Albedo enhancement by stratospheric sulfur injections: a contribution to resolve a policy dilemma? Clim Change 77:211–219
Curry CL, Sillmann J, Bronaugh D, Alterskjaer K, Cole JN, Ji D, Kravitz B, Kristjánsson JE, Moore JC, Muri H, Niemeier U, Robock A, Tilman S, Yang S (2014) A multimodel examination of climate extremes in an idealized geoengineering experiment. J Geophys Res 119:3900–3923
Cusack DF, Axsen J, Shwom R, Hartzell-Nichols L, White S, Mackey KRM (2014) An interdisciplinary assessment of climate engineering strategies. Front Ecol Env 12:280–287
Eliseev AV (2012) Climate change mitigation via sulfate injection to the stratosphere: impact on the global carbon cycle and terrestrial biosphere. Atm Ocean Opt 25:405–413
Ferraro AJ, Highwood EJ, Charlton-Perez AJ (2014) Weakened tropical circulation and reduced precipitation in response to geoengineering. Env Res Lett 9:014001. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/9/1/014001
Friend AD, Lucht W, Rademacher TT, Keribin RM, Betts R, Cadule P, Ciais P, Clark DB, Dankers R, Falloon P, Ito A, Kahana R, Kleidon A, Lomas MR, Nishina K, Ostberg S, Pavlick R, Peylin P, Schaphoff S, Vuichard N, Warszwski L, Wiltshire A, Woodward FI (2014) Carbon residence time dominates uncertainty in terrestrial vegetation responses to future climate and atmospheric CO2. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 111:3280–3285
Gabriel CJ, Robock A (2015) Stratospheric geoengineering impacts on El Niño/Southern Oscillation. Atm Chem Phys 15:11949–11966
Glienke S, Irvine PJ, Lawrence MG (2015) The impact of geoengineering on vegetation in experiment G1 to the GeoMIP. J Geophys Res Atm 120:10196–10213
Govindasamy B, Caldeira K (2000) Geoengineering Earth’s radiation balance to mitigate CO2-induced climate change. Geophys Res Lett 27:2141–2144
Govindasamy B, Thompson S, Duffy PB, Caldeira K, Delire C (2002) Impact of geoengineering schemes on the terrestrial biosphere. Geophys Res Lett 29:2061. doi:10.1029/2002GL015911
Gu L, Baldocchi D, Wofsy SC, Munger JW, Michalsky JJ, Urbanski S, Boden TA (2003) Response of a deciduous forest to the Mount Pinatubo eruption: enhanced photosynthesis. Science 299:2035–2038
Harris I, Jones PD, Osborn TJ, Lister DH (2014) Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations—the CRU TS3.10 dataset. Int J Climatol 34:623–642
Hegerl GC, Solomon S (2009) Risks of climate engineering. Science 325:955–956
Inatomi M, Ito A, Ishijima K, Murayama S (2010) Greenhouse gas budget of a cool temperate deciduous broadleaved forest in Japan estimated using a process-based model. Ecosystems 13:472–483
Irvine PJ, Sriver RL, Keller K (2012) Tension between reducing sea-level rise and global warming through solar-radiation management. Nat Clim Change 2:97–100
Ito A (2010) Changing ecophysiological processes and carbon budget in East Asian ecosystems under near-future changes in climate: implications for long-term monitoring from a process-based model. J Plant Res 123:577–588
Ito A (2011) A historical meta-analysis of global terrestrial net primary productivity: are estimates converging? Global Change Biol 17:3161–3175
Ito A, Inatomi M (2012) Water-use efficiency of the terrestrial biosphere: a model analysis on interactions between the global carbon and water cycles. J Hydromet 13:681–694
Ito A, Oikawa T (2002) A simulation model of the carbon cycle in land ecosystems (Sim-CYCLE): a description based on dry-matter production theory and plot-scale validation. Ecol Model 151:147–179
Jones A, Haywood JM, Alterskjær K, Boucher O, Cole JNS, Curry CL, Irvine PJ, Ji D, Kravitz B, Kristjánsson JE, Moore JC, Niemeier U, Robock A, Schmidt H, Singh B, Tilmes S, Watanabe S, Yoon J-H (2013) The impact of abrupt suspension of solar radiation management (termination effect) in experiment G2 of the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). J Geophys Res 118:9743–9752
Jones AC, Haywood JM, Jones A (2016) Climatic impacts of stratospheric geoengineering with sulfate, black carbon and titania injection. Atm Chem Phys 16:2843–2862
Kalidindi S, Bala G, Modak A, Caldeira K (2015) Modeling of solar radiation management: a comparison of simulations using reduced solar constant and stratospheric sulphate aerosols. Clim Dyn 44:2909–2925
Keith DW (2000) Geoengineering the climate: history and prospect. Ann Rev Energy Environ 25:245–284
Keith DW, Irvine PJ (2016) Solar geoengineering could substantially reduce climate risks—a research hypothesis for the next decade. Earth’s Future 4:549–559
Keith DW, MacMartin DG (2015) A temporary, moderate and responsive scenario for solar geoengineering. Nat Clim Change 5:201–206
Kleidon A, Kravitz B, Renner M (2015) The hydrological sensitivity to global warming and solar geoengineerging derived from thermodynamic constraints. Geophys Res Lett 42:138–144
Kravitz B, Caldeira K, Boucher O, Robock A, Rasch PJ, Alterskjær K, Irvine PJ, Ji D, Jones A, Kristjánsson JE, Lunt DJ, Moore JC, Niemeier U, Schmidt H, Schulz M, Singh B, Tilmes S, Watanabe S, Yang S, Yoon J-H (2013) Climate model response from the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). J Geophys Res 118:8320–8332
Kravitz B, MacMartin DG, Wang H, Rasch PJ (2016) Geoengineering as a design problem. Earth Sys Dyn 7:469–497
Le Quéré C, Andrew RM, Canadell JG, Sitch S, Korsbakken JI, Peters GP, Manning AC, Boden TA, Tans PP, Houghton RA, Keeling RF, Alin S, Andrews OD, Anthoni P, Barbero L, Bopp L, Chevallier F, Chini LP, Ciais P, Currie K, Delire C, Doney SC, Friedlingstein P, Gkritzalis T, Harris I, Hauck J, Haverd V, Hoppema M, Klein Goldewijk K, Jain AK, Kato E, Körtzinger A, Landschützer P, Lefèvre N, Lenton A, Lienert S, Lombrardozzi D, Melton JR, Metzl N, Millero F, Monteiro PMS, Munro DR, Nabel JEMS, Nakaoka S, O’Brien K, Olsen A, Omar AM, Ono T, Pierrot D, Poulter B, Rödenbeck C, Salisbury J, Schuster U, Schwinger J, Séférian R, Skjelvan I, Stocker BD, Sutton AJ, Takahashi T, Tian H, Tilbrook B, van der Laan-Luijkx IT, van der Werf GR, Viovy N, Walker AP, Wiltshire AJ, Zaehle S (2016) Global carbon budget 2016. Earth Sys Sci Data 8:605–649
Lenton TM, Vaughan NE (2009) The radiative forcing potential of different climate geoengineering options. Atm Chem Phys 9:5539–5561
Lunt DJ, Ridgwell A, Valdes PJ, Seale A (2008) “Sunshade world”: a fully coupled GCM evaluation of the climatic impacts of geoengineering. Geophys Res Lett 35:L12710. doi:10.1029/2008GL033674
MacMartin DG, Caldeira K, Keith DW (2014) Solar geoengineering to limit the rate of temperature change. Phil Trans Roy Soc A372:20140134. doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0134
MacMartin DG, Kravitz B, Long JCS, Rasch PJ (2016) Geoengineering with stratospheric aerosols: what do we not know after a decade of research? Earth’s Future 4:543–548
Matthews HD, Caldeira K (2007) Transient climate–carbon simulations of planetary geoengineering. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:9949–9954
McCormack CG, Born W, Irvine PJ, Achterberg EP, Amano T, Ardron J, Foster PN, Gattuso J-P, Hawkins SJ, Hendy E, Kissling WD, Lluch-Cota SE, Murphy EJ, Ostle N, Owens NJP, Perry RI, Pörtner HO, Scholes RJ, Schuur FM, Schweiger O, Settele J, Smith RK, Smith S, Thompson J, Tittensor DP, van Kleunen M, Vivian C, Vohland K, Warren R, Watkinson AR, Widdicombe S, Williamson P, Woods E, Blackstock JJ, Sutherland WJ (2016) Key impacts of climate engineering on biodiversity and ecosystems, with priorities for future research. J Integr Env Sci 13:103–128
McCusker KE, Armour KC, Bitz CM, Battisti DS (2014) Rapid and extensive warming following cessation of solar radiation management. Env Res Lett 9:024005. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/1089/1082/024005
McCusker KE, Battisti DS, Bitz CM (2012) The climate response to stratospheric sulfate injections and implications for addressing climate emergencies. J Clim 25:3096–3116
Mercado LM, Bellouin N, Sitch S, Boucher O, Huntingford C, Wild M, Cox PM (2009) Impact of changes in diffuse radiation on the global land carbon sink. Nature 458:1014–1017
Ming T, de Richter R, Liu W, Caillol S (2014) Fighting global warming by climate engineering: is the earth radiation management and the solar radiation management any options for fighting climate change? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 31:792–834
Moore JC, Grinsted A, Guo X, Yu X, Jevrejeva S, Rinke A, Cui X, Kravitz B, Lenton A, Watanabe S, Ji D (2015) Atlantic hurricane surge response to geoengineering. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 112:13794–13799
Moss RH, Edmonds JA, Hibbard KA, Manning MR, Rose SK, van Vuuren DP, Carter TR, Emori S, Kainuma M, Kram T, Meehl GA, Mitchell JFB, Nakicenovic N, Riahi K, Smith SJ, Stouffer RJ, Thomson AM, Weyant JP, Wilbanks TJ (2010) The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature 463:747–756
Muri H, Niemeier U, Kristjánsson JE (2015) Tropical rainforest response to marine sky brightening climate engineering. Geophys Res Lett 42:2951–2960
Naik V, Wuebbles DJ, Delucia EH, Foley JA (2003) Influence of geoengineered climate on the terrestrial biosphere. Env Manag 32:373–381
Nemani RR, Keeling CD, Hashimoto H, Jolly WM, Piper SC, Tucker CJ, Myneni RB, Running SW (2003) Climate-driven increases in global terrestrial net primary production from 1982 to 1999. Science 300:1560–1563
Oldham P, Szerszynski B, Stilgoe J, Brown C, Eacott B, Yuille A (2014) Mapping the landscape of climate engineering. Phil Trans Roy Soc A 372:20140065. doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0065
Parkes B, Challinor A, Nicklin K (2015) Crop failure rates in a geoengineered climate: impact of climate change and marine cloud brightening. Env Res Lett 10:084003. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/1010/1088/084003
Pongratz J, Lobell DB, Cao L, Caldeira K (2012) Crop yields in a geoengineered climate. Nat Clim Change 2:101–105
Robock A, MacMartin DG, Duren R, Christensen MW (2013) Studying geoengineering with natural and anthropogenic anoalogs. Clim Change 121:445–458
Robock A, Marquardt A, Kravitz B, Stenchikov G (2009) Benefits, risks, and costs of stratospheric geoengineering. Geophys Res Lett 36:L19703. doi:10.1029/2009GL039209
Russell LM, Rasch PJ, Mace GM, Jackson RB, Shepherd J, Liss P, Leinen M, Schimel D, Vaughan NE, Janetos AC, Boyd PW, Norby RJ, Caldeira K, Merikanto J, Artaxo P, Melillo J, Morgan MG (2012) Ecosystem impacts of geoengineering: a review for developing a science plan. Ambio 41:350–369
Schmidt H, Alterskjær K, Karam DB, Boucher O, Jones A, Kristjánsson JE, Niemeier U, Schulz M, Aaheim A, Benduhn F, Lawrence M, Timmreck C (2012) Solar irradiance reduction to counteract radiative forcing from a quadrupling of CO2: climate responses simulated by four earth system models. Earth Syst Dyn 3:63–78
Soden BJ, Wetherald RT, Stenchikov GL, Robock A (2002) Global cooling after the eruption of Mount Pinatubo: a test of climate feedback by water vapor. Science 296:727–730
Taylor KE, Stouffer RJ, Meehl GA (2012) An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 93:485–498
Tilmes S, Fasullo J, Lamarque J-F, Marsh DR, Mills M, Alterskjær K, Muri H, Kristjánsson JE, Boucher O, Schulz M, Cole JNS, Curry CL, Jones A, Haywood J, Irvine PJ, Ji D, Moore JC, Karam DB, Kravitz B, Rasch PJ, Singh B, Yoon J-H, Niemeier U, Schmidt H, Robock A, Yang S, Watanabe S (2013) The hydrological impact of geoengineering in the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). J Geophys Res 118:11036–11058
Tilmes S, Jahn A, Kay JE, Holland M, Lamarque J-F (2014) Can regional climate engineering save the summer Arctic Sea Ice? Geophys Res Lett 41:880–885
Trenberth KE, Dai A (2007) Effects of Mount Pinatubo volcanic eruption on the hydrological cycle as an analog of geoengineering. Geophys Res Lett 34:L15702. doi:10.1029/2007GL030524
Xia L, Robock A, Tilmes S, Neely RRI (2016) Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering could enhance the terrestrial photosynthesis rate. Atm Chem Phys 16:1479–1489
Yang H, Dobbie S, Ramirez-Villegas J, Feng K, Challinor AJ, Chen B, Gao Y, Lee L, Yin Y, Sun L, Watson J, Koehler A-K, Fan T, Ghosh S (2016) Potential negative consequences of geoengineering on crop production: a study of Indian groundnut. Geophys Res Lett 43:11786–11795
Yu X, Moore JC, Cui X, Rinke A, Ji D, Kravitz B, Yoon J-H (2015) Impacts, effectiveness and regional inequalities of the GeoMIP G1 to G4 solar radiation management scenarios. Global Planet Change 129:10–22
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted as a part of Integrated Climate Assessment—Risks, Uncertainties and Society (ICA-RUS), funded by the Environmental Research Fund of the Ministry of Environment, Japan, and it was also supported in part by a KAKENHI grant (no. 26281014) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The CMIP5 and GeoMIP model outputs were obtained from the Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, a node of the Earth System Grid Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 6177 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, A. Solar radiation management and ecosystem functional responses. Climatic Change 142, 53–66 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-017-1930-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-017-1930-3