Abstract
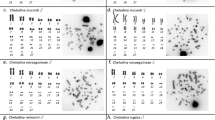
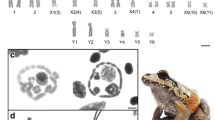
Chromosomal sex determination is the prevalent system found in animals but is rare among turtles. In fact, heteromorphic sex chromosomes are known in only seven of the turtles possessing genotypic sex determination (GSD), two of which correspond to cryptic sex microchromosomes detectable only with high-resolution cytogenetic techniques. Sex chromosomes were undetected in previous studies of Emydura macquarii, a GSD side-necked turtle. Using comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and GTG-banding, a heteromorphic XX/XY sex chromosome system was detected in E. macquarii. The Y chromosome appears submetacentric and somewhat larger than the metacentric X, the first such report for turtles. CGH revealed a male-specific chromosomal region, which appeared heteromorphic using GTG-banding, and was restricted to the telomeric region of the p arm. Based on our observations and the current phylogeny of chelid turtles, we hypothesize that the sex chromosomes of E. macquarii might be the result of a translocation of an ancestral Y microchromosome as found in a turtle belonging to a sister clade, Chelodina longicollis, onto the tip of an autosome. However, in the absence of data from an outgroup, the opposite (fission of a large XY into an autosome and a micro-XY) is theoretically equally likely. Alternatively, the sex chromosome systems of E. macquarii and C. longicollis may have evolved independently. We discuss the potential causes and consequences of such putative chromosome rearrangements in the evolution of sex chromosomes and sex-determining systems of turtles in general.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida-Toledo LF, Foresti F, Daniel MFZ, Toledo SA (2000) Sex chromosome evolution in fish: the formation of the neo-Y chromosome in Eigenmannia (Gymnotiformes). Chromosoma 109: 197–200.
Ayala FJ, Coluzzi M (2005) Chromosome speciation: Humans, Drosophila, and mosquitoes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 6535–6542.
Ayres M, Sampaio MM, Barros RMS, Dias LB, Cunha OR (1969) A karyological study of turtles from the Brazilian Amazon Region. Cytogenetics 8: 401–409.
Barros RM, Sampaio MM, Assis MF, Ayres M, Cunha OR (1976) General considerations on the Karyotypic Evolution of Chelonia from the Amazon Region of Brazil. Cytologia 41: 559–565.
Berry JF, Shine R (1980) Sexual size dimorphism and sexual selection in turtles (Order Testudines). Oecologia 44: 185–191.
Bull JJ (1983) Evolution of Sex Determining Mechanisms. Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings.
Bull JJ, Legler JM (1980) Karyotypes of side-necked turtles (Testudines: Pleurodira). Can J Zool 58: 828–841.
Bull JJ, Moon RG, Legler JM (1974) Male heterogamety in kinosternid turtles (genus Staurotypus). Cytogenet Cell Genet 13: 419–425.
Carr JL, Bickham JW (1981) Sex-chromosomes of the Asian black pond turtle, Siebenrockiella crassicollis (Testudines, Emydidae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 31: 178–183.
Carvalho AB, Clark AG (2005) Y chromosome of D-pseudoobscura is not homologous to the ancestral Drosophila Y. Science 307: 108–110.
Charlesworth B (1991) The evolution of sex chromosomes. Science 251: 1030–1033.
Charlesworth B, Coyne JA, Barton NH (1987) The relative rates of evolution of sex chromosomes and autosomes. Am Nat 130: 113–146.
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B, Marais G (2005) Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity 95: 118–128.
Coghlan A, Eichler EE, Oliver SG, Paterson AH, Stein L (2005) Chromosome evolution in eukaryotes: a multi-kingdom perspective. Trends Genet 21: 673–682.
Edwards SV, Kingan SB, Calkins JD et al. (2005) Speciation in birds: Genes, geography, and sexual selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 6550–6557.
Ezaz MT, McAndrew BJ, Penman DJ (2004) Spontaneous diploidization of the maternal chromosome set in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) eggs. Aquaculture Res 35: 271–277.
Ezaz T, Quinn AE, Miura I, Sarre SD, Georges A, Graves JAM (2005) The dragon lizard Pogona vitticeps has ZZ/ZW micro-sex chromosomes. Chromosome Res 13: 763–776.
Ezaz T, Valenzuela N, Grutzner F et al. (2006) An XX/XY sex microchromosome system in a freshwater turtle, Chelodina longicollis (Testudines: Chelidae) with genetic sex determination. Chromosome Res 14: 139–150.
Georges A, Thomson S (2006) Evolution and zoogeography of Australian freshwater turtles. In: Merrick JR, Archer M, Hickey G, Lee M, eds. Evolution and Zoogeography of Australasian Vertebrates. Sydney: Australia: AUSCIPUB (Australian Scientific Publishing) Pty Ltd.
Graves JAM (2002) The rise and fall of SRY. Trends Genet 18: 259–264.
Graves JAM (2006) Sex chromosome specialization and degeneration in mammals. Cell 124: 901–914.
Grutzner F, Rens W, Tsend-Ayush E et al. (2004) In the platypus a meiotic chain of ten sex chromosomes shares genes with the bird Z and mammal X chromosomes. Nature 432: 913–917.
Iverson JB, Brown RM, Akre TS et al. (2007) In search of the tree of life for turtles. Chelonian Res Monogr 4: 85–106.
Just W, Baumstark A, Sub A et al. (2007) Ellobius lutescens: sex determination and sex chromosome. Sex Dev 1: 211–221.
Kawai A, Nishida-Umehara C, Ishijima J, Tsuda Y, Ota H, Matsuda Y (2007) Different origins of bird and reptile sex chromosomes inferred from comparative mapping of chicken Z-linked genes. Cytogenet Genome Res 117: 92–102.
Killebrew F (1976) Mitotic chromosomes of turtles. II. The Chelidae. Texas J Sci 27: 149–154.
Lewis KR, John B (1963) Chromosome Marker. Boston : Little Brown.
Lindholm A, Breden F (2002) Sex chromosomes and sexual selection in poeciliid fishes. Am Nat 160: S214–S224.
Liu ZY, Moore PH, Ma H et al. (2004) A primitive Y chromosome in papaya marks incipient sex chromosome evolution. Nature 427: 348–352.
Masly JP, Jones CD, Noor MAF, Locke J, Orr HA (2006) Gene transposition as a cause of hybrid sterility in Drosophila. Science 313: 1448–1450.
Matsunaga S, Kawano S (2001) Sex determination by sex chromosomes in dioecious plants. Plant Biol 3: 481–488.
McBee K, Bickham JW, Rhodin AGJ, Mittermeier RA (1985) Karyotypic variation in the genus Platemys (Testudines, Pleurodira). Copeia 2: 445–449.
Ming R, Yu QY, Moore PH (2007) Sex determination in papaya. Semin Cell DevBiol 18: 401–408.
Modi WS, Crews D (2005) Sex chromosomes and sex determination in reptiles—Commentary. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15: 660–665.
Near TJ, Meylan PA, Shaffer HB (2005) Assessing concordance of fossil calibration points in molecular clock studies: an example using turtles. Am Nat 165: 137–146.
Ohno S (1967) Sex Chromosomes and Sex-linked Genes. Berlin: Springer.
Peichel CL, Ross JA, Matson CK et al. (2004) The master sex-determination locus in Threespine Sticklebacks is on a nascent Y chromosome. Curr Biol 14: 1416–1424.
Rhodin AGJ, Mittermeier RA, Gardner AL, Medem F (1978) Karyotypic analysis of the Podocnemis turtles. Copeia 4: 723–728.
Rhodin AGJ, Mittermeier RA, McMorris JR (1984) Platemys Macrocephala, a new species of Chelid turtle from Central Bolivia and the Pantanal Region of Brazil. Herpetologica 40: 38–46.
Rice WR (1984) Sex-chromosomes and the evolution of sexual dimorphism. Evolution 38: 735–742.
Sato M, Ikeda M (1992) Chromosomal complements of 2 forms of Neanthes japonica (Polychaeta, Nereeididae) with evidence of male-heterogametic sex-chromosomes. Mar Biol 112:299–307.
Saether SA, Saetre GP, Borge T et al. (2007) Sex chromosome-linked species recognition and evolution of reproductive isolation in flycatchers. Science 318: 95–97.
Schmid M, Steinlein C (1991) Chromosome-banding in Amphibia .16. High-resolution replication banding-patterns in Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma 101: 123–132.
Sharma GP, Kaur P, Nakhasi U (1975) Female heterogamety in the Indian crytodiran Chelonian, Kachuga Smithi Gray. In Tiwari KK, Srivistava CB, eds. Dr. B.S. Chauhan Commemoration Volume 359–368. Zoological Society of India, Orissa.
Sites JWJ, Bickham JW, Haiduk MW, Iverson JB (1979) Banded karyotypes of six taxa of kinosternid turtles. Copeia 4: 692–698.
Solari AJ (1994) Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determination in Vertebrates. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Thompson MB (1988) Influence of incubation temperature and water potential on sex determination in Emydura macquarii (Testudines: Pleurodira). Herpetologica 44: 86–90.
Valenzuela N (2004) Temperature-dependent sex determination. In: Deeming DC, ed. Reptilian Incubation: Environment & Behaviour. Nottingham, UK: Nottingham University Press, pp. 211–227.
Valenzuela N, Lance VA, eds. (2004) Temperature Dependent Sex Determination in Vertebrates. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Books.
Valenzuela N, Adams DC, Janzen FJ (2003) Pattern does not equal process: exactly when is sex environmentally determined? Am Nat 161: 676–683.
Vallender EJ, Lahn BT (2004) How mammalian sex chromosomes acquired their peculiar gene content. Bioessays 26: 159–169.
Van Doorn GS, Kirkpatrick M (2007) Turnover of sex chromosomes induced by sexual conflict. Nature 449: 909–912.
Waters PD, Wallis MC, Graves JAM (2007) Mammalian sex—Origin and evolution of the Y chromosome and SRY. Semin Cell Dev Biol 18: 389–400.
White MJD (1968) Models of speciation. Science 159: 1065–1070.
White MJD (1973) Animal Cytology and Evolution, 3rd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, P.A., Ezaz, T., Valenzuela, N. et al. An XX/XY heteromorphic sex chromosome system in the Australian chelid turtle Emydura macquarii: A new piece in the puzzle of sex chromosome evolution in turtles. Chromosome Res 16, 815–825 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-008-1228-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-008-1228-4