Abstract
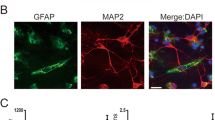
DIX domain containing 1 (Dixdc1), a positive regulator of Wnt signaling pathway, is recently reported to play a role in the neurogenesis. However, the distribution and function of Dixdc1 in the central nervous system (CNS) after brain injury are still unclear. We used an acute traumatic brain injury (TBI) model in adult rats to investigate whether Dixdc1 is involved in CNS injury and repair. Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry showed a time-dependent up-regulation of Dixdc1 expression in ipsilateral cortex after TBI. Double immunofluorescent staining indicated a colocalization of Dixdc1 with astrocytes and neurons. Moreover, we detected a colocalization of Ki-67, a cell proliferation marker with GFAP and Dixdc1 after TBI. In primary cultured astrocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide, we found enhanced expression of Dixdc1 in parallel with up-regulation of Ki-67 and cyclin A, another cell proliferation marker. In addition, knockdown of Dixdc1 expression in primary astrocytes with Dixdc1-specific siRNA transfection induced G0/G1 arrest of cell cycle and significantly decreased cell proliferation. In conclusion, all these data suggest that up-regulation of Dixdc1 protein expression is potentially involved in astrocyte proliferation after traumatic brain injury in the rat.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bullock MR, Lyeth BG, Muizelaar JP (1999) Current status of neuroprotection trials for traumatic brain injury: lessons from animal models and clinical studies. Neurosurgery 45(2):207–217 (discussion 217–220)
Busch SA, Silver J (2007) The role of extracellular matrix in CNS regeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 17(1):120–127. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2006.09.004
Cernak I, Stoica B, Byrnes KR, Di Giovanni S, Faden AI (2005) Role of the cell cycle in the pathobiology of central nervous system trauma. Cell Cycle 4(9):1286–1293
Chen X, Cao X, Tao G, Cao Z, Wang S, Zhou F, Cui Z (2012) FOXJ2 expression in rat spinal cord after injury and its role in inflammation. J Mol Neurosci 47(1):158–165. doi:10.1007/s12031-011-9704-2
Di Giovanni S, Knoblach SM, Brandoli C, Aden SA, Hoffman EP, Faden AI (2003) Gene profiling in spinal cord injury shows role of cell cycle in neuronal death. Ann Neurol 53(4):454–468. doi:10.1002/ana.10472
Ewing-Cobbs L, Brookshire B, Scott MA, Fletcher JM (1998) Children’s narratives following traumatic brain injury: linguistic structure, cohesion, and thematic recall. Brain Lang 61(3):395–419. doi:10.1006/brln.1997.1884
Gean AD, Fischbein NJ (2010) Head trauma. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 20(4):527–556. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2010.08.001
Hansson E, Rönnbäck L (2003) Glial neuronal signaling in the central nervous system. FASEB J 17(3):341–348
Inglese M, Makani S, Johnson G, Cohen BA, Silver JA, Gonen O, Grossman RI (2005) Diffuse axonal injury in mild traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neurosurg 103(2):298–303. doi:10.3171/jns.2005.103.2.0298
Jing XT, Wu HT, Wu Y, Ma X, Liu SH, Wu YR, Fan M (2009) DIXDC1 promotes retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation and inhibits gliogenesis in P19 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29(1):55–67. doi:10.1007/s10571-008-9295-9
Karimi-Abdolrezaee S, Billakanti R (2012) Reactive astrogliosis after spinal cord injury-beneficial and detrimental effects. Mol Neurobiol 46(2):251–264. doi:10.1007/s12035-012-8287-4
Kato H, Takahashi A, Itoyama Y (2003) Cell cycle protein expression in proliferating microglia and astrocytes following transient global cerebral ischemia in the rat. Brain Res Bull 60(3):215–221
Kleindienst A, Harvey HB, Rice AC, Müller C, Hamm RJ, Gaab MR, Bullock MR (2004) Intraventricular infusion of the neurotrophic protein S100B improves cognitive recovery after fluid percussion injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 21(5):541–547
Kleindienst A, McGinn MJ, Harvey HB, Colello RJ, Hamm RJ, Bullock MR (2005) Enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis by intraventricular S100B infusion is associated with improved cognitive recovery after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 22(6):645–655
Konigsmark BW, Murphy EA (1970) Neuronal populations in the human brain. Nature 228(5278):1335–1336
Lin Y, Xu D, Li X, Liu C, Liu X, Huang S, Liu X (2016) Upregulation of interferon regulatory factor 6 promotes neuronal apoptosis after traumatic brain injury in adult rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36(1):27–36. doi:10.1007/s10571-015-0217-3
Liu Y, Wang Y, Cheng C, Chen Y, Shi S, Qin J, Shen A (2010) A relationship between p27(kip1) and Skp2 after adult brain injury: implications for glial proliferation. J Neurotrauma 27(2):361–371. doi:10.1089/neu.2008.0581
Luo W, Zou H, Jin L, Lin S, Li Q, Ye Z, Lin SC (2005) Axin contains three separable domains that confer intramolecular, homodimeric, and heterodimeric interactions involved in distinct functions. J Biol Chem 280(6):5054–5060. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412340200
Ridet JL, Malhotra SK, Privat A, Gage FH (1997) Reactive astrocytes: cellular and molecular cues to biological function. Trends Neurosci 20(12):570–577
Shi W, Gong P, Fan J, Yan YH, Ni L, Wu X, Chen J (2012) The expression pattern of ADP-ribosyltransferase 3 in rat traumatic brain injury. J Mol Histol 43(1):37–47. doi:10.1007/s10735-011-9366-y
Singh KK, Ge X, Mao Y, Drane L, Meletis K, Samuels BA, Tsai LH (2010) Dixdc1 is a critical regulator of DISC1 and embryonic cortical development. Neuron 67(1):33–48. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.002
Soma K, Shiomi K, Keino-Masu K, Masu M (2006) Expression of mouse coiled-coil-DIX1 (Ccd1), a positive regulator of Wnt signaling, during embryonic development. Gene Expr Patterns 6(3):325–330. doi:10.1016/j.modgep.2005.06.013
Tawfik VL, Lacroix-Fralish ML, Bercury KK, Nutile-McMenemy N, Harris BT, Deleo JA (2006) Induction of astrocyte differentiation by propentofylline increases glutamate transporter expression in vitro: heterogeneity of the quiescent phenotype. Glia 54(3):193–203. doi:10.1002/glia.20365
Tian DS, Yu ZY, Xie MJ, Bu BT, Witte OW, Wang W (2006) Suppression of astroglial scar formation and enhanced axonal regeneration associated with functional recovery in a spinal cord injury rat model by the cell cycle inhibitor olomoucine. J Neurosci Res 84(5):1053–1063. doi:10.1002/jnr.20999
Urrea C, Castellanos DA, Sagen J, Tsoulfas P, Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD (2007) Widespread cellular proliferation and focal neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury in the rat. Restor Neurol Neurosci 25(1):65–76
Wang X, Zheng L, Zeng Z, Zhou G, Chien J, Qian C, Liu W (2006) DIXDC1 isoform, l-DIXDC1, is a novel filamentous actin-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 347(1):22–30. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.06.050
Wang L, Cao XX, Chen Q, Zhu TF, Zhu HG, Zheng L (2009) DIXDC1 targets p21 and cyclin D1 via PI3 K pathway activation to promote colon cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Sci 100(10):1801–1808. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01246.x
White RE, Jakeman LB (2008) Don’t fence me in: harnessing the beneficial roles of astrocytes for spinal cord repair. Restor Neurol Neurosci 26(2-3):197–214
Wu W, Liu Q, Liu Y, Yu Z, Wang Y (2016) Dixdc1 targets CyclinD1 and p21 via PI3 K pathway activation to promote Schwann cell proliferation after sciatic nerve crush. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478(2):956–963. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.058
Xu T, Fan X, Tan Y, Yue Y, Chen W, Gu X (2014) Expression of PHB2 in rat brain cortex following traumatic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci 15(2):3299–3318. doi:10.3390/ijms15023299
Yao L, Liu YH, Li X, Ji YH, Yang XJ, Hang XT, Shen AG (2014) CRMP1 interacted with Spy1 during the collapse of growth cones induced by Sema3A and acted on regeneration after sciatic nerve crush. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9049-2
Zhang H, Liu Y, Li Y, Zhou Y, Chen D, Shen J, Cheng C (2014) The expression of CAP1 after traumatic brain injury and its role in astrocyte proliferation. J Mol Neurosci 54(4):653–663. doi:10.1007/s12031-014-0363-y
Zhang W, Liu Y, Zhu X, Cao Y, Liu Y, Mao X, Shen A (2015) SCY1-Like 1-binding protein 1 (SCYL1BP1) suppressed sciatic nerve regeneration by enhancing the RhoA pathway. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9531-5
Zhao W, Wang Y, Shi W, Chen Y, Cai G, Chen J, Xu W (2013) The expression of FBP1 after traumatic brain injury and its role in astrocyte proliferation. J Mol Neurosci 51(3):687–694. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-0049-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Lu and R. Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Jiang, R., Tao, X. et al. Expression of Dixdc1 and its Role in Astrocyte Proliferation after Traumatic Brain Injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37, 1131–1139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0446-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0446-0