Abstract
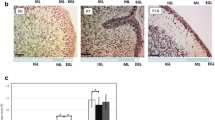
The insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) are considered to play important roles in brain development; and their cognate receptors -InsR and IGF-1R- localized within distinct brain regions including cerebellum. Using Real-Time PCR and western blot analysis, we compared the expression of InsR and IGF-1R in male and female developing rat cerebellum at P0, P7, and P14. At all time points studied, the cerebellar expression of IGF-1R, both at mRNA and protein levels was higher than that of InsR. The lowest InsR and IGF-1R mRNA and protein levels were measured in the neonate cerebellum, independent of gender. In males, the highest InsR and IGF-1R mRNA and protein expression were found at P7. InsR and IGF-1R expression increased significantly between P0 and P7, followed by a marked downregulation at P14. In contrast, in females, mRNA and protein levels of InsR and IGF-1R remain unchanged between P0 and P7, and are upregulated at P14. Therefore, peaked InsR and IGF-1R expression in female cerebelli occurred at P14. Interestingly, changes in mRNA expression and in protein levels followed the same developmental pattern, indicating that InsR and IGF-1R transcription is not subject to modulatory effects during the first 2 weeks of development. These findings indicate that there are prominent sexual differences in InsR and IGF-1R expression in the developing rat cerebellum, suggesting a probable mechanism for the control of gender differences in development and function of the cerebellum.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abel JM, Witt DM, Rissman EF (2011) Sex differences in the cerebellum and frontal cortex: roles of estrogen receptor alpha and sex chromosome genes. Neuroendocrinol 93:230–240
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C (2011) Insulin receptor signaling in rat hippocampus: a study in STZ (ICV) induced memory deficit model. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:261–273
Allen G, Buxton RB, Wong EC, Courchesne E (1997) Attentional activation of the cerebellum independent of motor involvement. Science 275:1940–1943
Altman J, Bayer SA (1996) Development of the cerebellar system. CRC Press, Oxford
Anderson MF, Aberg MA, Nilsson M, Eriksson PS (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-I and neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 134(1–2):115–122
Andreano JM, Cahill L (2009) Sex influences on the neurobiology of learning and memory. Learn Mem 16:248–266
Andreasen NC, O’Leary DS, Cizadlo T, Arndt S, Rezai K, Ponto L (1996) Schizophrenia and cognitive dysmetria: a positron-emission tomography study of dysfunctional pre-frontal-thalamic-cerebellar circuitry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9985–9990
Anlar B, Sullivan KA, Feldman EL (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-I and central nervous system development. Horm Metab Res 31(2–3):120–125
Bach MA, Shen-Orr Z, Lowe WL Jr, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D (1991) Insulin-like growth factor I mRNA levels are developmentally regulated in specific regions of the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 10(1):43–48
Bains M, Florez-McClure ML, Heidenreich KA (2009) Insulin-like growth factor-I prevents the accumulation of autophagic vesicles and cell death in purkinje neurons by increasing the rate of autophagosome-to-lysosome fusion and degradation. J Biol Chem 284:20398–20407
Baron-Van Evercooren A, Olichon-Berthe C, Kowalski A, Visciano G, Van Obberghen E (1991) Expression of IGF-I and insulin receptor genes in the rat central nervous system: a developmental, regional, and cellular analysis. J Neurosci Res 28(2):244–253
Bartlett WP, Li XS, Williams M, Benkovic S (1991) Localization of insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA in murine central nervous system during postnatal development. Dev Biol 147(1):239–250
Baskin DG, Wilcox BJ, Figlewicz DP, Dorsa DM (1988) Insulin and insulin-like growth factors in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 11(3):107–111
Beaton A, Marien P (2010) Language, cognition and the cerebellum: grappling with an enigma. Cortex 46:811–820
Beck F, Samani NJ, Byrne S, Morgan K, Gebhard R, Brammar WJ (1988) Histochemical localization of IGF-I and IGF-II mRNA in the rat between birth and adulthood. Development 104(1):29–39
Beck KD, Powell-Braxton L, Widmer HR, Valverde J, Hefti F (1995) Igf1 gene disruption results in reduced brain size, CNS hypomyelination, and loss of hippocampal granule and striatal parvalbumin-containing neurons. Neuron 14(4):717–730
Bondy CA (1991) Transient IGF-I gene expression during the maturation of functionally related central projection neurons. J Neurosci 11(11):3442–3455
Bondy CA, Cheng CM (2004) Signaling by insulin-like growth factor 1 in brain. Eur J Pharmacol 490(1–3):25–31
Brooks VB (1981) Comment: on functions of the “cerebellar circuit” in movement control. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 59:776–778
Bugalho P, Correa B, Viana-Baptista M (2006) Role of cerebellum in cognitive and behavioral control: scientific basis and investigation models. Acta Med Port 19:257–268
Carson MJ, Behringer RR, Brinster RL, McMorris FA (1993) Insulin-like growth factor I increases brain growth and central nervous system myelination in transgenic mice. Neuron 10(4):729–740
Cheng CM, Cohen M, Tseng V, Bondy CA (2001) Endogenous IGF1 enhances cell survival in the postnatal dentate gyrus. J Neurosci Res 64:341–347
Chiu SL, Cline HT (2010) Insulin receptor signaling in the development of neuronal structure and function. Neural Dev 5:7
Chrysis D, Calikoglu AS, Ye P, D’Ercole AJ (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-I overexpression attenuates cerebellar apoptosis by altering the expression of Bcl family proteins in a developmentally specific manner. J Neurosci 21:1481–1489
Chung SC, Lee BY, Tack GRL, S.Y, Eom JS, Sohn JH (2005) Effects of age, gender, and weight on the cerebellar volume of Korean people. Brain Res 1042(2):233–235
Cohen-Bendahan CC, van de Beek C, Berenbaum SA (2005) Prenatal sex hormone effects on child and adult sex-typed behavior: methods and findings. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:353–384
Cosgrove KP, Mazure CM, Staley JK (2007) Evolving knowledge of sex differences in brain structure, function, and chemistry. Biol Psychiatry 62:847–855
Dalla C, Shors TJ (2009) Sex differences in learning processes of classical and operant conditioning. Physiol Behav 97:229–238
de Pablo F, de la Rosa EJ (1995) The developing CNS: a scenario for the action of proinsulin, insulin and insulin-like growth factors. Trends Neurosci 18(3):143–150
de Vries GJ, de Bruin JPC, Uylings HMM, Corner MA (1984) Sex differences in the brain: the relation between structure and function. Prog Brain Res 61:VII–VIII
Dean SL, McCarthy MM (2008) Steroids, sex and the cerebellar cortex: implications for human disease. Cerebellum 7:38–47
D’Ercole AJ, Ye P, Calikoglu AS, Gutierrez-Ospina G (1996) The role of the insulin-like growth factors in the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 13(3):227–255
D’Ercole AJ, Ye P, O’Kusky JR (2002) Mutant mouse models of insulin-like growth factor actions in the central nervous system. Neuropeptides 36(2–3):209–220
Diamond A (2000) Close interrelation of motor development and cognitive development and of the cerebellum and prefrontal cortex. Child Dev 71:44–56
Dolan RJ (1998) A cognitive affective role for the cerebellum. Brain 121:545–546
Dou JT, Chen M, Dufour F, Alkon DL, Zhao WQ (2005) Insulin receptor signaling in long-term memory consolidation following spatial learning. Learn Mem 12(6):646–655
Eccles JC (1981) Physiology of motor control in man. Appl Neurophysiol 44:5–15
Escalona PR, McDonald WM, Doraiswamy PM, Boyko OB, Husain MM, Figiel GS, Laskowitz D, Ellinwood EH Jr, Krishnan KR (1991) In vivo stereological assessment of human cerebellar volume: effects of gender and age. Am J Neuroradiol 12:927–929
Filipek PA, Richelme C, Kennedy DN, Caviness VS Jr (1994) The young adult human brain: an MRI-based morphometric analysis. Cereb Cortex 4:344–360
Gammeltoft S, Fehlmann M, Van Obberghen E (1985) Insulin receptors in the mammalian central nervous system: binding characteristics and subunit structure. Biochimie 67:1147–1153
Ghez C, Fahn S (1985) The cerebellum, in, principles of neural science. Elsevier, New York, pp 502–522
Giedd JN, Snell JW, Lange N, Rajapakse JC, Casey BJ, Kozuch PL, Vaituzis AC, Vauss YC, Hamburger SD, Kaysen D et al (1996) Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of human brain development: ages 4–18. Cereb Cortex 6:551–560
Goldowitz D, Hamre K (1998) The cells and molecules that make a cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 21:375–382
Gowen E, Miall RC (2007) The cerebellum and motor dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders. Cerebellum 6:268–279
Hall TC, Miller AKH, Corsellis JAN (1975) Variations in the human Purkinje cell population according to sex and age. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1:267–292
Hami J, Sadr-Nabavi A, Sankian M, Haghir H (2012) Sex differences and left-right asymmetries in expression of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptors in developing rat hippocampus. Brain Struct Funct 217(2):293–302
Hayter AL, Langdon DW, Ramnani N (2007) Cerebellar contributions to working memory. Neuroimage 36:943–954
Hill JM, Lesniak MA, Pert CB, Roth J (1986) Autoradiographic localization of insulin receptors in rat brain: prominence in olfactory and limbic areas. Neuroscience 17(4):1127–1138
Hodge RD, D’Ercole AJ, O’Kusky JR (2004) Insulin-like growth factor-I accelerates the cell cycle by decreasing G1 phase length and increases cell cycle reentry in the embryonic cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 24:10201–10210
Hoppenbrouwers SS, Schutter DJ, Fitzgerald PB, Chen R, Daskalakis ZJ (2008) The role of the cerebellum in the pathophysiology and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders: a review. Brain Res Rev 59(1):185–200
Hu D, Shen H, Zhou Z (2008) Functional asymmetry in the cerebellum: a brief review. Cerebellum 7:304–313
Jazin E, Cahill L (2010) Sex differences in molecular neuroscience: from fruit flies to humans. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:9–17
Kar S, Chabot JG, Quirion R (1993) Quantitative autoradiographic localization of [125I]insulin-like growth factor I, [125I]insulin-like growth factor II, and [125I]insulin receptor binding sites in developing and adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol 333(3):375–397
Keller A, Castellanos FX, Vaituzis AC, Jeffries NO, Giedd JN, Rapoport JL (2003) Progressive loss of cerebellar volume in childhood-onset schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatr 160:128–133
Kern JK (2002) The Possible role of the cerebellum in autism/PDD: disruption of a multisensory feedback loop. Med Hypoth 59:255–260
Kibby MY, Fancher JB, Markanen R, Hynd GW (2008) A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging analysis of the cerebellar deficit hypothesis of dyslexia. J Child Neurol 23:368–380
Klugmann M, Schwab MH, Pühlhofer A, Schneider A, Zimmermann F, Griffiths IR, Nave KA (1997) Assembly of CNS myelin in the absence of proteolipid protein. Neuron 18:59–70
Konarski JK, McIntyre RS, Grupp LA, Kennedy SH (2005) Is the cerebellum relevant in the circuitry of neuropsychiatric disorders? J Psychiatry Neurosci 30:178–186
Kornack DR, Lu B, Black IB (1991) Sexually dimorphic expression of the NGF receptor gene in the developing rat brain. Brain Res 542:171–174
Luft AR, Skalej M, Welte D, Kolb R, Burk K, Schulz JB, Klockgether T, Voigt K (1998) A new semiautomated, three-dimensional technique allowing precise quantification of total and regional cerebellar volume using MRI. Diabetes Care Magn Reson 40:143–151
Marks JL, Porte D Jr, Stahl WL, Baskin DG (1990) Localization of insulin receptor mRNA in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Endocrinol 127(6):3234–3236
Marks JL, Porte D Jr, Baskin DG (1991) Localization of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor messenger RNA in the adult rat brain by in situ hybridization. Mol Endocrinol 5(8):1158–1168
Martins IP, Castro-Caldas A, Townes BD, Ferreira G, Rodrigues P, Marques S, Derouen T (2005) Age and sex differences in neurobehavioral performance: a study of portuguese elementary school children. Int J Neurosci 115:1687–1709
Middlenton FA, Strick PL (1994) Anatomical evidence for cerebellar and basal ganglia involvement in higher cognitive function. Science 266:458–461
Nakae J, Kido Y, Accili D (2001) Distinct and overlapping functions of insulin and IGF-I receptors. Endocr Rev 22(6):818–835
Navarro I, Leibush B, Moon TW, Plisetskaya EM, Banos N, Mendez E, Planas JV, Gutierrez J (1999) Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and glucagon: the evolution of their receptors. Comp Biochem Physiol B 122(2):137–153
Nelson TJ, Sun MK, Hongpaisan J, Alkon DL (2008) Insulin, PKC signaling pathways and synaptic remodeling during memory storage and neuronal repair. Eur J Pharmacol 585(1):76–87
Nguon K, Ladd B, Baxter MG, Sajdel-Sulkowska EM (2005) Sexual dimorphism in cerebellar structure, function, and response to environmental perturbations. Prog Brain Res 148:341–351
Parker G, Brotchie H (2010) Gender differences in depression. Int Rev Psychiatr (Abingdon, England) 22(5):429–436
Piek JP, Gasson N, Barrett N, Case I (2002) Limb and gender differences in the development of coordination in early infancy. Hum Mov Sci 21(5–6):621–639
Plum L, Schubert M, Bruning JC (2005) The role of insulin receptor signaling in the brain. Trends Endocrinol Metab 16(2):59–65
Popken GJ, Hodge RD, Ye P, Zhang J, Ng W, O’Kusky JR, D’Ercole AJ (2004) In vivo effects of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on prenatal and early postnatal development of the central nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 19(8):2056–2068
Raz N, Dupuis JH, Briggs SD, McGavran C, Acker JD (1998) Differential effects of age and sex on the cerebellar hemispheres and the vermis: a prospective MR study. Am J Neuroradiol 19:65–71
Raz N, Gunning-Dixon F, Head D, Williamson A, Acker JD (2001) Age and sex differences in the cerebellum and the ventral pons: a prospective MR study of healthy adults. Am J Neuroradiol 22:1161–1167
Reagan LP (2007) Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7(6):633–637
Rucklidge JJ (2010) The Gender differences in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am 33(2):357–373
Russo VC, Gluckman PD, Feldman EL, Werther GA (2005) The insulin-like growth factor system and its pleiotropic functions in brain. Endocr Rev 26(7):916–943
Schmahmann JD, Caplan D (2006) Cognition, emotion and the cerebellum. Brain Res 129:290–292
Schmahmann JD, Sherman JC (1998) The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain Res 121:561–579
Schmahmann JD, Loeber RT, Marjani J, Hurwitz AS (1998) Topographic organization of cognitive function in the human cerebellum. A meta-analysis of functional imaging studies. NeuroImage 7:S721
Schutter DJ, van Honk J (2006) An electrophysiological link between the cerebellum, cognition and emotion: frontal theta EEG activity to single-pulse cerebellar TMS. Neuroimage 33:1227–1231
Smeyne RJ, Chu T, Lewin A, Bian F, S-Crisman S, Kunsch C, Lira SA, Oberdick J (1995) Local control of granule cell generation by cerebellar Purkinje cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 6:230–251
Swinny JD, van der Want JJL, Gramsbergen A (2005) Cerebellar development and plasticity: perspectives for motor coordination strategies, for motor skills, and for therapy. Neural Plasticity 12(2–3):153
Szeszko PR, Gunning-Dixon F, Ashtari M, Snyder PJ, Lieberman JA, Bilder RM (2003) Reversed cerebellar asymmetry in men with first-episode schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatr 53:450–459
Tavano A, Grasso R, Gagliardi C, Triulzi F, Bresolin N, Fabbro F (2007) Disorders of cognitive and affective development in cerebellar malformations. Brain 130:2646–2660
Touwen B (1976) Neurological development in infancy. Spastics International Medical Publications, London
Turner BM, Paradiso S, Marvel CL, Pierson R, Boles Ponto LL, Hichwa RD (2007) The cerebellum and emotional experience. Neuropsychol 45:1331–1341
Wang YW, Zoghibi HY (2001) Genetic regulation of cerebellar development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:484–491
Wechsler-Reya RJ, Scott MP (1999) Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by Sonic hedgehog. Neuron 22:103–114
Werther GA, Abate M, Hogg A, Cheesman H, Oldfield B, Hards D, Hudson P, Power B, Freed K, Herington AC (1990) Localization of insulin-like growth factor-I mRNA in rat brain by in situ hybridization–relationship to IGF-I receptors. Mol Endocrinol 4:773–778
Zhao WQ, Alkon DL (2001) Role of insulin and insulin receptor in learning and memory. Mol Cell Endocrinol 177(1–2):125–134
Zhao W, Chen H, Xu H, Moore E, Meiri N, Quon MJ, Alkon DL (1999) Brain insulin receptors and spatial memory. Correlated changes in gene expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and signaling molecules in the hippocampus of water maze trained rats. J Biol Chem 274(49):34893–34902
Zhao WQ, Chen H, Quon MJ, Alkon DL (2004) Insulin and the insulin receptor in experimental models of learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 490(1–3):71–81
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS) grant (No. 88631).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghir, H., Rezaee, AAR., Nomani, H. et al. Sexual Dimorphism in Expression of Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptors in Developing Rat Cerebellum. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 369–377 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9903-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-012-9903-6