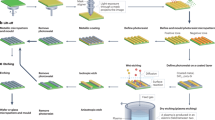
Abstract
In recent years, micropatterning techniques have gained increasing popularity from a broad range of engineering and biology communities for the promise to establish highly quantitative investigations on miniature biological objects (e.g., cells and bacteria) with spatially defined microenvironments. However, majority of the existing techniques rely on cleanroom-based microfabrication and cannot be easily extended to a regular biological laboratory. In this paper, we present a simple versatile printing-based method, referred to as Print-to-Print (P2P), to form multi-object micropatterns for potential biological applications, along with our recent efforts to deliver out-of-cleanroom microfabrication solutions to the general public (Zhao et al. 2009), (Xing et al. 2011), (Wang et al. 2009), (Pan and Wang 2011), (Zhao et al. 2011). The P2P method employs only a commercially available solid-phase printer and custom-made superhydrophobic films. The entire patterning process does not involve any thermal or chemical treatment. Moreover, the non-contact nature of droplet transferring and printing steps can be highly advantageous for sensitive biological uses. Using the P2P process, a minimal feature resolution of 229 ± 17 μm has been successfully demonstrated. In addition, this approach has been applied to form biological micropatterning on various substrates as well as multi-object co-patterns on the commonly used surfaces. Finally, the reusability of superhydrophobic substrates has also been illustrated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Zhao, H. Cong, T. Pan, Lab Chip 9, 1128–1132 (2009)
S. Xing, R.S. Harake, T. Pan, Lab Chip 11, 3642–3648 (2011)
W. Wang, S. Zhao, T. Pan, Lab Chip 9, 1133–1137 (2009)
T. Pan, W. Wang, Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39, 600–620 (2011)
S. Zhao, A. Chen, A. Revzin, T. Pan, Lab Chip 11, 224–230 (2011)
S.H. Lee, J.J. Moon, J.L. West, Biomaterials 29, 2962–2968 (2008)
E. Gottwald, S. Giselbrecht, C. Augspurger, B. Lahni, N. Dambrowsky, R. Truckenmuller, V. Piotter, T. Gietzelt, O. Wendt, W. Pfleging, A. Welle, A. Rolletschek, A.M. Wobus, K.F. Weibezahn, Lab Chip 7, 777–785 (2007)
A. Khademhosseini, L. Ferreira, J. Blumling, J. Yeh, J.M. Karp, J. Fukuda, R. Langer, Biomaterials 27, 5968–5977 (2006)
B. Dykstra, J. Ramunas, D. Kent, L. McCaffrey, E. Szumsky, L. Kelly, K. Farn, A. Blaylock, C. Eaves, E. Jervis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 8185–8190 (2006)
R. McBeath, D.M. Pirone, C.M. Nelson, K. Bhadriraju, C.S. Chen, Dev. Cell 6, 483–495 (2004)
Y. Lu, W. Shi, L. Jiang, J. Qin, B. Lin, Electrophoresis 30, 1497–1500 (2009)
E. Carrilho, A.W. Martinez, G.M. Whitesides, Anal. Chem. 81, 7091–7095 (2009)
E.E. Hui, S.N. Bhatia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 5722–5726 (2007)
H. Zhu, G. Stybayeva, M. Macal, E. Ramanculov, M.D. George, S. Dandekar, A. Revzin, Lab Chip 8, 2197–2205 (2008)
M.P. Lutolf, R. Doyonnas, K. Havenstrite, K. Koleckar, H.M. Blau, Integr. Biol. (Camb) 1, 59–69 (2009)
D.M. Pirone, C.S. Chen, J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 9, 405–417 (2004)
B.D. Martin, B.P. Gaber, C.H. Patterson, D.C. Turner, Langmuir 14, 3971–3975 (1998)
S.C. Lin, F.G. Tseng, H.M. Huang, Y.-F. Chen, Y.C. Tsai, C.E. Ho, C.C. Chieng, Sensors and Actuators B: Chem. 99, 174–185 (2004)
L. Libioulle, A. Bietsch, H. Schmid, B. Michel, E. Delamarche, Langmuir 15, 300–304 (1998)
E. Delamarche, A. Bernard, H. Schmid, B. Michel, H. Biebuyck, Science 276, 779–781 (1997)
E. Delamarche, A. Bernard, H. Schmid, A. Bietsch, B. Michel, H. Biebuyck, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 500–508 (1998)
S. Takayama, J.C. McDonald, E. Ostuni, M.N. Liang, P.J.A. Kenis, R.F. Ismagilov, G.M. Whitesides, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 5545–5548 (1999)
I. Barbulovic-Nad, M. Lucente, Y. Sun, M. Zhang, A.R. Wheeler, M. Bussmann, Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 26, 237–259 (2006)
L. Hong, T. Pan, Microfluidics. Nanofluidics. 10, 991–997 (2011)
L. Hong, T. Pan, Lab Chip 10, 3271–3276 (2010)
L. Hong, T. Pan, J. Microelectromech, S. 19, 246–253 (2010)
B. Nie, S. Xing, J.D. Brandt, T. Pan, Lab Chip 12, 1110–1118 (2012)
J.B. Segur, H.E. Oberstar, Ind. Eng. Chem. 43, 2117–2120 (1951)
CR. Handbook of Chmeistry and Physics, 92nd edn, edited by W.M. Haynes (CR. Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2009).
Y. Ding, L. Hong, B. Nie, K.S. Lam, T. Pan, Lab Chip 11, 1464–1469 (2011)
H. Cong, A. Revzin, T. Pan, Nanotechnology 20, 075307 (2009)
P. G. Gennes, F. Brochard-Wyart and D. Quéré, Capillarity and wetting phenomena: drops, bubbles, pearls, waves, Springer, 2004.
T.-Y. Chen, J.A. Tsamopoulos, R.J. Good, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 151, 49–69 (1992)
L. Vagharchakian, F. Restagno, L. Léger, J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 3769–3775 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work is in part supported by the National Science Foundation CAREER Program (ECCS-0846502). The authors would like to thank Yuzhe Ding for valuable discussion on capillary printing and Arnold Chen’s help for taking pictures. SX would like to acknowledge the financial support from China Scholarship Council (CSC) and Center for Information Technology Research in the Interest of Society (CITRIS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, S., Zhao, S. & Pan, T. Print-to-print: a facile multi-object micro-patterning technique. Biomed Microdevices 15, 233–240 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9723-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9723-y