Abstract
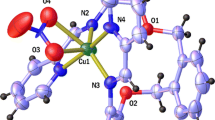
Alkaline-earth metal complexes of the monoanionic form of the polyether ionophore monensin A were isolated for the first time in solid state and were structurally characterized using various spectroscopic methods (IR, NMR, FAB-MS). The stoichiometric reaction of monensic acid (MonH) with M2+ (M = Mg, Ca) in the presence of an organic base leads to the formation of mononuclear complexes of composition [M(Mon)2(H2O)2]. The structures of magnesium (1) and calcium (2) monensin complexes in the solid state were established by single crystal X-ray crystallography. The complexes crystallize as [Mg(Mon)2(H2O)2]·5MeCN (1) and [Ca(Mon)2(H2O)2]·H2O·5MeCN (2) in the monoclinic P21 space group. The alkaline-earth metal ion is placed in a distorted octahedral environment, defined by two monensin anions acting as bidentate ligands in the equatorial plane of the complex as well as by two water molecules occupying the axial positions of the inner coordination sphere. The bactericidal activity of 1 and 2 was evaluated against aerobic Gram-positive microorganisms applying the double layer agar hole diffusion method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agtarap A, Chamberlin JW, Pinkerton M, Steinrauf LK (1967) The structure of monensic acid, a new biologically active compound. J Am Chem Soc 89:5737–5739
Ajaz AA, Robinson JA, Turner DL (1987) Biosynthesis of the polyether ionophore antibiotic monensin A: assignment of the carbon-13 and proton n. m. r. spectra of monensin A by two-dimensional spectroscopy. Incorporation of oxygen-18 labeled molecular oxygen. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1:27–36
Andrews JM (2001) Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J Antimicrob Chemother 48:5–16
Augustine PC, Smith CK, Danforth HD, Ruff MD (1987) Effect of ionophorous anticoccidials on invasion and development of Eimeria: comparison of sensitive and resistant isolates and correlation with drug uptake. Poultry Sci 66:960–965
Augustine PC, Watkins KL, Danforth HD (1992) Effect of monensin on ultrastructure and cellular invasion by the turkey coccidia Eimeria adenoeides and Eimeria meleagrimitis. Poultry Sci 71:970–978
Berg HH, Hamill RL (1978) The isolation and characterization of narazin, a new polyether antibiotic. J Antibiot 31:1–6
Briggs RW, Hinton JF (1978) Thallium-205 and proton nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the complexation of thallium by the ionophores monensin and nigericin. Biochemistry 17:5576–5578
Chamberlin JW, Agtarap A (1970) Observations on the mass spectrometry of monensin and related compounds. Org Mass Spectrom 3:271–285
Chappe LR (1979) The site of action of the anticoccidial salinomycin (Coxistac). J Parasitol 65:137–143
Cox BG, Vantruong N, Rzeszotarska J, Schneider H (1984) Rates and equilibria of alkali metal and silver ion complex formation with monensin in ethanol. J Am Chem Soc 106:5965–5969
Dassie SA, Baruzzi AM (2002) Alkaline-earth cation transfer assisted by monensin across the water vertical bar 1,2-dichloroethane interface in the presence of alkali cations. J Electroanal Chem 522:158–166
Dorkov P, Pantcheva IN, Sheldrick WS, Mayer-Figge H, Petrova R, Mitewa M (2008) Synthesis, structure and antimicrobial activity of manganese(II) and cobalt(II) complexes of the polyether ionophore antibiotic sodium monensin A. J Inorg Biochem 102:26–32
Duax WL, Smith GD, Strong PD (1980) Complexation of metal ions by monensin—crystal and molecular structure of hydrated and anhydrous crystal forms of sodium monensin. J Am Chem Soc 102:6725–6729
Folz SD, Lee BL, Nowakowski LH, Conder GA (1988) Anticoccidial evaluation of halofuginone, lasalocid, maduramicin, monensin and salinomycin. Vet Parasitol 28:1–9
Garcla-Rosas J, Schneider H, Cox BG (1983) Silver complexation by the ionophorous antibiotic monensin in nonaqueous solvents. J Phys Chem 87:5467–5472
Gertenbach PG, Popov AI (1975) Solution chemistry of monensin and its alkali-metal ion complexes—potentiometric and spectroscopic studies. J Am Chem Soc 97:4738–4744
Hamidinia SA, Shimelis OI, Tan B, Erdahl WL, Chapman CJ, Renkes GD, Taylor RW, Pfeiffer DR (2002) Monensin mediates a rapid and selective transport of Pb2+—possible application of monensin for the treatment of Pb2+ intoxication. J Biol Chem 277:38111–38120
Hamidinia SA, Tan B, Erdahl WL, Chapman CJ, Taylor RW, Pfeiffer DR (2004) The ionophore nigericin transports Pb2+ with high activity and selectivity: a comparison to monensin and ionomycin. Biochemistry 43:15956–15965
Hebrant M, Mimouni M, Tissier M, Pointud Y, Juillard J, Dauphin G (1992) Complexing ability of ionophore monensin for divalent cations. New J Chem 16:999–1008
Huczynski A, Michalak D, Przybylski P, Brzezinski B, Bartl F (2006a) Monensin A benzyl ester and its complexes with monovalent metal cations studied by spectroscopic, mass spectrometry and semiempirical methods. J Mol Struct 797:99–110
Huczynski A, Przybylski P, Brzezinski B (2006b) Complexes of monensin A methyl ester with Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ cations studied by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and PM5 semiempirical method. J Mol Struct 788:176–183
Huczynski A, Przybylski P, Brzezinski B, Bartl F (2006c) Monensin A methyl ester complexes with Li+, Na+ and K+ cations studied by ESI–MS, 1H- and 13C-NMR, FTIR, as well as PM5 semiempirical method. Biopolymers 81:282–294
Huczynski A, Przybylski P, Brzezinski B, Bartl F (2006d) Spectroscopic, mass spectrometry, and semiempirical investigation of a new ester of monensin A with ethylene glycol and its complexes with monovalent metal cations. Biopolymers 82:491–503
Huczynski A, Przybylski P, Brzezinski B (2007a) NMR, FTIR, ESI–MS and semiempirical study of a new 2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl ester of monensin A and its complexes with alkali metal cations. Tetrahedron 63:8831–8839
Huczynski A, Przybylski P, Schroeder G, Brzezinski B (2007b) Investigation of complex structures of a new 2-hydroxyethyl ester of monensin A with Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ cations using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and semiempirical PM5 methods. J Mol Struct 829:111–119
Huczynski A, Ratajczak-Sitarz M, Katrusiak A, Brzezinski B (2007c) Molecular structure of the 1:1 inclusion complex of monensin A lithium salt with acetonitrile. J Mol Struct 871:92–97
Huczynski A, Brzezinski B, Bartl F (2008a) Structures of complexes of benzyl and allyl esters of monensin A with Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+ cations studied by ESI–MS and PM5 methods. J Mol Struct 886:9–16
Huczynski A, Lowicki D, Brzezinski B, Bartl F (2008b) Spectroscopic, mass spectrometry and semiempirical investigation of a new 2-methoxyethyl ester of monensin A and its complexes with Li+, Na+ and K+ cations. J Mol Struct 874:89–100
Huczynski A, Lowicki D, Brzezinski B, Bartl F (2008c) Spectroscopic, mass spectrometry, and semiempirical investigations of a new 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl ester of monensin A and its complexes with monovalent cations. J Mol Struct 879:14–24
Huczynski A, Ratajczak-Sitarz M, Katrusiak A, Brzezinski B (2008d) Molecular structure of rubidium six-coordinated dihydrate complex with monensin A. J Mol Struct 888:224–229
Johnson SM, Herrin J, Liu SJ, Paul IC (1970a) Crystal structure of a barium complex of antibiotic X-537A, Ba(C34H53O8)2·H2O. J Chem Soc D Chem Commun 2:72–73
Johnson SM, Herrin J, Liu SJ, Paul IC (1970b) Crystal and molecular structure of the barium salt of an antibiotic containing a high proportion of oxygen. J Am Chem Soc 92:4428–4435
Kevin DA II, Meujo DAF, Hamann MT (2009) Polyether ionophores: broad-spectrum and promising biologically active molecules for the control of drug resistant bacteria and parasites. Expert Opin Drug Discov 4:109–146
Koinarski V, Sherkov SN (1987) Effect of anticoccidial preparations in the prevention of coccidiosis in turkeys caused by Eimeria adenoides. Vet Med Nauki 24:81–85
Liu WC, Slusarchyk DS, Astle G, Trejo WH, Brown NE, Meyers E (1978) Ionomycin, a new polyether antibiotic. J Antibiot 9:815–819
Long PL, Jeffers TK (1982) Studies on the stage of action of ionophorous antibiotics against Eimeria. J Parasitol 68:363–371
Lutz WK, Winkler FK, Dunitz JD (1971) Crystal structure of the antibiotic monensin: similarities and differences between free acid and metal complex. Helv Chim Acta 54:1103–1108
Martinek T, Riddell FG, Wilson C, Weller CT (2000) The conformations of monensin A metal complexes in solution determined by NMR spectroscopy. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2:35–41
Mimouni M, Pointud Y, Juillard J (1994) Interactions in methanol of divalent metal cations with bacterial ionophores, lasalocid and monensin—thermodynamical aspects. Bull Soc Chim Fr 131:58–65
Mimouni M, Hebrant M, Dauphin G, Juillard J (1996) Monovalent cation salts of the bacterial ionophore monensin in methanol. Structural aspects from NMR experiments. J Chem Res 6:278–279
Pangborn W, Duax WL, Langs D (1987) The hydrated potassium complex of the ionophore monensin A. J Am Chem Soc 109:2163–2165
Pantcheva IN, Mitewa M, Sheldrick WS, Oppel IM, Zhorova R, Dorkov P (2008) First divalent metal complexes of the polyether ionophore monensin A: X-ray structures of [Co(Mon)2(H2O)2] and [Mn(Mon)2(H2O)2] and their bactericidal properties. Curr Drug Discov Technol 5:154–161
Pantcheva IN, Dorkov P, Atanasov VN, Mitewa M, Shivachev BL, Nikolova RP, Mayer-Figge H, Sheldrick WS (2009) Crystal structure and properties of the copper(II) complex of sodium monensin A. J Inorg Biochem. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2009.08.007
Paz FAA, Gates PJ, Fowler S, Gallimore A, Harvey B, Lopes NP, Stark CBW, Staunton J, Klinowski J, Spencer JB (2003) Sodium monensin dihydrate. Acta Cryst E59:m1050–m1052
Riddell FG (2002) Structure, conformation, and mechanism in the membrane transport of alkali metal ions by ionophoric antibiotics. Chirality 14:121–125
Rzeszotarska J, Wagner-Czauderna E, Kalinowski MK (1994) Complexation of Tl+ ions by monensin anion in binary mixtures of dipolar aprotic solvents. J Chem Res 10:400–401
Sheldrick G (1990) SHELXS-97. Program for crystal structure solution. Institut für Anorganische Chemie der Universität, Göttingen, Germany
Sheldrick G (1997) SHELXL-97. Program for crystal structure refinement. Institut für Anorganische Chemie der Universität, Göttingen, Germany
Stern PH (1977) Ionophores: chemistry, physiology and potential applications to bone biology. Clin Orthop Relat Res 122:273–298
Stiles MK, Craig ME, Gunnel SL, Pfeiffer DR, Taylor DR (1991) The formation constants of ionomycin with divalent cations in 80% methanol/water. J Biol Chem 266:8336–8342
Varga I, Sreter T (1996) Efficacy of a monensin-duokvin combination against Eimeria acervulina in chickens. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 43:153–155
Volmer DA, Lock CM (1998) Electrospray ionization and collision-induced dissociation of antibiotic polyether ionophores. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 12:157–164
Wagner-Czauderna E, Rzeszotarska J, Orlowska E, Kalinowski MK (1997) Complexing ability of monensin anion for alkali metal cations in binary mixtures of dipolar aprotic solvents. Phys Chem Chem Phys 101:1154–1157
Walba DM, Hermsmeier M, Haltiwanger RC, Noordik JH (1986) Crystal structures of monensin B lithium and silver salts. J Org Chem 51:245–247
Wang Z, Suo X, Xia X, Shen J (2006) Influence of monensin on cation influx and Na+ -K+ -ATPase activity of Eimeria tenella sporozoites in vitro. J Parasitol 92:1092–1096
Westley JW, Liu CM, Evans RHJr, Sello LH, Troupe N, Hermann T (1983) Preparation, properties and biological activity of natural and semisynthetic urethanes of monensin. J Antibiot 36:1195–1200
Yildirim SO, McKee V, Khardli FZ, Mimouni M, Hadda TB (2007) Rubidium(I) monensinate dihydrate. Acta Cryst E64:m154–m155
Acknowledgements
The present research is financially supported from the National Science Fund (NSF), DO-02-84/2009. SS is grateful to NSF (UNA-17/2005) for the purchase of Bruker Avance AVII+ 600 NMR spectrometer. The authors are thankful to Assoc. Prof. A. Nakov and MSci P. Dorkov (BIOVET Ltd.) for supplying sodium monensin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pantcheva, I.N., Zhorova, R., Mitewa, M. et al. First solid state alkaline-earth complexes of monensic acid A (MonH): crystal structure of [M(Mon)2(H2O)2] (M = Mg, Ca), spectral properties and cytotoxicity against aerobic Gram-positive bacteria. Biometals 23, 59–70 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9269-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-009-9269-5