Abstract
Objectives
To identify and characterize a novel antimicrobial peptide, catesbeianin-1.
Results
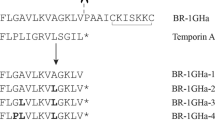
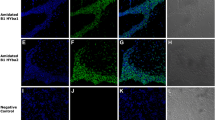
Catesbeianin-1 is 25 amino acids long and is α-helical, cationic and amphipathic. It had antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It was resistant against trypsin and pepsin. Catesbeianin-1 exhibited moderate hemolytic activity (approx 8%) at 100 μg/ml, and its HC50 (50% hemolytic concentration) was 300 μg/ml. Its cytotoxicity was approx 10–20% at 100 μg/ml, and its CC50 (50% cytotoxic concentration) was >100 μg/ml. The LD50 of catesbeianin-1 in mice was 80 mg/kg. At 3.1 µg/ml, catesbeianin-1 significantly inhibited the growth of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Conclusions
A new antimicrobial peptide from the skin of Lithobates catesbeianus (American bullfrog) may represent a template for the development of novel antimicrobial agents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker MA, Maloy WL, Zasloff M, Jacob LS (1993) Anticancer efficacy of Magainin2 and analogue peptides. Cancer Res 53:3052–3057
Banerjee TK (1993) Estimation of acute toxicity of ammonium sulphate to the fresh water catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis I. Analysis of LC50 values determined by various methods. Biomed Environ Sci 6:31–36
Dang XL, Tian JH, Yang WY, Wang WX, Ishibashi J, Asaoka A, Yi HY, Li YF, Cao Y, Yamakawa M, Wen SY (2009) Bactrocerin-1: a novel inducible antimicrobial peptide from pupae of oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 71:117–129
Fitton JE, Dell A, Shaw WV (1980) The amino acid sequence of the delta haemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett 115:209–212
Goraya J, Knoop FC, Conlon JM (1998) Ranatuerins: antimicrobial peptides isolated from the skin of the American bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 250:589–592
Halverson T, Basir YJ, Knoop FC, Conlon JM (2000) Purification and characterization of antimicrobial peptides from the skin of the North American green frog Rana clamitans. Peptides 21:469–476
Larrick JW, Hirata M, Shimomoura Y, Yoshida M, Zheng H, Zhong J, Wright SC (1993) Antimicrobial activity of rabbit CAP18-derived peptides. Antimicrob Ag Chemother 37:2534–2539
Li Z, Xu X, Meng L, Zhang Q, Cao L, Li W, Wu Y, Cao Z (2014) Hp1404, a new antimicrobial peptide from the scorpion Heterometrus petersii. PLoS ONE 9:1–9
Ling G, Gao J, Zhang S, Xie Z, Wei L, Yu H, Wang Y (2014) Cathelicidins from the bullfrog Rana catesbeiana provides novel template for peptide antibiotic design. PLoS ONE 9:e93216
Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, Daum RS, Fridkin SK, Gorwitz RJ, Kaplan SL, Karchmer AW, Levine DP, Murray BE, Rybak MJ, Talan DA, Chambers HF (2011) Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of america for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children: executive summary. Clin Infect Dis 52:285–292
Liu WP, Chen YH, Ming X, Kong Y (2015) Design and synthesis of a novel cationic peptide with potent and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Biomed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2015/578764
Mygind PH, Fischer RL, Schnorr KM, Hansen MT, Sonksen CP, Ludvigsen S, Raventos D, Buskov S, Christensen B, De Maria L, Taboureau O, Yaver D, Elvig-Jorgensen SG, Sorensen MV, Christensen BE, Kjaerulff S, Frimodt-Moller N, Lehrer RI, Zasloff M, Kristensen HH (2005) Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 437:975–980
Nguyen LT, Haney EF, Vogel HJ (2011) The expanding scope of antimicrobial peptide structures and their modes of action. Trends Biotechnol 29:464–472
Park S, Park SH, Ahn HC, Kim S, Kim SS, Lee BJ, Lee BJ (2001) Structural study of novel antimicrobial peptides, nigrocins, isolated from Rana nigromaculata. FEBS Lett 507:95–100
Wakabayashi H, Hiratani T, Uchida K, Yamaguchi H (1996) Antifungal spectrum and fungicidal mechanism of an N-terminal peptide of bovine lactoferrin. J Infect Chemother 1:185–189
Wei L, Gao J, Zhang S, Wu S, Xie Z, Ling G, Kuang YQ, Yang Y, Yu H, Wang Y (2015) Identification and characterization of the first cathelicidin from sea snakes with potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity and special mechanism. J Biol Chem 290:16633–16652
Wiesner J, Vilcinskas A (2010) Antimicrobial peptides: the ancient arm of the human immune system. Virulence 1:440–464
Zeng XC, Wang SX, Zhu Y, Zhu SY, Li WX (2004) Identification and functional characterization of novel scorpion venom peptides with no disulfide bridge from Buthus martensii Karsch. Peptides 25:143–150
Zeng XC, Zhou L, Shi W, Luo X, Zhang L, Nie Y, Wang J, Wu S, Cao B, Cao H (2013) Three new antimicrobial peptides from the scorpion Pandinus imperator. Peptides 45:28–34
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Meiye Li, Li Liu, Fengguang Pan and Yan Zhang for generously providing the necessary experimental equipment. This research was supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of China (20130061130001).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Strains of bacteria used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Zhang, Y., Feng, X. et al. Catesbeianin-1, a novel antimicrobial peptide isolated from the skin of Lithobates catesbeianus (American bullfrog). Biotechnol Lett 39, 897–903 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2312-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2312-7