Abstract
Objectives
To identify novel pullulanases from microorganisms and to investigate their biochemical characterizations.
Results
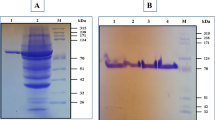
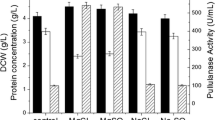
A novel pullulanase gene (BmPul) from Bacillus megaterium WW1210 was cloned and heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli. The gene has an ORF of 2814 bp encoding 937 amino acids. The recombinant pullulanase (BmPul) was purified to homogeneity and biochemically characterized. BmPul has an MW of approx. 112 kDa as indicated by SDS-PAGE. Optimum conditions were at 55 °C and pH 6.5. The enzyme was stable below 40 °C and from pH 6.5−8.5. The Km values of BmPul towards pullulan and amylopectin were 3.3 and 3.6 mg/ml, respectively. BmPul hydrolyzed pullulan to yield mainly maltotriose, indicating that it should be a type I pullulanase.
Conclusions
A novel type I pullulanase from Bacillus megaterium was identified, heterologously expressed and biochemically characterized. Its properties makes this enzyme as a good candidate for the food industry.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashwar BA, Gani A, Wani IA, Shaha A, Masoodia FA, Saxena DC (2016) Production of resistant starch from rice by dual autoclaving-retrogradation treatment: in vitro digestibility, thermal and structural characterization. Food Hydrocoll 56:108–117
Ayadi DZ, Ali MB, Jemli S, Mabrouk SB, Mezghani M, Messaoud EB, Bejar S (2008) Heterologous expression, secretion and characterization of the Geobacillus thermoleovorans US105 type I pullulanase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:473–481
Chen WB, Nie Y, Xu Y (2013) Signal peptide-independent secretory expression and characterization of pullulanase from a newly isolated Klebsiella variicola SHN-1 in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:41–54
Elleuche S, Qoura FM, Lorenz U, Rehn T, Brück T, Antranikian G (2015) Cloning, expression and characterization of the recombinant cold-active type-I pullulanase from Shewanella arctica. J Mol Catal B Enzym 116:70–77
Hatada YJ, Masuda N, Akita M (2006) Oxidatively stable maltopentaose-producing α-amylase from a deep-sea Bacillus, isolate, and mechanism of its oxidative stability validated by site-directed mutagenesis. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:1333–1340
Hii SL, Tan JS, Ling TC, Ariff AB (2012) Pullulanase: role in starch hydrolysis and potential industrial applications. Enzyme Res 1:921362
Kang JH, Park KM, Choi KH, Park CS, Kim GE, Kim D, Cha J (2011) Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a heat-stable type I pullulanase from Thermotoga neapolitana. Enzyme Microb Technol 48:260–266
Kunamneni A, Singh S (2006) Improved high thermal stability of pullulanase from a newly isolated thermophilic Bacillus sp. AN-7. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:1399–1404
Li MR, Wang XB, Huang Y, Huang JL, Liang JY, Huang RL, Du QL, Wei YT (2012a) Gene expression and characterisation of three pullulanases from Bacillus cereus GXBC-3. Chin J Biotechnol 28:466–475
Li YR, Zhang L, Niu DD, Wang ZX, Shi G (2012b) Cloning, expression, characterization, and biocatalytic investigation of a novel bacilli thermostable type I pullulanase from Bacillus sp. CICIM 263. J Agric Food Chem 60:11164–11172
Liu JJ, Liu Y, Yan F, Jiang ZQ, Yang SQ, Yan QJ (2016) Gene cloning, functional expression and characterisation of a novel type I pullulanase from Paenibacillus barengoltzii and its application in resistant starch production. Protein Expr Purif 172:1562–1568
Nie Y, Yan W, Xu Y, Chen WB, Mu XQ, Wang XY, Xiao R (2013) High-level expression of Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase from recombinant Escherichia coli with auto-induction: effect of Iac operator. PLoS ONE 8:e78416
Song W, Nie Y, Mu XQ, Xu Y (2016) Enhancement of extracellular expression of Bacillus naganoensis pullulanase from recombinant Bacillus subtilis: effects of promoter and host. Protein Expr Purif 124:23–31
Wasko A, Polak-Berecka M, Targonski Z (2011) Purification and characterization of pullulanase from Lactococcus lactis. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 41:252–261
Wei W, Ma J, Guo S, Wei DZ (2014) A type I pullulanase of Bacillus cereus Nws-bc5 screening from stinky tofu brine: functional expression in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis and enzyme characterization. Proc Biochem 49:1893–1902
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 31325021) and the Program for Changjiang Scholars (No. T2014055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Yan, Q., Bao, Q. et al. Expression and biochemical characterization of a novel type I pullulanase from Bacillus megaterium . Biotechnol Lett 39, 397–405 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2255-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2255-4