Abstract
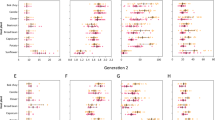
The efficiency of the biological control strategies based on parasitoids, either as a release or a conservative measure, depends on the timely arrival or release of the parasitoids after colonization of the field by the pest. In this study, the effects of the delay between the cabbage aphid Brevicoryne brassicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) infestation and the release of its parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and of the number of parasitoid releases on aphid population dynamics and host plant growth were investigated. When the parasitoids were released at the start of the infestation, 89.6 % of the aphids were parasitized one month later, and the damage to cabbage was low. The identical number of parasitoids released two weeks after the start of the infestation partially controlled the aphid population, but the growth of the cabbage was altered. The earliest introduction of the parasitoid to the crop led to an efficient host regulation, and the release in three times rather than in one time did not improve the control efficiency at this release delay. The implications for biological control strategies that use parasitoids of aphids are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askew RR, Shaw MR (1986) Parasitoid communities: their size, structure and development. In: Waage JK, Greathead DJ (eds) Insect parasitoids. Academic Press, London, UK, pp 225–264
Bahana J, Karhioc GK (1986) The role of Diaeretiella rapae in population control of cabbage aphid. J Insect Sc 7:605–607
Bernal J, Gonzalez D (1997) Reproduction of Diaeretiella rapae on Russian wheat aphid hosts at different temperatures. Entomol Exp Appl 82:159–166
Bianchi FJJA, Booij CJH, Tscharntke T (2006) Sustainable pest regulation in agricultural landscapes: a review on landscape composition, biodiversity and natural pest control. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 273:1715–1727
Bianchi FJJA, Schellhorn NA, van der Werf W (2009) Predicting the time to colonization of the parasitoid Diadegma semiclausum: the importance of the shape of spatial dispersal kernels for biological control. Biol Control 50:267–274
Blackman RL and Eastop VF (2000) Aphids of the world’s crop: an identification and information guide, 2nd edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, UK
Bradburne RP, Mithen R (2000) Glucosinolate genetics and the attraction of the aphid parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae to Brassica. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 267:89–95
Ceron-Hernandez OJ, Salguero V (1995) Population fluctuation of aphid species (Aphididae: Hom.) and their distribution on brocoli plants (Brassica oleracea var. italica). Manejero integrado de plagas, Costa Rica 37:21–25
Chang GC, Kareiva P (1999) The case for indigenous generalists in biological control. In: Hawkins BA, Cornell HV (eds) Theoretical approaches to biological control. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 103–115
Chaplin-Kramer R, O’Rourke E, Blitzer EJ, Kremen C (2011) A meta-analysis of crop pest and natural enemy response to landscape complexity. Ecol Lett 14:922–932
Chua TH (1977) Population studies of Brevicoryne brassicae (L.), its parasites and hyperparasites in England. Res Popul Ecol 19:125–139
Chua TH (1979) A comparative study of the searching efficiencies of a parasite and a hyperparasite. Res Popul Ecol 20:179–187
Cividanes FJ, Santos DMM (2003) Population fluctuation and vertical (within plant) distribution of Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on kale. Bragantia 62:61–67
Dennis P, Thomas MB, Sotherton NW (1994) Structural features of field boundaries which influence the overwintering densities of beneficial arthropods predators. J Appl Ecol 31:361–370
Dhiman SC, Goel SC (2006) Diaeretiella rapae (M’Intosh) (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) a potential biocontrol agent of mustard aphid Lipaphis erysimi (Kalt.) In: Goel SC (ed) Advances in indian entomology: productivity and health. A silver jubilee, Supplement No. 3, Volume II; Insect and Environment. Uttar Pradesh Zoological Society, Muzaffarnagar, India, pp 101–109
Doutt RL, DeBach P (1964) Some biological control concepts and questions. In: DeBach P (ed) Biological control of insect pests and weeds. Chapman and Hall, London, UK, pp 118–142
Elzen GW, King EG (1999) Periodic release and manipulation of natural enemies. In: Bellows T, Fisher T (eds) Handbook of biological control: principles and application of biological control. Academic Press, San Diego, USA, pp 253–270
Fathipour Y, Hosseini A, Talebi AA, Moharramipour S (2006) Functional response and mutual interference of Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) on Brevicoryne brassicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Entomol Fenn 17:90–97
Fernandez-Arhex V, Corley JC (2003) The functional response of parasitoids and its implications for biological control. Biocontrol Sc Technol 13:403–413
Freuler J, Fischer S, Mittaz C (2001) Rôle des plantes relais pour renforcer l’action de Diaeretiella rapae, principal parasitoïde du puceron cendré du chou. Revue Suisse Vitic Arboric Hortic 33:329–335
Gabrys B, Gadomski H, Sobota G, Halarewicz-Pacan A (1998) Reduction of the cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae (L.), population by Diaeretiella rapae (M’Intosh) on oilseed rape, white mustard, and Brassica vegetables. IOBC/WPRS Bull 21:197–203
Gadomski H (1994) The effectiveness of Diaeretiella rapae (McIntosh) in the reduction of the cabbage aphid Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) on cruciferous crops. Aphids and other homopterous insects. PAS, Skierniewice 4:41–46
Geiger F, Bianchi FJJA, Wäckers FL (2005) Winter ecology of the cabbage aphid Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) (Homo., Aphididae) and its parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (McIntosh) (Hym., Braconidae: Aphidiidae). J Appl Entomol 129:563–566
Godfray HCJ (1994) Parasitoids: behavioral and evolutionary ecology. Godfrat HCJ (ed). Princeton University Press, Princeton, USA, 484 pp
Godfray HJC, Hassell MP, Holt RD (1994) The population dynamic consequences of phenological asynchrony between parasitoids and their hosts. J Anim Ecol 63:1–10
Gurr GM, Wratten SD, Altieri M (2004) Ecological engineering for pest management: Advances in habitat manipulation for arthropods. Gurr GM, Wratten SD, Altieri M (eds). CABI Publishing; Wallingford, UK, 232 pp
Hackett-Jones E, White A, Cobbold CA (2011) The evolution of developmental timing in natural enemy systems. J Theor Biol 275:1–11
Hafez M (1961) Seasonal fluctuations of population density of the cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae (L.), in the Netherlands, and the role of its parasite Aphidius (Diaeretiella) rapae (Curtis). Tijdschr Plantenziekten 67:445–548
Hassell MP (2000) The spatial and temporal dynamics of host-parasitoid interactions. Oxford series in Ecology and Evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Holling CS (1959) Some characteristics of simple type of predation and parasitism. Can Entomol 91:293–320
Hullé M, Turpeau-Ait Ighil E, Robert Y, Monnet Y (1999) Les pucerons des plantes maraîchères. Cycles biologiques et activités de, vol. INRA-Quae, Paris, France, p 136
Jervis MA, Heimpel GE, Ferns PN, Harvey JA, Kidd NA (2001) Life-history strategies in parasitoid wasps: a comparative analysis of ‘ovigeny’. J Anim Ecol 70:442–458
Jones WA, Greenberg SM, Legaspi B (1999) The effect of varying Bemisia argentifolii and Eretmocerus mundus ratios on parasitism. BioControl 44:13–28
Kant R, Sandanayaka WRM, He XZ, Wang Q (2008) Effect of host age on searching and oviposition behaviour of Diaeretiella rapae (M’Intosh) (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). N Z Plant Prot 61:355–361
Kant R, Minor M, Sandanayaka M, Trewick S (2013) Effects of mating and oviposition delay on parasitism rate and sex allocation behaviour of Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Biol Control 65:265–270
Landis DA, van Der Werf W (1997) Early-season predation impacts the establishment of aphids and spread of beet yellows virus in sugar beet. Entomophaga 42:499–516
Le Guigo P, Maingeneau A, Le Corff J (2012) Performance of an aphid Myzus persicae and its parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae on wild and cultivated Brassicae. J Plant Interact 7:326–332
Le Ralec A, Ribulé A, Barragan A, Outreman Y (2011) Host range limitation caused by incomplete host regulation in an aphid parasitoid. J Insect Physiol 57:363–371
Liang KY, Zeger SL (1986) Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika 73:13–22
Liu SS, Hommes M, Hildenhagen R (1994) Damage to white cabbage by the aphid Brevicoryne brassicae (L.): influence of aphid density and stage of plant growth. IOBC/WPRS Bull 17:75–89
Lopes C, Spataro T, Lapchin L, Arditi R (2009) Optimal release strategies for the biological control of aphids in melon greenhouses. Biol Control 48:12–21
Lopez ER, van Driesche RG, Elkinton JS (1990) Rates of parasitism by Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) for cabbage aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) in and outside of colonies: why do they differ? J Kansas Entomol Soc 63:158–165
McCullagh P, Nelder JA (1989) Generalized linear models. Second edition. Chapman and Hall, London, UK, 532 pp
Moayeri H, Madadi H, Pouraskari H, Enkegaard A (2013) Temperature dependant response of Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera:Aphidiidae) to the cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae (Hemiptera:Aphididae). Eur J Entomol 110:109–113
Murdoch WW, Nisbet RM, Blythe SP, Gurney WSC, Reeve JD (1987) An invulnerable age class and stability in delay-differential parasitoid-host models. Am Nat 129:263–282
Nemec V, Stary P (1984) Population diversity of Diaeretiella rapae (M’Int.) (Hym., Aphidiidae), an aphid parasitoid in agroecosystems. J Appl Entomol 97:223–233
Nieto DJ, Sheennan C, Settle WH, O’Malley R, Bros S, Honda JY (2006) How natural enemies and cabbage aphid (Brevicoryne brassicae L.) population dynamics affect organic broccoli harvest. Environ Entomol 35:94–101
Pfiffner L, Luka H (2000) Overwintering of arthropods in soils of arable fields and adjacent semi-natural habitats. Agric Ecosyst Environ 78:215–222
Pike KS, Stary P, Miller T, Allison D, Boydston L, Graf G (1999) Host range and habitats of the aphid parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera : Aphidiidae) in Washington State. Environ Entomol 28:61–71
Ponti L, Altieri MA, Gutierrez AP (2007) Effects of crop diversification levels and fertilization regimes on abundance of Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) and its parasitization by Diaeretiella rapae (M’Intosh) in broccoli. Agric For Entomol 9:209–214
Powell W, Nickless A (1996) The foraging efficiency of the parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (Hymeoptera: Braconidae) in relation to the spatial distribution of aphids on plants. In: Booij CJH, den Nijs LJMF (eds) Arthropod natural enemies in arable land. II Survival, reproduction and enhancement. Aarhus University Press, Aarhus, Denmark, pp 97–106
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Rauwald KS, Ives AR (2001) Biological control in disturbed agricultural systems and the rapid recovery of parasitoid populations. Ecol Appl 11:1224–1234
Rochat J (1997) Delayed effects in aphid-parasitoid systems: consequences for evaluating biological control species and their use in augmentation strategies. Entomophaga 42:201–213
Satar S, Kersting U, Ulusoy MR (2005) Temperature dependent life history traits of Brevicoryne brassicae (L.) (Hom., Aphididae) on white cabbage. Turk J Agric For 29:341–346
Shea K, Possingham HP (2000) Optimal release strategies for biological control agents: an application of stochastic dynamic programming to population management. J Appl Ecol 37:77–86
Snyder WE, Ives AR (2003) Interactions between specialist and generalist natural enemies: parasitoids, predators, and pea aphid biocontrol. Ecology 84:91–107
Souza BM, Bueno VHP, Paes Bueno VH (1992) Parasitoids and hyperparasitoids of mummies of Brevicoryne brassicae (Linneaus). Rev Agric Piracicaba 67:55–62
van Lenteren JC, Bakker K (1976) Functional responses in invertebrates. Neth J Zool 26:567–572
van Nouhuys S, Lei G (2004) Parasitoid-host metapopulation dynamics: the causes and consequences of phenological asynchrony. J Anim Ecol 73:526–535
Vaughn TT, Antolin MF (1998) Population genetics of an opportunistic parasitoid in an agricultural landscape. Heredity 80:152–162
Wiedenmann RN, Smith JW (1997) Attributes of natural enemies in ephemeral crop habitats. Biol Control 10:16–22
Wilson B, Lambdin L (1987) Suitability of Brevicoryne brassicae and Myzus persicae (Homoptera : Aphididae) as hosts of Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera : Aphidiidae). Entomol News 98:140–146
Wissinger SA (1997) Cyclic colonization in predictably ephemeral habitats: a template for biological control in annual crop systems. Biol Control 10:4–15
Zaki FN, Shaarawy MF, Farag NA (1999) Release of two predators and two parasitoids to control aphids and whiteflies. J Pest Sci 72:19–20
Zhang WQ, Hassan SA (2003) Use of the parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae (McIntoch) to control the cabbage aphid Brevicoryne brassicae (L.). J Appl Entomol 127:522–526
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stefano Colazza.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuville, S., Le Ralec, A., Outreman, Y. et al. The delay in arrival of the parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae influences the efficiency of cabbage aphid biological control. BioControl 61, 115–126 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-015-9702-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-015-9702-3