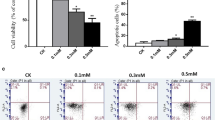
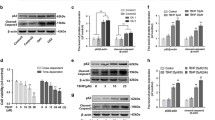
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the effect of AOPPs on apoptosis in human chondrocytes. Chondrocytes were treated with AOPPs. Cell death, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase activity, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and the expression of apoptotic proteins were detected in vitro. AOPPs levels were detected by colorimetric method. The results in vitro demonstrated that AOPPs induced cell death in human chondrocyte through a redox-dependent pathway, including RAGE-mediated, NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation, and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) activation. Targeting AOPPs-induced cellular mechanisms might emerge as a promising therapeutic option for patients with RA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polzer K, Schett G, Zwerina J (2007) The lonely death: chondrocyte apoptosis in TNF-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 40(4):333–336
Kim HA, Song YW (1999) Apoptotic chondrocyte death in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 42(7):1528–1537
Bazzichi L, Ciompi ML, Betti L, Rossi A, Melchiorre D, Fiorini M, Giannaccini G, Lucacchini A (2002) Impaired glutathione reductase activity and levels of collagenase and elastase in synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20(6):761–766
Seven A, Guzel S, Aslan M, Hamuryudan V (2008) Lipid, protein, DNA oxidation and antioxidant status in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem 41(7–8):538–543
Baskol G, Demir H, Baskol M, Kilic E, Ates F, Karakukcu C, Ustdal M (2006) Investigation of protein oxidation and lipid peroxidation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Biochem Funct 24(4):307–311
Hitchon CA, El-Gabalawy HS (2004) Oxidation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 6(6):265–278
Nakamura K, Endo H, Kashiwazaki S (1987) Serum oxidation activities and rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Tissue React 9(4):307–316
Lunec J, Halloran SP, White AG, Dormandy TL (1981) Free-radical oxidation (peroxidation) products in serum and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 8(2):233–245
Lo YY, Conquer JA, Grinstein S, Cruz TF (1998) Interleukin-1 beta induction of c-fos and collagenase expression in articular chondrocytes: involvement of reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biochem 69(1):19–29
Henrotin YE, Bruckner P, Pujol JP (2003) The role of reactive oxygen species in homeostasis and degradation of cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 11(10):747–755
Tiku ML, Allison GT, Naik K, Karry SK (2003) Malondialdehyde oxidation of cartilage collagen by chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 11(3):159–166
Henrotin Y, Kurz B, Aigner T (2005) Oxygen and reactive oxygen species in cartilage degradation: friends or foes? Osteoarthritis Cartilage 13(8):643–654
Schiller J, Fuchs B, Arnhold J, Arnold K (2003) Contribution of reactive oxygen species to cartilage degradation in rheumatic diseases: molecular pathways, diagnosis and potential therapeutic strategies. Curr Med Chem 10(20):2123–2145
Mantle D, Falkous G, Walker D (1999) Quantification of protease activities in synovial fluid from rheumatoid and osteoarthritis cases: comparison with antioxidant and free radical damage markers. Clin Chim Acta 284(1):45–58
Firuzi O, Spadaro A, Spadaro C, Riccieri V, Petrucci R, Marrosu G, Saso L (2008) Protein oxidation markers in the serum and synovial fluid of psoriatic arthritis patients. J Clin Lab Anal 22(3):210–215
Witko-Sarsat V, Gausson V, Nguyen AT, Touam M, Drueke T, Santangelo F, Descamps-Latscha B (2003) AOPP-induced activation of human neutrophil and monocyte oxidative metabolism: a potential target for N-acetylcysteine treatment in dialysis patients. Kidney Int 64(1):82–91
Zhou LL, Cao W, Xie C, Tian J, Zhou Z, Zhou Q, Zhu P, Li A, Liu Y, Miyata T et al (2012) The receptor of advanced glycation end products plays a central role in advanced oxidation protein products-induced podocyte apoptosis. Kidney Int 82(7):759–770
Cao W, Xu J, Zhou ZM, Wang GB, Hou FF, Nie J (2013) Advanced oxidation protein products activate intrarenal renin-angiotensin system via a CD36-mediated, redox-dependent pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(1):19–35
Zhou LL, Hou FF, Wang GB, Yang F, Xie D, Wang YP, Tian JW (2009) Accumulation of advanced oxidation protein products induces podocyte apoptosis and deletion through NADPH-dependent mechanisms. Kidney Int 76(11):1148–1160
Guo ZJ, Niu HX, Hou FF, Zhang L, Fu N, Nagai R, Lu X, Chen BH, Shan YX, Tian JW et al (2008) Advanced oxidation protein products activate vascular endothelial cells via a RAGE-mediated signaling pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(10):1699–1712
Xie F, Sun S, Xu A, Zheng S, Xue M, Wu P, Zeng JH, Bai L (2014) Advanced oxidation protein products induce intestine epithelial cell death through a redox-dependent, c-jun N-terminal kinase and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-mediated pathway. Cell Death Dis 5:e1006
Zheng S, Zhong ZM, Qin S, Chen GX, Wu Q, Zeng JH, Ye WB, Li W, Yuan K, Yao L et al (2013) Advanced oxidation protein products induce inflammatory response in fibroblast-like synoviocytes through NADPH oxidase -dependent activation of NF-kappaB. Cell Physiol Biochem 32(4):972–985
Zhong ZM, Bai L, Chen JT (2009) Advanced oxidation protein products inhibit proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblast-like cells via NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 24(1–2):105–114
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, Coombs C, Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Poirier GG, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2002) Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by apoptosis-inducing factor. Science 297(5579):259–263
van Wijk SJ, Hageman GJ (2005) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 mediated caspase-independent cell death after ischemia/reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med 39(1):81–90
Zhang F, Lau SS, Monks TJ (2012) A dual role for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 during caspase-dependent apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 128(1):103–114
Loor G, Kondapalli J, Schriewer JM, Chandel NS, Vanden Hoek TL, Schumacker PT (2010) Menadione triggers cell death through ROS-dependent mechanisms involving PARP activation without requiring apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 49(12):1925–1936
Alderman CJ, Shah S, Foreman JC, Chain BM, Katz DR (2002) The role of advanced oxidation protein products in regulation of dendritic cell function. Free Radic Biol Med 32(5):377–385
Akhtar N, Rasheed Z, Ramamurthy S, Anbazhagan AN, Voss FR, Haqqi TM (2010) MicroRNA-27b regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 62:1361–1371
Chiarugi A, Moskowitz MA (2002) Cell biology. PARP-1—a perpetrator of apoptotic cell death? Science 297(5579):200–201
Gunther C, Neumann H, Neurath MF, Becker C (2013) Apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis: cell death regulation in the intestinal epithelium. Gut 62(7):1062–1071
Almenier HA, Al Menshawy HH, Maher MM, Al Gamal S (2012) Oxidative stress and inflammatory bowel disease. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 4:1335–1344
Loeser RF, Yammani RR, Carlson CS, Chen H, Cole A, Im HJ, Bursch LS, Yan SD (2005) Articular chondrocytes express the receptor for advanced glycation end products: Potential role in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 52(8):2376–2385
Yu H, Ye WB, Zhong ZM, Ding RT, Chen JT (2015) Effect of advanced oxidation protein products on articular cartilage and synovium in a rabbit osteoarthritis model. Orthop Surg 7(2):161–167
Cai H, Harrison DG (2000) Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res 87(10):840–844
Meyer JW, Holland JA, Ziegler LM, Chang MM, Beebe G, Schmitt ME (1999) Identification of a functional leukocyte-type NADPH oxidase in human endothelial cells:a potential atherogenic source of reactive oxygen species. Endothelium 7(1):11–22
Gorlach A, Brandes RP, Nguyen K, Amidi M, Dehghani F, Busse R (2000) A gp91phox containing NADPH oxidase selectively expressed in endothelial cells is a major source of oxygen radical generation in the arterial wall. Circ Res 87(1):26–32
Wu Q, Zhong ZM, Zhu SY, Liao CR, Pan Y, Zeng JH, Zheng S, Ding RT, Lin QS, Ye Q et al (2016) Advanced oxidation protein products induce chondrocyte apoptosis via receptor for advanced glycation end products-mediated, redox-dependent intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Apoptosis 21(1):36–50
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This manuscript is our original work. Not any part of the entire paper has been published or accepted elsewhere. It is not being submitted to any other journal. We also confirm that all listed authors have participated actively in this study. All authors have read the manuscript and have approved to submit to your journal. The authors do not have any possible conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Wenbin Ye and Siyuan Zhu have contributed equally to this work.
The authors have requested to retract their paper. Their paper reported the advanced oxidation protein products (AOPPs) stimulation cause cell death of human chondrocyte of RA patients with PARP-1 over-expression and characterized the apoptosis mechanisms underlying the redox condition. Many of the figure panels in the paper summarize data from multiple experiments. The authors have now detected a number of errors in these panels. The authors believe that the most responsible course of action is to retract our paper. The authors sincerely apologize for their carelessness and poor arrangement of results and apologize to the community.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1373-3.
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, W., Zhong, Z., Zhu, S. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Advanced oxidation protein products induce chondrocyte death through a redox-dependent, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-mediated pathway. Apoptosis 22, 86–97 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1314-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1314-6