Abstract
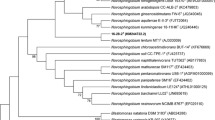
A marine bacterial strain, F72T, was isolated from a solitary scleractinian coral, collected in Yap seamounts in the Pacific Ocean. Strain F72T is a Gram-negative, light-yellow-pigmented, motile, rod-shaped bacterium. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain F72T is related to the genus Novosphingobium and has high 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities with the type strains of Novosphingobium pentaromativorans US6-1T (97.7 %), Novosphingobium panipatense SM16T (97.6 %), Novosphingobium mathurense SM117T (97.2 %) and Novosphingobium barchaimii LL02T (97.1 %). Ubiquinone Q-10 was detected as the dominant quinone. The predominant cellular fatty acids were C18:1ω7c and C17:1ω6c. The genomic DNA G+C content of strain F72T was 63.4 mol %. The polar lipids profile contained phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylmethylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, sphingoglycolipid and one uncharacterized lipid. Strain F72T shared DNA relatedness of 25 % with N. pentaromativorans JCM 12182T, 31 % with N. panipatense DSM 22890T, 21 % with N. mathurense DSM 23374T and 26 % with N. barchaimii DSM 25411T. Combined data from phenotypic, phylogenetic and DNA–DNA relatedness studies demonstrated that the strain F72T is a representative of a novel species of the genus Novosphingobium, for which we propose the name Novosphingobium profundi sp. nov. (type strain F72T = KACC 18566T = CGMCC 1.15390T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenburger P, Kämpfer P, Makristathis A, Lubitz W, Busse H-J (1996) Classification of bacteria isolated from a medieval wall painting. J Biotechnol 47:39–52
Balkwill DL, Drake GR, Reeves RH, Fredrickson JK, White DC, Ringelberg DB, Chandler DP, Romine MF, Kennedy DW, Spadoni CM (1997) Taxonomic study of aromatic degrading bacteria from deep-terrestrial-subsurface sediments and description of Sphingomonas aromaticivorans sp. nov., Sphingomonas subterranea sp. nov., and Sphingomonas stygia sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:191–201
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Brosius J, Palmer ML, Kennedy PJ, Noller HF (1978) Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4801–4805
Busse H-J, Denner EBM, Buczolits S, Salkinoja-Salonen M, Bennasar A, Kämpfer P (2003) Sphingomonas aurantiaca sp. nov., Sphingomonas aerolata sp. nov. and Sphingomonas faeni sp. nov., air- and dustborne and Antarctic, orange-pigmented, psychrotolerant bacteria, and emended description of the genus Sphingomonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1253–1260
Chen Q, Zhang J, Wang C-H, Jiang J, Kwon S-W, Sun L-N, Shen W-B, He J (2014) Novosphingobium chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov., a chloroacetamide herbicide-degrading bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2573–2578
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Gupta SK, Lal D, Lal R (2009) Novosphingobium panipatense sp. nov. and Novosphingobium mathurense sp. nov., from oil-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:156–161
Huo Y-Y, You H, Li ZY, Wang C-S, Xu X-W (2015) Novosphingobium marinum sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:676–680
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schleifer K-H (1983) Studies on the spectrometric determination of DNA hybridisation from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Kämpfer P, Martin K, McInroy JA, Glaeser SP (2015) Novosphingobium gossypii sp. nov., isolated from Gossypium hirsutum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:2831–2837
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA Gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Lee L-H, Azman A-S, Zainal N, Eng S-K, Fang C-M, Hong K, Chan K-G (2014) Novosphingobium malaysiense sp. nov. isolated from mangrove sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1194–1201
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
Maruyama T, Park H-D, Ozawa K, Tanaka Y, Sumino T, Hamana K, Hiraishi A, Kato K (2006) Sphingosinicella microcystinivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a microcystin-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:85–89
Niharika N, Moskalikova H, Kaur J, Sedlackova M, Hampl A, Damborsky J, Prokop Z, Lal R (2013) Novosphingobium barchaimii sp. nov., isolated from hexachlorocyclohexane-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:667–672
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Frisch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI, Newark Technical note 101
Saxena A, Anand S, Dua A, Sangwan N, Khan F, Lal R (2013) Novosphingobium lindaniclasticum sp. nov., a hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-degrading bacterium isolated from HCH dumpsite. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2160–2167
Sohn JH, Kwon KK, Kang J-H, Jung H-B, Kim S-J (2004) Novosphingobium pentaromatovorans sp. nov., a high-molecular-mass polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from estuarine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1483–1487
Stolz A, Busse H-J, Kämpfer P (2007) Pseudomonas knackmussii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:572–576
Süßmuth R, Eberspächer J, Haag R, Springer W (1987) Biochemisch-mikrobiologisches Praktikum. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart
Suzuki S, Hiraishi A (2007) Novosphingobium naphthalenivorans sp. nov., a naphthalene-degrading bacterium isolated from polychlorinated-dioxin-contaminated environments. J Gen Appl Microbiol 53:221–228
Takeuchi M, Hamana K, Hiraishi A (2001) Proposal of the genus Sphingomonas sensu stricto and three new genera, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium and Sphingopyxis, on the basis of phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic analyses. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1405–1417
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tindall BJ (1990a) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990b) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Letts 66:199–202
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RM, Kreig NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf G, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. ASM Press, Washington DC, pp 330–393
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR et al (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Yabuuchi E, Yano I, Oyaizu H, Hashimoto Y, Ezaki T, Yamamoto H (1990) Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis gen. nov. and comb. nov., Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp. nov., Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp. nov., Sphingomonas capsulata comb. nov., and two genospecies of the genus Sphingomonas. Microbiol Immunol 34:99–119
Yuan J, Lai Q, Zheng T, Shao Z (2009) Novosphingobium indicum sp. nov., a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from a deep-sea environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2084–2088
Zhang D-C, Wang H-X, Liu H-C, Dong X-Z, Zhou P-J (2006) Flavobacterium glaciei sp. nov., a novel psychrophilic bacterium isolated from the China No.1 glacier. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2921–2925
Zhang D-C, Redzic M, Schinner F, Margesin R (2011) Glaciimonas immobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Oxalobacteraceae isolated from alpine glacier cryoconite. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2186–2190
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA11030201) and the “135” fund of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2012IO060105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, DC., Liu, YX. & Huang, HJ. Novosphingobium profundi sp. nov. isolated from a deep-sea seamount. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 19–25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0769-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0769-3