Abstract
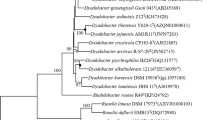
A Gram-stain negative, white-pigmented bacterial strain, designated D78T, was isolated from soil obtained from Dokdo in Korea. The strain was observed to be aerobic, asporogenous and rod-shaped. The strain was observed to grow at 15–40 °C (optimum 37 °C), at pH 6.0–8.0 (optimum 7.0–7.5) and in the presence of 0–1 % (w/v) NaCl. Phylogenetically, the strain was found to be closely related to members of the genus Dongia and showed 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity with Dongia mobilis LM22T and Dongia rigui 04SU4-PT of 94.6 and 94.4 %, respectively. The major fatty acids were identified as C16:0, C19:0 cyclo ω8c and summed feature 8 (C18:1 ω7c and/or C18:1 ω6c). Q-10 was identified as the only ubiquinone. The polar lipids profile was found to contain phosphatidylethanolamine, hydroxyphosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, an unidentified aminolipid and three unidentified polar lipids. The DNA G+C content of the strain was found to be 54.7 mol%. Based on the phenotypic, genotypic and chemotaxonomic data, strain D78T represents a novel species in the genus Dongia, for which the name Dongia soli sp. nov. (=KACC 13941T =LMG 29193T) is proposed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baik KS, Hwang YM, Choi JS, Kwon J, Seong CN (2013) Dongia rigui sp. nov., isolated from freshwater of a large wetland in Korea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:1143–1150
Breznak JA, Costilow RN (2007) Physicochemical factors in growth. In: Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society For Microbiology, Washington, pp 309–329
Counsell T, Murray R (1986) Polar lipid profiles of the genus Deinococcus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 36:202–206
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Gonzalez J, Saiz-Jimenez C (2002) A fluorimetric method for the estimation of G+C mol% content in microorganisms by thermal denaturation temperature. Environ Microbiol 4:770–773
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Monro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Kim DU, Ka JO (2014) Roseomonas soli sp. nov., isolated from an agricultural soil cultivated with Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1024–1029
Kim OS et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Liu Y, Jin JH, Liu YH, Zhou YG, Liu ZP (2010) Dongia mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Rhodospirillaceae isolated from a sequencing batch reactor for treatment of malachite green effluent. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2780–2785
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 607–654
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant from the Regional Subgenebank Support Program of Rural development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DU., Lee, H., Kim, H. et al. Dongia soli sp. nov., isolated from soil from Dokdo, Korea. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 109, 1397–1402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0738-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0738-x