Abstract
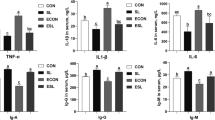
This study was conducted with a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged piglet model to determine the effects of diets containing Lactobacillus acidophilus on the performance, intestinal barrier function, rectal microflora and serum immune function. A total of 150 piglets (initial body weight (BW) 7.53 ± 0.21 kg) were allotted to one of the following diets, including a basal diet, a basal diet supplemented with 250 mg/kg Flavomycin, or basal diet plus 0.05, 0.1 or 0.2 % L. acidophilus. On day 28 of the trial, the pigs were given an intraperitoneal injection of LPS (200 μg/kg body weight) followed by blood collection 3 h later. Diets with either antibiotics, 0.1 or 0.2 % Lactobacillus increased (P < 0.05) the final BW and decreased (P < 0.05) feed gain ratio (F/G) compared with the control group. Pigs fed diets containing antibiotic or Lactobacillus had greater average daily gain (ADG) (P < 0.05) than pigs fed the control diet. The rectal content Lactobacillus counts for pigs fed diet containing Lactobacillus were significant higher (P < 0.01) than those fed antibiotic or control diet. Feeding the Lactobacillus diets decreased the Escherichia coli counts of rectal content (P < 0.01). Pigs fed diets containing 0.1 or 0.2 % Lactobacillus decreased serum DAO activity (P < 0.05) compared with pigs fed the control diet. Serum IL-10 concentration was enhanced in pigs fed the diet with Lactobacillus compared to pigs fed the control diet and antibiotic diet. Feeding a diet with Lactobacillus reduced (P < 0.05) IFN-γ concentration compared to the control diet. Inclusion of Lactobacillus in diets fed to pigs reduced TNF-α concentration compared with pigs fed no Lactobacillus (P < 0.05). These results indicate that feeding with L. acidophilus improved growth performance and protected against LPS-induced inflammatory status.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhandari SK, Xu B, Nyachoti CM, Giesting DW, Krause DO (2008) Evaluation of alternatives to antibiotics using an Escherichia coli K88+ model of piglet diarrhea: effects on gut microbial ecology. J Anim Sci 86:836–847
Broom LJ, Miller HM, Kerr KG, Knapp JS (2006) Effects of zinc oxide and Enterococcus faecium SF68 dietary supplementation on the performance, intestinal microbiota and immune status of weaned piglets. Res Vet Sci 80:45–54
Carroll IM, Andrus JM, Bruno-Barcena JM, Klaenhammer TR, Hassan HM, Threadgill DS (2007) Anti-inflammatory properties of Lactobacillus gasseri expressing manganese superoxide dismutase using the interleukin 10-deficient mouse model of colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 293:G729–G738
Castillo NA, Perdigón G, de Moreno de LeBlanc A (2011) Oral administration of a probiotic Lactobacillus modulates cytokine production and TLR expression improving the immune response against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in mice. BMC Microbiol 11:177–188
Christensen HR, Frøkiær H, Pestka JJ (2002) Lactobacilli differentially modulate expression of cytokines and maturation surface markers in murine dendritic cells. J Immunol 168:171–178
Cui C, Shen CJ, Jia G, Wang KN (2013) Effect of dietary Bacillus subtilis on proportion of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes in swine intestine and lipid metabolism. Genet Mol Res 12:1766–1776
de Lange CFM, Pluske J, Gong J, Nyachoti CM (2010) Strategic use of feed ingredients and feed additives to stimulate gut health and development in young pigs. Livest Sci 134:124–134
de Moreno de LeBlanc A, Castillo NA, Perdigón G (2010) Anti-infective mechanisms induced by a probiotic Lactobacillus strain against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection. Int J Food Microbiol 138:223–231
Dieleman LA, Goerres MS, Arends A, Sprengers D, Torrice C, Hoentjen F, Grenther WB, Sartor RB (2003) Lactobacillus GG prevents recurrence of colitis in HLA-B27 transgenic rats after antibiotic treatment. Gut 52:370–376
FAO/WHO (2001) Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live Lactic acid bacteria. [http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/en/probiotics.pdf]
Goyal N, Shukla G (2013) Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Modulates the Mucosal Immune Response in Giardia intestinalis-Infected BALB/c Mice. Dig Dis Sci 58:1218–1225
Heo JM, Opapeju FO, Pluske JR, Kim JC, Hampson DJ, Nyachoti CM (2013) Gastrointestinal health and function in weaned pigs: a review of feeding strategies to control post-weaning diarrhoea without using in-feed antimicrobial compounds. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 97:207–237
Hou YQ, Wang L, Zhang W, Yang ZG, Ding BY, Zhu HL, Liu YL, Qiu YS, Yin YL, Wu GY (2012) Protective effects of N-acetylcysteine on intestinal functions of piglets challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Amino Acids 43:1233–1242
Huang CH, Qiao SY, Li DF, Piao XS, Ren JP (2004) Effects of Lactobacilli on the performance, diarrhea incidence, VFA concentration and gastrointestinal microbial flora of weaning pigs. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 17:401–409
Inoue R, Tsukahara T, Nakanishi N, Ushida K (2005) Development of the intestinal microbiota in the piglet. J Gen App MIcrobiol 51:257–265
Jost M, Bracher JA (1999) The effect of Sanobiotic RS, a multiactive probiotic growth promoter, in rearing piglets. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4200–4204
Kazmierczak SC, Robertson AF (1992) Evaluation of a spectrophotometric method for measurement of activity of diamine oxidase in newborn infants. Ann Clin Lab Sci 22:155–161
Lallès JP, Bosi P, Smidt H, Stokes CR (2007) Nutritional management of gut health in pigs around weaning. Proc Nutr Soc 66:260–268
Lee JS, Awji EG, Lee SJ, Tassew DD, Park YB, Park KS, Kim MK, Kim B, Park SC (2012) Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum CJLP243 on the growth performance and cytokine response of weaning pigs challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Anim Sci 90:3709–3717
Li JY, Yu Y, Hu S, Sun D, Yao YM (2002) Preventive effect of glutamine on intestinal barrier dysfunction induced by severe trauma. World J Gastroenterol 8:168–171
Liu YJ, Soumelis V, Watanabe N, Ito T, Wang YH, Malefyt Rde W, Omori M, Zhou B, Ziegler SF (2007) TSLP: an epithelial cell cytokine that regulates T cell differentiation by conditioning dendritic cell maturation. Annu Rev Immunol 25:193–219
Liu YL, Huang JJ, Hou YQ, Zhu HL, Zhao SJ, Ding BY, Yin YL, Yi GF, Shi JY, Fan W (2008) Dietary arginine supplementation alleviates intestinal mucosal disruption induced by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide in weaned pigs. Br J Nutr 100:552–560
Luk GD, Bayless TM, Baylin SB (1980) Diamine oxidase (histaminase): a circulating marker for rat intestinal mucosal maturation and integrity. J Clin Invest 66:66–70
Luk GD, Bayless TM, Baylin SB (1983) Plasma postheparin diamine oxidase. Sensitive provocative test for quantitating length of acute intestinal mucosal injury in the rat. J Clin Invest 71:1308–1315
Luongo D, Miyamoto J, Bergamo P, Nazzaro F, Baruzzi F, Sashihara T, Tanabe S, Rossi M (2013) Differential modulation of innate immunity in vitro by probiotic strains of Lactobacillus gasseri. BMC Microbiol 13:298–309
Mennigen R, Nolte K, Rijcken E, Utech M, Loeffler B, Senninger N, Bruewer W (2009) Probiotic mixture VSL#3 protects the epithelial barrier by maintaining tight junction protein expression and preventing apoptosis in a murine model of colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:G1140–G1149
Mercer DW, Smith GS, Cross JM, Russell DH, Chang L, Cacioppo J (1996) Effects of lipopolysaccharide on intestinal injury: potential role of nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation. J Surg Res 63:185–192
Metzler B, Bauer E, Mosenthin R (2005) Microfl ora management in the gastrointestinal tract of piglets. Asian-Aust. J Anim Sci 18:1353–1362
Mileti E, Matteoli G, Iliev ID, Rescigno M (2009) Comparison of the immunomodulatory properties of three probiotic strains of Lactobacilli using complex culture systems: prediction for in vivo efficacy. PLoS ONE 4(9):e7056
NRC (2012) Nutrient requirements of swine. 11th Revised Edition. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Otte JM, Cario E, Podolsky DK (2004) Functional modulation of enterocytesby gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G613–G626
Pluske JR, Hampson DJ, Williams IH (1997) Factors influencing the structure and function of the small intestine in the weaned pig: a review. Livest Prod Sci 51:215–236
Roselli M, Finamore A, Britti MS, Konstantinov SR, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Mengheri E (2007) The novel porcine Lactobacillus sobrius strain protects intestinal cells from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 infection and prevents membrane barrier damage. J Nutr 137:2709–2716
Ulisse S, Giochetti P, D’Alò S, Russo FP, Pesce I, Ricci G, Rizzello F, Helwig U, Cifone MG, Campieri M, De Simone C (2001) Expression of cytokines, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and matrix metalloproteinases in pouchitis: effects of probiotic treatment. Am J Gastroenterol 96:2691–2699
Vella A, Farrugia G (1998) D-lactic acidosis: pathologic consequence of saprophytism. Mayo Clin Proc 73:451–456
Villena J, Kitazawa H (2014) Modulation of intestinal TLR4-inflammatory signaling pathways by probiotic microorganisms: lessons learned from Lactobacillus jensenii TL2937. Front Immunol 4:512–523
Wang A, Yu H, Gao X, Li X, Qiao S (2009) Influence of Lactobacillus fermentum I5007 on the intestinal and systemic immune responses of healthy and E. coli challenged piglets. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 96:89–98
Weber TE, Ziemer CJ, Kerr BJ (2008) Effects of adding fibrous feedstuffs to the diet of young pigs on growth performance, intestinal cytokines, and circulating acute-phase proteins. J Anim Sci 86:871–881
Yang KM, Jiang ZY, Zheng CT, Wang L, Yang XF (2014) Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum on diarrhea and intestinal barrier function of young piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. J Anim Sci 92:1496–1503
Zhang W, Wen K, Azevedo MS, Gonzalez A, Saif LJ, Li G, Yousef AE, Yuan L (2008) Lactic acid bacterial colonization and human rotavirus infection influence distribution and frequencies of monocytes/macrophages and dendritic cells in neonatal gnotobiotic pigs. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 121:222–231
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants (31402087) from the National Science Grant of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors would like to declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, J., Li, H., Wang, Z. et al. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus dietary supplementation on the performance, intestinal barrier function, rectal microflora and serum immune function in weaned piglets challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 883–891 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0380-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0380-z