Abstract
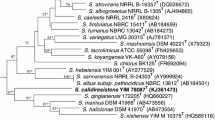
A novel actinomycete, designated strain NEAU-C3T, was isolated from volcanic sediment collected from Longwan, Jilin province, north China and characterized using a polyphasic approach. The organism was found to have morphological and chemotaxonomic characteristics typical of the members of the genus Streptomyces. EzTaxon-e analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated strain NEAU-C3T to be most closely related to Streptomyces hygroscopicus subsp. ossamyceticus JCM 4965T (97.7 % sequence similarity) and Streptomyces torulosus JCM 4872T (97.7 %). Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain NEAU-C3T belongs within the genus Streptomyces and forms a separate subclade, an association that was supported by a bootstrap value of 72 % in the neighbour-joining tree and also recovered with the maximum-likelihood algorithm. The DNA–DNA hybridization values between strain NEAU-C3T and the two most closely related type strains were low enough to justify the assignment of the strain to a novel species. On the basis of these phenotypic, phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic characteristics, it is concluded that strain NEAU-C3T represents a novel species of the genus Streptomyces, for which the name Streptomyces vulcanius sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is NEAU-C3T (=CGMCC 4.7177T=DSM 42139T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bérdy J (2005) Bioactive microbial metabolites, a personal view. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 58:1–26
Collins MD (1985) Isoprenoid quinone analyses in bacterial classification and identification. In: Goodfellow M, DE Minnikin (eds) Chemical methods in bacterial systematics. Academic Press, London, pp 267–284
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gao RX, Liu CX, Zhao JW, Jia FY, Yu C, Yang LY, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2014) Micromonospora jinlongensis sp. nov., isolated from muddy soil in China and emended description of the genus Micromonospora. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105:307–315
Gordon RE, Barnett DA, Handerhan JE, Pang C (1974) Nocardia coeliaca, Nocardia autotrophica, and the nocardin strain. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:54–63
Hayakawa M, Nonomura H (1987) Humic acid-vitamin agar, a new medium for the selective isolation of soil actinomycetes. J Ferment Technol 65:501–509
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schleifer KH (1983) Studies on the spectrometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Jia FY, Liu CX, Wang XJ, Zhao JW, Liu QF, Zhang J, Gao RX, Xiang WS (2013) Wangella harbinensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Micromonosporaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:399–408
Jones KL (1949) Fresh isolates of actinomycetes in which the presence of sporogenous aerial mycelia is a fluctuating characteristic. J Bacteriol 57:141–145
Kampfer P, Labeda DP (2006) International committee on systematics of prokaryotes; subcommittee on the taxonomy of the Streptomycetaceae: minutes of the meeting, 25 July 2005, San Francisco, CA, USA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:495
Kelly KL (1964) Inter-society color council-national bureau of standards color-name charts illustrated with centroid colors published in US
Kim SB, Brown R, Oldfield C, Gilbert SC, Iliarionov S, Goodfellow M (2000) Gordonia amicalis sp. nov., a novel dibenzothiophene-desulphurizing actinomycete. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:2031–2036
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Labeda DP, Goodfellow M, Brown R, Ward AC, Lanoot B, Vanncanneyt M, Swings J, Kim SB, Liu Z, Chun J, Tamura T, Oguchi A, Kikuchi T, Kikuchi H, Nishii T, Tsuji K, Yamaguchi Y, Tase A, Takahashi M, Sakane T, Suzuki KI, Hatano K (2012) Phylogenetic study of the species within the family Streptomycetaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:73–104
Lazzarini A, Cavaletti L, Toppo G, Marinelli F (2000) Rare genera of actinomycetes as potential producers of new antibiotics. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 78:399–405
Lechevalier HA, Lechevalier MP (1970a) A critical evaluation of the genera of aerobic actinomycetes. In: The actinomycetes, p 393–405
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1970b) Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 20:435–443
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1980) The chemotaxonomy of actinomycetes. In: Dietz A, Thayer DW (eds) Actinomycete taxonomy, vol 6. (Special Publication) Society of Industrial Microbiology, Arlington, pp 227–291
Lechevalier MP, De Bièvre C, Lechevalier HA (1977) Chemotaxonomy of aerobic actinomycetes: phospholipid composition. Biochem Syst Ecol 5:249–260
Lodders N, Kämpfer P (2007) Streptomycetaceae: phylogeny, ecology and pathogenicity eLS
Mandel M, Marmur J (1968) Use of ultraviolet absorbance temperature profile for determining the guanine plus cytosine content of DNA. Methods Enzymol 12B:195–206
Manfio GP, Zakrzewska-Czerwinska J, Atlan E, Goodfellow M (1995) Towards minimal standards for the description of Streptomyces species. Biotechnologia 7–8:242–253
McCarthy AJ, Williams ST (1992) Actinomycetes as agents of biodegradation in environment. Gene 115:189–192
McKerrow J, Vagg S, McKinney T, Seviour EM, Maszenan AM, Brooks P, Se-viour RJ (2000) A simple HPLC method for analysing diaminopimelic acid diastereomers in cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria. Lett Appl Microbiol 30:178–182
Minnikin DE, Hutchinson IG, Caldicott AB, Goodfellow M (1980) Thin-layer chromatography of methanolysates of mycolic acid-containing bacteria. J Chromatogr 188:221–233
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal K, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Parte AC (2014) LPSN—list of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 42:613–616
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 607–654
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Waksman SA (1961) The Actinomycetes, vol. 2, Classification, identification and descriptions of genera and species. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins
Waksman SA (1967) The Actinomycetes. A summary of current knowledge. Ronald, New York
Waksman SA, Henrici AT (1943) The nomenclature and classification of the actinomycetes. J Bacteriol 46:337–341
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE (1987) International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G (1989) Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943, 399AL. In: Bergey’s Manual of Sytematic Bacteriology 4:2452–2492
Wu C, Lu X, Qin M, Wang Y, Ruan J (1989) Analysis of menaquinone compound in microbial cells by HPLC. Microbiology [English translation of Microbiology (Beijing)] 16:176–178
Xiang WS, Liu CX, Wang XJ, Du J, Xi LJ, Huang Y (2011) Actinoalloteichus nanshanensis sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of a fig tree (Ficus religiosa). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1165–1169
Yokota A, Tamura T, Hasegawa T, Huang LH (1993) Catenuloplanes japonicas gen. nov., sp. nov., nom. rev., a new genus of the order Actinomycetales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:805–812
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Outstanding Youth Foundation (No. 31225024), the National Key Project for Basic Research (No. 2010CB126102), the National Key Technology R&D Program (No. 2012BAD19B06), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-11-0953), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31372006, 31171913, 31071750 and 31471832), the Outstanding Youth Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (JC201201), the Chang Jiang Scholar Candidates Program for Provincial Universities in Heilongjiang (CSCP), the Science and Technology Research Project of Heilongjiang Provincial Educational Commission (No. 12541001) and the Youth Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. QC2014C013). We are grateful to Prof. Aharon Oren for helpful advice on the specific epithet.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, F., Liu, C., Zhao, J. et al. Streptomyces vulcanius sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from volcanic sediment. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 15–21 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0299-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0299-9