Abstract
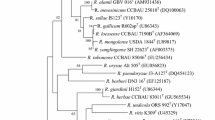
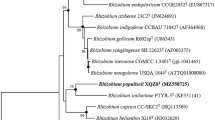
During a study of the diversity and phylogeny of rhizobia isolated from root nodules of Oxytropis ochrocephala grown in the northwest of China, four strains were classified in the genus Rhizobium on the basis of their 16S rRNA gene sequences. These strains have identical 16S rRNA gene sequences, which showed a mean similarity of 94.4 % with the most closely related species, Rhizobium oryzae. Analysis of recA and glnA sequences showed that these strains have less than 88.1 and 88.7 % similarity with the defined species of Rhizobium, respectively. The genetic diversity revealed by ERIC-PCR fingerprinting indicated that the isolates correspond to different strains. Strain CCNWQLS01T contains Q-10 as the predominant ubiquinone. The major fatty acids were identified as feature 8 (C18: 1ω7c and/or C18: 1ω6c; 67.2 %). Therefore, a novel species Rhizobium qilianshanense sp. nov. is proposed, and CCNWQLS01T (= ACCC 05747T = JCM 18337T) is designated as the type strain.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen ON, Allen EK (1981) The Leguminosae: A source book of characteristics, Uses, and Nodulation. The University of Wisconsin Press, Madison
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Dazzo FB (1982) Leguminous root nodules. In: Burns R, Slater J (eds) Experimental Microbial Ecology. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Determinative Manual for Routine Bacteriology. Scientific Press, Beijing
Elliott GN, Chen WM, Bontemps C, Chou JH, Young JPW, Sprent JI, James EK (2007) Nodulation of Cyclopia spp. (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae) by Burkholderia tuberum. Ann Bot (London) 100:1403–1411
Galtier N, Gouy M, Gautier C (1996) SEAVIEW and PHYLO_WIN: two graphic tools for sequence alignment and molecular phylogeny. Comput Appl Biosci 12:543–548
Gao JL, Sun JG, Li Y, Wang ET, Chen WX (1994) Numerical taxonomy and DNA relatedness of tropical rhizobia isolated from Hainan Province, China. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:151–158
Gaunt MW, Turner SL, Rigottier-Gois L, Lloyd-Macgilp SA, Young JPW (2001) Phylogenies of atpD and recA support the small subunit rRNA-based classification of rhizobia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2037–2048
Graham PH, Sadowsky MJ, Keyser HH, Barnet YM, Bradley RS, Cooper JE, De Ley DJ, Jarvis BDW, Roslycky EB (1991) Proposed minimal standards for the description of new genera and species of root- and stem-nodulating bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41:582–587
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Kuklinsky-Sobral J, Araujo WL, Mendes R, Geraldi IO, Pizzirani-Kleiner AA, Azevedo JL (2004) Isolation and characterization of soybean-associated bacteria and their potential for plant growth promotion. Environ Microbiol 6:1244–1251
Laguerre G, Nour SM, Macheret V, Sanjuan J, Drouin P, Amarger N (2001) Classification of rhizobia based on nodC and nifH gene analysis reveals a close phylogenetic relationship among Phaseolus vulgaris symbionts. Microbiology 147:981–993
Liu L, Feng Y, Jia ZH, Zhao BY (2010) Research progress on development and utilization of locoweed in China. Acta Ecologiae Animalis Domastici 31:103–105 (in Chinese)
Menna P, Pereira AA, Bangel EV, Hungria M (2009) Rep-PCR of tropical rhizobia for strain fingerprinting, biodiversity appraisal and as a taxonomic and phylogenetic tool. Symbiosis 48:120–130
Moulin L, Munive A, Dreyfus B, Boivin-Masson C (2001) Nodulation of legumes by members of the beta-subclass of proteobacteria. Nature 411:948–950
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc., Newark
Sy A, Giraud E, Jourand P (2001) Methylotrophic methylobacterium bacteria nodulate and fix nitrogen in symbiosis with legumes. J Bacteriol 183:214–220
Terefework Z, Kaijalainen S, Lindström K (2001) AFLP fingerprinting as a tool to study the genetic diversity of Rhizobium galegae. J Biotechnol 91:169–180
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tighe SW, de Lajudie P, Dipietro K, Lindström K, Nick G, Jarvis BD (2000) Analysis of cellular fatty acids and phenotypic relationships of Agrobacterium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium species using the Sherlock Microbial Identification System. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:787–801
Turner SL, Young JPW (2000) The glutamine synthetases of rhizobia: phylogenetics and evolutionary implications. Mol Biol Evol 17:309–319
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of root nodule bacteria. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Wei GH, Zhu ME, Wang ET, Tan ZY, Chen WX (2002) Rhizobium indigoferae sp. nov. and Sinorhizobium kummerowiae sp. nov. isolated from Indigofera spp. and Kummerowia stipulacea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:2231–2239
Zehr JP, Jenkins BD, Short SM, Steward GF (2003) Nitrogenase gene diversity and microbial community structure: a cross-system comparison. Environ Microbiol 5:539–554
Zhang YJ, Yuan QP, Liang H (2003) The biosynthesis of coenzyme Q10 in Bullera pseudoalba. Microbiology 30:65–69
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by projects from National Science Foundation of China (31125007, 30970003), and the 863 Project of China (2012AA100602). We would like to express our gratitude to Professor Ruibo Jiang and Xiaoxia Zhang (Agricultural Cultural Collection of China, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China) for providing the type strains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Comparison of partial recA sequences. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method from Jukes-Cantor distance matrices of the sequences. Bootstrap percentages above 50 % are indicated for phylogenies constructed by neighbor-joining method (PPT 79 kb)
Fig. S2
Comparison of partial glnA sequences. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method from Jukes-Cantor distance matrices of the sequences. Bootstrap percentages above 50 % are indicated for phylogenies constructed by neighbor-joining method (PPT 61 kb)
Fig. S3
Comparison of partial nodA sequences. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method from Jukes-Cantor distance matrices of the sequences. Bootstrap percentages above 50 % are indicated for phylogenies constructed by neighbor-joining method (PPT 63 kb)
Fig. S4
ERIC-PCR profiles showing the relationship among Rhizobium qilianshanense sp. nov. Lanes: 1, CCNWQLS21; 2, CCNWQLS01T; 3, CCNWQLS97; 4, CCNWQLS111. Lane M, molecular mass marker (PPT 103 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Zhang, Y., Deng, Z.S. et al. Rhizobium qilianshanense sp. nov., a novel species isolated from root nodule of Oxytropis ochrocephala Bunge in China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103, 559–565 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9840-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9840-x