Abstract
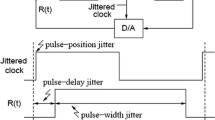
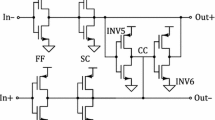
Excess loop delay is one of the most critical non-idealities of continuous-time delta–sigma modulators as it leads to degradation of the signal-to-noise-ratio or even instability. A comprehensive study of the impact of excess loop delay on tunable continuous-time bandpass delta–sigma modulators using RC-resonators is performed in this paper, both analytically and by simulations. Moreover, a detailed analysis of the conventional compensation techniques for single-band continuous-time bandpass modulators as well as their adaptability to tunable bandpass modulators is performed. The results indicate that only tuning of the scaling coefficients is suitable to compensate for excess loop delay in high-speed tunable bandpass modulators. Based on this result, an approach to the compensation of excess loop delay is proposed which maps the poles of the noise transfer function (NFT) to almost ideal and thus stable positions. Excess loop delay equal to one clock cycle may thus be compensated while the available tuning range of the center frequency depends on the order and the out-of-band-gain of the NFT. A prototype implemented on a printed circuit board proves the feasibility of the proposed approach.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shahein, A., Afifi, M., Becker, M., Lotze, N., & Manoli, Y. (2010). A power-efficient tunable narrow-band digital front end for bandpass sigma delta ADCs in digital FM receivers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 57(11), 883–887.
Ortmanns, M., Gerfers, F., & Manoli, Y. (2005). A continuous-time sigma delta modulator with reduced sensitivity to clock jitter through SCR feedback. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems - Part I, 52(5), 875–884.
Cherry, J. A., & Snelgrove, W. M. (1999). Excess loop delay in continuous-time delta–sigma modulators. Circuits and Systems II, 46(4), 376–389.
Gao, W., Shoaei, O., & Snelgrove, W. M. (1997). Excess loop delay effects in continuous-time delta–sigma modulators and the compensation solution. Proceedings - IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 65–68.
Benabes, P., Keramat, M., & Kielbasa, R. (1997). A methodology for designing continuous-time sigma–delta modulators. Proceedings of the IEEE European Design and Test Conference, pp. 46–50.
Adams, R. W. (1986). Design and implementation of an audio 18-bit A/D converter using oversampling techniques. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society, 34, 153–166.
Aboushady, H., & Louerat, M. (2004). Loop delay compensation in bandpass continuous-time sigma delta modulators without additional feedback coefficients. Proceedings - IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1124–1127.
Henkel, F., & Langmann, U. (2003). Excess loop delay effects in continuous-time quadrature bandpass sigma–delta modulators. Proceedings - IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1029–1032.
Schreier, R., Temes, G. C., & Martin, W. (2005). Understanding delta–sigma data converters. Piscataway: IEEE Press.
Beilleau, N., Aboushady, H., & Louerat, M.M. (2003). Systematic approach for scaling coefficients of discrete-time and continuous-time sigma–delta modulators. Proceedings of the IEEE Midwest Symposium on Circuits System, pp. 233–236.
Schreier, R. (2000). Delta–sigma toolbox. [Online]. Available: http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/19.
Buhmann, A., Keller, M., Maurer, M., Ortmanns, M., & Manoli, Y. (2007). DISCO—A toolbox for the discrete-time simulation of continuous-time sigma–delta modulators using MATLAB. Proceedings of the IEEE Midwest Symposium on Circuits System, pp.1082–1085.
Cherry, J. A., & Snelgrove, W. M. (2005). Continuous-time delta-sigma modulators for high-speed A/D conversion: Theory, practice and fundamental performance limits. New Jersey: IEEE press.
Keller, M., Buhmann, A., Gerfers, F., Ortmanns, M., & Manoli, Y. (2007). On the implicit anti-aliasing feature of continuous-time cascaded sigma delta modulators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 54(12), 2639–2645.
Pavan, S. (2011). Alias rejection of continuous-time delta–sigma modulators with switched-capacitor feedback DACs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 58(2), 233–243.
Pavan, S. (2011). On continuous-time delta–sigma modulators with return-to-open DACs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 58(5), 284–288.
Shoaei, O., & Snelgrove, W. M. (1997). Design and implementation of a tunable 40–70 MHz Gm-C bandpass delta sigma modulator. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 44(7), 521–530.
Nary, K.R., Beccue, S., Nubling, R., Pierson, R., Wang, K.C., Zampardi, P., & Jayaraman, A. (2002). Second order delta sigma modulators using AlGaAs/GaAs HBTS. Proceedings of the Symposium Gallium Arsenide Integrated Circuit, pp. 232–235.
Cherry, J. A., Snelgrove, W. M., & Schvan, P. (1997). Signal-dependent timing jitter in continuous-time sigma delta modulators. Electronics Letters, 33(13), 1118–1119.
Cherry, J. A., Snelgrove, W. M., & Schvan, P. (1999). Clock jitter and quantizer metastability in continuous-time delta–sigma modulators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 46(6), 661–676.
Keller, M., Buhmann, A., Sauerbrey, J., Ortmanns, M., & Manoli, Y. (2008). A comparative study on excess-loop-delay compensation techniques for continuous-time sigma–delta modulators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems - Part I, 55(11), 3480–3487.
Afifi, M., Keller, M., Manoli, Y., & Ortmanns, M. (2009). Excess loop delay compensation technique for tunable bandpass delta sigma modulators. Proceedings of the IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 365–368.
Ortmanns, M., Gerfers, F., & Manoli, Y. (2004). Compensation of finite gain-bandwidth induced errors in continuous-time sigma–delta modulators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems - Part I, 51(6), 1088–1099.
Quintanilla, L., Arias, J., Segundo, J., Enriquez, L., Hernandez-Mangas, J. M., & Vicente, J. (2009). A comprehensive analysis of the effect of finite amplifier bandwidth and excess loop delay in continuous-time sigma-delta modulators. Microelectronics Journal, 40, 1736–1745.
Ortmanns, M., & Gerfers, F. (2006). Continuous-time sigma-delta A/D conversion. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer.
Afifi, M., Shahein, A., Maurer, M., Keller, M., & Manoli, Y. (2012). A self calibration technique for tunable continuous-time bandpass delta–sigma modulators. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 2977–2980.
Gupta, A., Ahmadi, S., & Zaghloul, M. (2012). A 400 MHz delta–sigma modulator for bandpass IF digitization around 100MHz with excess loop delay compensation. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1375–1378.
Shoaei, O., & Snelgrove, W.M. (1995). A multi-feedback design for LC bandpass delta–sigma modulators. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 171–174.
Kammoun, A., Beilleau, N., & Aboushady, H. (2006). Undersampled LC bandpass sigma–delta modulators with feedback FIRDACs. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 4427–4430.
Pavan, S. (2014). Continuous-time delta–sigma modulator design using the method of moments. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems - Part I, to be published 2014, available online as IEEE early access article. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=6728623&refinements%3D4280088616%26sortType%3Dasc_p_Sequence%26filter%3DAND%28p_IS_Number%3A4358591%29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Equations for the \(4{th}\)-order CT BP \({\Delta }{\Sigma }\) modulator
The DT equivalent of the ELD afflicted CT \(4{th}\)-order loop filter including the additional compensation path scaled by \(b_5\) yields
where
with
and
For \(b_5\) and \(\tau _d\) equal to zero, (34)–(45) simplify to the equations of the ideal fourth-order modulator.
Equivalent to (21), the coefficient \(b_5\) results in
Replacing the CT scaling coefficients \(b_i\) by their corresponding equations based on the original DT coefficients \(a_i\) and setting \(\tau _d\) equal to 1, (46) simplifies to \(a_3+a_4\). As in case of the second-order modulator, \(a_3+a_4\) and thus \(b_5\) yields zero only for a center frequency equal to \(f_s/4\).
Scaling coefficients for a fourth-order NTF with an OOBG equal to 1.6 are summarized in Table 3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afifi, M., Manoli, Y. & Keller, M. A study of excess loop delay in tunable continuous-time bandpass delta–sigma modulators using RC-resonators. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 79, 555–568 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0294-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0294-0