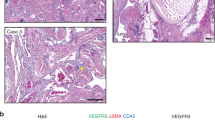
Abstract
Lymphatic malformations (LM) are characterized by abnormal formation of lymphatic vessels and tissue overgrowth. The lymphatic vessels present in LM lesions may become blocked and enlarged as lymphatic fluid collects, forming a mass or cyst. Lesions are typically diagnosed during childhood and are often disfiguring and life threatening. Available treatments consist of sclerotherapy, surgical removal and therapies to diminish complications. We isolated lymphatic endothelial cells (LM-LEC) from a surgically removed microcystic LM lesion. LM-LEC and normal human dermal-LEC (HD-LEC) expressed endothelial (CD31, VE-Cadherin) as well as lymphatic endothelial (Podoplanin, PROX1, LYVE1)-specific markers. Targeted gene sequencing analysis in patient-derived LM-LEC revealed the presence of two mutations in class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K) genes. One is an inherited, premature stop codon in the PI3K regulatory subunit PIK3R3. The second is a somatic missense mutation in the PI3K catalytic subunit PIK3CA; this mutation has been found in association with overgrowth syndromes and cancer growth. LM-LEC exhibited angiogenic properties: both cellular proliferation and sprouting in collagen were significantly increased compared with HD-LEC. AKT-Thr308 was constitutively hyper-phosphorylated in LM-LEC. Treatment of LM-LEC with PI3-Kinase inhibitors Wortmannin and LY294 decreased cellular proliferation and prevented the phosphorylation of AKT-Thr308 in both HD-LEC and LM-LEC. Treatment with the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin also diminished cellular proliferation, sprouting and AKT phosphorylation, but only in LM-LEC. Our results implicate disrupted PI3K-AKT signaling in LEC isolated from a human lymphatic malformation lesion.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LM:
-
Lymphatic malformation
- LEC:
-
Lymphatic endothelial cells
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
References
Wigle JT, Harvey N, Detmar M, Lagutina I, Grosveld G, Gunn MD, Jackson DG, Oliver G (2002) An essential role for Prox1 in the induction of the lymphatic endothelial cell phenotype. EMBO J 21(7):1505–1513
Wigle JT, Oliver G (1999) Prox1 function is required for the development of the murine lymphatic system. Cell 98(6):769–778
Srinivasan RS, Dillard ME, Lagutin OV, Lin FJ, Tsai S, Tsai MJ, Samokhvalov IM, Oliver G (2007) Lineage tracing demonstrates the venous origin of the mammalian lymphatic vasculature. Genes Dev 21(19):2422–2432
Mulliken JB, Glowacki J (1982) Classification of pediatric vascular lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg 70(1):120–121
Padwa BL, Hayward PG, Ferraro NF, Mulliken JB (1995) Cervicofacial lymphatic malformation: clinical course, surgical intervention, and pathogenesis of skeletal hypertrophy. Plast Reconstr Surg 95(6):951–960
Whimster IW (1976) The pathology of lymphangioma circumscriptum. Br J Dermatol 94(5):473–486
Brouillard P, Vikkula M (2003) Vascular malformations: localized defects in vascular morphogenesis. Clin Genet 63(5):340–351
Garzon MC, Huang JT, Enjolras O, Frieden IJ (2007) Vascular malformations—part I. J Am Acad Dermatol 56(3):353–370
Fageeh N, Manoukian J, Tewfik T, Schloss M, Williams HB, Gaskin D (1997) Management of head and neck lymphatic malformations in children. J Otolaryngol 26(4):253–258
Hancock BJ, Stvil D, Luks FI, Dilorenzo M, Blanchard H (1992) Complications of lymphangiomas in children. J Pediatr Surg 27(2):220–226
Jackson IT, Carreno R, Potparic Z, Hussain K (1993) Hemangiomas, vascular malformations, and lymphovenous malformations—classification and methods of treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 91(7):1216–1230
Uebelhoer M, Boon LM, Vikkula M (2012) Vascular anomalies: from genetics toward models for therapeutic trials. Csh Perspect Med 2:a009688
Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC (1998) Phosphoinositide kinases. Ann Rev Biochem 67:481–507
Whitman M, Downes CP, Keeler M, Keller T, Cantley L (1988) Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature 332(6165):644–646
Lawlor MA, Alessi DR (2001) PKB/Akt: a key mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J Cell Sci 114(Pt 16):2903–2910
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ et al (2004) High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304(5670):554
Samuels Y, Ericson K (2006) Oncogenic PI3K and its role in cancer. Curr Opin Oncol 18(1):77–82
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J, Sjoblom T, Leary RJ, Shen D, Boca SM, Barber T, Ptak J et al (2007) The genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 318(5853):1108–1113
Bader AG, Kang S, Vogt PK (2006) Cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA are oncogenic in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(5):1475–1479
Kurek KC, Luks VL, Ayturk UM, Alomari AI, Fishman SJ, Spencer SA, Mulliken JB, Bowen ME, Yamamoto GL, Kozakewich HP et al (2012) Somatic mosaic activating mutations in PIK3CA cause CLOVES syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 90(6):1108–1115
Maclellan RA, Luks VL, Vivero MP, Mulliken JB, Zurakowski D, Padwa BL, Warman ML, Greene AK, Kurek KC (2014) PIK3CA activating mutations in facial infiltrating lipomatosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 133(1):12e–19e
Riviere JB, Mirzaa GM, O’Roak BJ, Beddaoui M, Alcantara D, Conway RL, St-Onge J, Schwartzentruber JA, Gripp KW, Nikkel SM et al (2012) De novo germline and postzygotic mutations in AKT3, PIK3R2 and PIK3CA cause a spectrum of related megalencephaly syndromes. Nat Genet 44(8):934–940
Kandoth C, McLellan MD, Vandin F, Ye K, Niu B, Lu C, Xie M, Zhang Q, McMichael JF, Wyczalkowski MA et al (2013) Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature 502(7471):333–339
Mouta-Bellum C, Kirov A, Miceli-Libby L, Mancini ML, Petrova TV, Liaw L, Prudovsky I, Thorpe PE, Miura N, Cantley LC et al (2009) Organ-specific lymphangiectasia, arrested lymphatic sprouting, and maturation defects resulting from gene-targeting of the PI3K regulatory isoforms p85alpha, p55alpha, and p50alpha. Dev Dyn 238(10):2670–2679
Soroceanu L, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Soriano RH, Aldape K, Misra A, Zha J, Forrest WF, Nigro JM, Modrusan Z et al (2007) Identification of IGF2 signaling through phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 3 as a growth-promoting axis in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(9):3466–3471
Flores MV, Hall CJ, Crosier KE, Crosier PS (2010) Visualization of embryonic lymphangiogenesis advances the use of the zebrafish model for research in cancer and lymphatic pathologies. Dev Dyn 239(7):2128–2135
Huber S, Bruns CJ, Schmid G, Hermann PC, Conrad C, Niess H, Huss R, Graeb C, Jauch KW, Heeschen C et al (2007) Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin impedes lymphangiogenesis. Kidney Int 71(8):771–777
Kobayashi S, Kishimoto T, Kamata S, Otsuka M, Miyazaki M, Ishikura H (2007) Rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin, suppresses lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Sci 98(5):726–733
Patel V, Marsh CA, Dorsam RT, Mikelis CM, Masedunskas A, Amornphimoltham P, Nathan CA, Singh B, Weigert R, Molinolo AA et al (2011) Decreased lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by mTOR inhibition in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 71(22):7103–7112
Deng Y, Atri D, Eichmann A, Simons M (2013) Endothelial ERK signaling controls lymphatic fate specification. J Clin Invest. 123(3):1202–1215
Ren B, Deng Y, Mukhopadhyay A, Lanahan AA, Zhuang ZW, Moodie KL, Mulligan-Kehoe MJ, Byzova TV, Peterson RT, Simons M (2010) ERK1/2-Akt1 crosstalk regulates arteriogenesis in mice and zebrafish. J Clin Invest 120(4):1217–1228
Brouillard P, Boon L, Vikkula M (2014) Genetics of lymphatic anomalies. J Clin Invest 124(3):898–904
Francois M, Short K, Secker GA, Combes A, Schwarz Q, Davidson TL, Smyth I, Hong YK, Harvey NL, Koopman P (2012) Segmental territories along the cardinal veins generate lymph sacs via a ballooning mechanism during embryonic lymphangiogenesis in mice. Dev Biol 364(2):89–98
Hagerling R, Pollmann C, Andreas M, Schmidt C, Nurmi H, Adams RH, Alitalo K, Andresen V, Schulte-Merker S, Kiefer F (2013) A novel multistep mechanism for initial lymphangiogenesis in mouse embryos based on ultramicroscopy. EMBO J 32(5):629–644
Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM (2014) Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management. Semin Pediatr Surg 23(4):178–185
Zhang X, Groopman JE, Wang JF (2005) Extracellular matrix regulates endothelial functions through interaction of VEGFR-3 and integrin alpha5beta1. J Cell Physiol 202(1):205–214
Xu Y, Yuan L, Mak J, Pardanaud L, Caunt M, Kasman I, Larrivee B, Del Toro R, Suchting S, Medvinsky A et al (2010) Neuropilin-2 mediates VEGF-C-induced lymphatic sprouting together with VEGFR3. J Cell Biol 188(1):115–130
Yuan L, Moyon D, Pardanaud L, Breant C, Karkkainen MJ, Alitalo K, Eichmann A (2002) Abnormal lymphatic vessel development in neuropilin 2 mutant mice. Development 129(20):4797–4806
Partanen TA, Vuola P, Jauhiainen S, Lohi J, Salminen P, Pitkaranta A, Hakkinen SK, Honkonen K, Alitalo K, Yla-Herttuala S (2013) Neuropilin-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 are up-regulated in human vascular malformations. Angiogenesis 16(1):137–146
Coso S, Zeng Y, Opeskin K, Williams ED (2012) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 directly interacts with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to regulate lymphangiogenesis. PLoS ONE 7(6):e39558
Zhou F, Chang Z, Zhang L, Hong YK, Shen B, Wang B, Zhang F, Lu G, Tvorogov D, Alitalo K et al (2010) Akt/protein kinase B is required for lymphatic network formation, remodeling, and valve development. Am J Pathol 177(4):2124–2133
Makinen T, Veikkola T, Mustjoki S, Karpanen T, Catimel B, Nice EC, Wise L, Mercer A, Kowalski H, Kerjaschki D et al (2001) Isolated lymphatic endothelial cells transduce growth, survival and migratory signals via the VEGF-C/D receptor VEGFR-3. EMBO J 20(17):4762–4773
Gordon K, Schulte D, Brice G, Simpson MA, Roukens MG, van Impel A, Connell F, Kalidas K, Jeffery S, Mortimer PS et al (2013) Mutation in vascular endothelial growth factor-C, a ligand for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3, is associated with autosomal dominant milroy-like primary lymphedema. Circ Res 112(6):956–960
Irrthum A, Karkkainen MJ, Devriendt K, Alitalo K, Vikkula M (2000) Congenital hereditary lymphedema caused by a mutation that inactivates VEGFR3 tyrosine kinase. Am J Hum Genet 67(2):295–301
Irrthum A, Devriendt K, Chitayat D, Matthijs G, Glade C, Steijlen PM, Fryns JP, Van Steensel MA, Vikkula M (2003) Mutations in the transcription factor gene SOX18 underlie recessive and dominant forms of hypotrichosis-lymphedema-telangiectasia. Am J Hum Genet 72(6):1470–1478
Connell F, Kalidas K, Ostergaard P, Brice G, Homfray T, Roberts L, Bunyan DJ, Mitton S, Mansour S, Mortimer P et al (2010) Linkage and sequence analysis indicate that CCBE1 is mutated in recessively inherited generalised lymphatic dysplasia. Hum Genet 127(2):231–241
Au AC, Hernandez PA, Lieber E, Nadroo AM, Shen YM, Kelley KA, Gelb BD, Diaz GA (2010) Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN14 is a regulator of lymphatic function and choanal development in humans. Am J Hum Genet 87(3):436–444
Osborn AJ, Dickie P, Neilson DE, Glaser K, Lynch KA, Gupta A, Hsi Dickie B (2014) Activating PIK3CA alleles and lymphangiogenic phenotype of lymphatic endothelial cells isolated from lymphatic malformations. Hum Mol Genet. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu505
Lindhurst MJ, Parker VE, Payne F, Sapp JC, Rudge S, Harris J, Witkowski AM, Zhang Q, Groeneveld MP, Scott CE et al (2012) Mosaic overgrowth with fibroadipose hyperplasia is caused by somatic activating mutations in PIK3CA. Nat Genet 44(8):928–933
Hussain K, Challis B, Rocha N, Payne F, Minic M, Thompson A, Daly A, Scott C, Harris J, Smillie BJ et al (2011) An activating mutation of AKT2 and human hypoglycemia. Science 334(6055):474
Lindhurst MJ, Sapp JC, Teer JK, Johnston JJ, Finn EM, Peters K, Turner J, Cannons JL, Bick D, Blakemore L et al (2011) A mosaic activating mutation in AKT1 associated with the Proteus syndrome. N Engl J Med 365(7):611–619
Poduri A, Evrony GD, Cai X, Elhosary PC, Beroukhim R, Lehtinen MK, Hills LB, Heinzen EL, Hill A, Hill RS et al (2012) Somatic activation of AKT3 causes hemispheric developmental brain malformations. Neuron 74(1):41–48
Huang HY, Ho CC, Huang PH, Hsu SM (2001) Co-expression of VEGF-C and its receptors, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3, in endothelial cells of lymphangioma. Implication in autocrine or paracrine regulation of lymphangioma. Lab Invest 81(12):1729–1734
Lokmic Z, Mitchell GM, Chong NKW, Bastiaanse J, Gerrand YW, Zeng Y, Williams ED, Penington AJ (2014) Isolation of human lymphatic malformation endothelial cells, their in vitro characterization and in vivo survival in a mouse xenograft model. Angiogenesis 17(1):1–15
Deng Y, Atri D, Eichmann A, Simons M (2013) Endothelial ERK signaling controls lymphatic fate specification. J Clin Investig 123(3):1202–1215
Fruman DA, Rommel C (2014) PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 13(2):140–156
Luo Y, Liu L, Rogers D, Su W, Odaka Y, Zhou H, Chen W, Shen T, Alexander JS, Huang S (2012) Rapamycin inhibits lymphatic endothelial cell tube formation by downregulating vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 protein expression. Neoplasia 14(3):228–237
Hammill AM, Wentzel M, Gupta A, Nelson S, Lucky A, Elluru R, Dasgupta R, Azizkhan RG, Adams DM (2011) Sirolimus for the treatment of complicated vascular anomalies in children. Pediatr Blood Cancer 57(6):1018–1024
Ingram DA, Caplice NM, Yoder MC (2005) Unresolved questions, changing definitions, and novel paradigms for defining endothelial progenitor cells. Blood 106(5):1525–1531
Melero-Martin JM, Khan ZA, Picard A, Wu X, Paruchuri S, Bischoff J (2007) In vivo vasculogenic potential of human blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Blood 109(11):4761–4768
Acknowledgments
Research reported in this manuscript was supported by a Translational Research Program Pilot Study Grant from Boston Children’s Hospital (J.B.), the Charles Hood Foundation (E.B.), the Manton Center for Orphan Disease Research (E.B.) and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, under Award Number R01 HL117952 (E.B.). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. We thank Dr. Steven Fishman, and Lan Huang for helpful discussions, Drs. Camille L. Stewart and Annie Kulungowski for initial characterization of the LM-LEC, Dr. Tanya Mayadas for providing HUVECs, the Cytogenetics Core of Dana Farber Harvard Cancer Center (P30 CA006516), Jill Wylie-Sears for technical assistance and Kristin Johnson for the preparation of figures.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical statement
The experiments in this manuscript comply with the current laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boscolo, E., Coma, S., Luks, V.L. et al. AKT hyper-phosphorylation associated with PI3K mutations in lymphatic endothelial cells from a patient with lymphatic malformation. Angiogenesis 18, 151–162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-014-9453-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-014-9453-2