Abstract
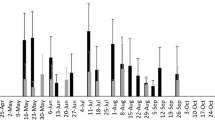
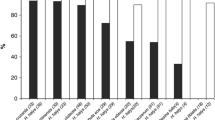
Halyomorpha halys was accidentally introduced into Switzerland around 2004 and has recently spread to several additional areas in Europe, with established populations documented in France, Italy, Greece and Hungary. To test whether generalist egg parasitoids of European Pentatomidae have the potential to control H. halys, and whether these could be as effective as their related Asian species, sentinel egg masses of H. halys and six native European pentatomids were exposed in two regions of Switzerland. Freeze-killed sentinel egg masses of H. halys were attacked by the platygastrid Trissolcus cultratus and the eupelmid Anastatus bifasciatus, whereas fresh egg masses of native Pentatomidae occassionally yielded four Scelionidae species: Trissolcus semistriatus, T. scutellaris, T. cultratus and Telenomus chloropus. In no-choice tests, T. chloropus and T. semistratus produced no offspring from fresh H. halys eggs, whereas T. cultratus and T. scutellaris were sporadically able to complete development. Stopping embryogenesis by freezing egg masses of H. halys at -80 °C enabled T. cultratus and T. semistriatus to produce a high number of offspring without influencing the behaviour of the parasitoids. In contrast to European platygastrids, the Asian parasitoids Trissolcus japonicus and T. cultratus (Chinese strain) caused significantly higher parasitism of fresh H. halys eggs. Differences in developmental success may be related to less efficient venom of European scelionids injected during oviposition. To date, A. bifasciatus is the only potential candidate for augmentaive biological control of H. halys in Europe as it was the only European parasitoid capable of consistent, successful development on fresh H. halys eggs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Latief M, Hilker M (2008) Innate immunity: eggs of Manduca sexta are able to respond to parasitism by Trichogramma evanescens. Insect Biochem Mol 38:136–145
Abram PK, Gariepy TD, Boivin G, Brodeur J (2014a) An invasive stink bug as an evolutionary trap for an indigenous egg parasitoid. Biol Invasions 16:1387–1395
Abram PK, Doyonal J, Brodeur J, Gariepy TD, Boivin G (2014b) Susceptibility of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) eggs to different life stages of three generalist predators. Can Entomol. doi:10.4039/tce.2014.41
Arnold K (2009) Halyomorpha halys (Stål, 1855), eine für die europäische Fauna neu nachgewiesene Wanzenart (Insecta: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae: Cappaeini). Mitt Thürin Entomol 16:19
Artem’ev VP, Oleshchenko IN, Gaidarov PG (1971) The effect of sterilization of the noxious Pentatomid on its natural enemies. Zashchita Rast 16:24–25
Callot H, Brua C (2013) Halyomorpha halys (Stål, 1855), la Punaise diabolique, nouvelle espèce pour la faune de France (Heteroptera Pentatomidae). L’Entomologiste 69:69–71
Cantón-Ramos JM, Callejón-Ferre AJ (2010) Raising Trissolcus basalis for the biological control of Nezara viridula in greenhouses of Almería (Spain). Afr J Agric Res 5:3207–3212
Cesari M, Maistrello L, Ganzerli F, Dioli P, Rebecchi L, Guidetti R (2015) A pest alien invasion in progress: potential pathways of origin of the brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys populations in Italy. J Pest Sci 88:1–7
Clarke AR (1990) The control of Nezara viridula (L) with introduced egg parasitoids in Australia. A review of a landmark example of classical biological control. Aust J Agr Res 41:1127–1146
Colazza S, Rosi MC, Sebastiani P, Ursini M (1996) Host acceptance behaviour in the egg parasitoid Trissolcus basalis (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Acta Oecol 17:109–125
Cornell HV, Hawkins BA (1993) Accumulation of native parasitoid species on introduced herbivores-a comparison of hosts as natives and hosts as invaders. Am Nat 141:847–865
Drooz AT, Bustillo AE, Fedde GF, Fedde VH (1977) North American egg parasite successfully controls a different host genus in South America. Science 197:390–391
Egwuata RI, Taylor TA (1977) Development of Gryon gnidus (Nixon) (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) in eggs of Acnthomia tomntosicollis (Stål) (Hemiptera: Coreidae) killed either by gamma irradiation or by freezing. B Entomol Res 67:31–33
Field SA (1998) Patch exploitation, patch leaving and pre-emptive patch defence in the parasitoid wasp Trissolcus basalis (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Ethology 104:323–338
Fogain R, Graff S (2011) First records of the invasive pest, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), in Ontario and Quebec. J Entomol Soc Ontario 142:45–48
Gariepy TD, Haye T, Zhang J (2013) Occurrence, genetic diversity, and potential pathways of entry of Halyomorpha halys in newly-invaded areas of Canada and Switzerland. J Pest Sci 87:17–28
Genduso P (1977) Difesa del nocciolo dagli artropodi dannosi. IX. Osservazioni sulla morfologia degli stadi preimmaginali e notizie bio-etologiche dell’ Anastatus bifasciatus (Geoffroy). Bollettino dell’Istituto di Entomologia Agraria e dell’Osservatorio di Fitopatologia di Palermo 9:1–22
Godfray HCJ (1994) Parasitoids: behaviroal and evolutionary ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Greathead DJ (1986) Parasitoids in classical biological control. In: Waage J, Greathead D (eds) Insect parasitoids. Academic Press, London, pp 289–318
Hawkins BA, Cornell HV (1994) Patterns of parasitoid accumulation on introduced herbivores. In: Hawkins BA, Sheehan W (eds) Parasitoid community ecology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 77–90
Haye T, Abdallah S, Gariepy T, Wyniger D (2014a) Phenology, life table analysis, and temperature requirements of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys in Europe. J Pest Sci 87(3):407–418
Haye T, Wyniger D, Gariepy T (2014b) Recent range expansion of brown marmorated stink bug in Europe. In: Müller G, Pospischi R, Robinson WH (eds). Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Urban Pests, Zurich, 20–23 July, p 309–314
Herting, B. (1971) A catalog of parasites and predators of terrestrial arthropods. Section A-Host or prey/enemy. Vol. I-Arachnida to Heteroptera. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Slough
Hoebeke ER, Carter ME (2003) Halyomorpha halys (Stål) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae): a polyphagous plant pest from Asia newly detected in North America. P Entomol Soc Wash 105:225–237
Holt RD (1977) Predation, apparent competition and the structure of prey communities. Theor Popul Biol 12:197–229
Hou Z, Liang H, Chen Q, Hu Y, Tian H (2009) Application of Anastatus sp. against Halyomorpha halys. For Pest Dis 28:39–43
Huang MD, Mai H, Wu WN, Poo CL (1974) The bionomics of Anastatus sp. and its utilisation for control of Tessaratoma papillosa Drury. Acta Entomol Sin 17:362–375
Jones WA (1988) World review of the parasitoids of the southern green stink bug, Nezara viridula (L.) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 81:262–273
Jones AL, Jennings DE, Hooks CRR, Shrewsbury PM (2014) Sentinel eggs underestimate rates of parasitism of the exotic brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys. Biol Control 78:61–66
Kenis M, Auger-Rozenberg M, Roques A, Timms L, Péré C, Cock MJW, Settele J, Augustin S, Lopez-Caamonde C (2009) Ecological effects of invasive alien insects. Biol Invasions 11:21–45
Kivan M, Kilic N (2005) Effects of storage at low-temperature of various heteropteran host eggs on the egg parasitoid, Trissolcus semistriatus. Biocontrol 50:589–600
Lee DH, Short BD, Joseph SV, Bergh JC, Leskey TC (2013) Review of the biology, ecology, and management of Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea. Environ Entomol 42:627–641
Leskey TC, Hamilton GC, Nielsen AL et al (2012a) Pest status of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys in the USA. Outlooks Pest Manag 23:218–226
Leskey TC, Lee DH, Short BD, Wright SE (2012b) Impact of insecticides on the invasive Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): analysis of insecticide lethality. J Econ Entomol 105:1726–1735
Leskey TC, Short BD, Butler BR, Wright SE (2012c) Impact of the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål), in mid-atlantic tree fruit orchards in the United States: case studies of commercial management. Psyche 2012:1–14
Leskey TC, Wright SE, Short BD, Khrimian A (2012d) Development of behaviorally based monitoring tools for the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stål)(Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in commercial tree fruit orchards. J Entomol Sci 47:76–85
Luck RF (1981) Parasitic insects introduced as biological control agents for arthropod pests. In: Pimentel D (ed) Handbook of pest management in agriculture. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 125–184
Mahmoud AMA, Lim UT (2007) Evaluation of cold-stored eggs of Dolycoris baccarum (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) for parasitization by Trissolcus nigripedius (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Biol Control 43:287–293
Maistrello L, Dioli P, Vaccari G, Nannini P, Bortolotti S, Caruso S, Costi E, Montermini A, Casoli L, Bariselli M (2014) Primi rinvenimenti in Italia della cimice esotica Halyomorpha halys, una nuova minaccia per la frutticoltura. Atti Giornate Fitopatol 1(2014):283–288
Martin HE, Javahery M, Radjabi G (1969) Note sur la punaise des Céréales Eurygaster integriceps Put. et de ses parasites du genre Asolcus en Iran. Entomol Phytoptah Appl 28:38–46
Milonas PG, Partsinevelos GK (2014) First report of brown marmorated stink bug Halyomorpha halys Stål (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in Greece. EPPO Bull 44:183–186
Mineo G, Lucido G (1977) Difesa del nocciolo dagli artropodi dannosi. XI Prove di controllo biologico del Gonocerus acuteangulatus (Goeze) con lanci inoculativi di alcuni suoi parassitoidi: Gryon muscaeformis (Nees), Trissolcus flavipes (Thoms.), Ooencyrtus gonoceri Vigg. Bollettino dell’Istituto di Entomologia Agraria e dell’Osservatorio di Fitopatologia di Palermo 9:109–128
Noyes JS (2014) Universal Chalcidoidea Database. World Wide Web electronic publication. http://www.nhm.ac.uk/chalcidoids. Accessed February 2015
Northeastern IPM Center (2014) Host Plants of the brown marmorated stink bug in the U.S. http://www.stopbmsb.org/where-is-bmsb/host-plants/. Accessed Feb 27 2015
Orr DB (1988) Scelionid wasps as biological control agents: a review. Fla Entomol 71:501–506
Pansa MG, Asteggiano L, Costamagna C, Vittone G, Tavella L (2013) First discovery of Halyomorpha halys in peach orchards in Piedmont. L’Inf Agrario 69:60–61
Piek T (ed) (1986) Venoms of hymenoptera. Academic Press, London
Reed DA, Luhring KA, Stafford CA, Hansen AK, Millar JG, Hanks LM, Paine TD (2007) Host defensive response against an egg parasitoid involves cellular encapsulation and melanisation. Biol Control 41:214–222
Rice K, Bergh C, Bergman E, Biddinger D, Dieckhoff C, Dively G, Fraser H, Gariepy T, Hamilton G, Haye T, Herbert A, Hoelmer K, Hooks C, Jones A, Krawczyk G, Kuhar T, Mitchell W, Nielsen A, Pfeiffer D, Raupp M, Rodriguez-Saona C, Shearer P, Shrewsbury P, Venugopal PD, Whalen J, Wiman N, Leskey T, Tooker J (2014) Biology, ecology, and management of brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys). J Integr Pest Manag. doi:10.1603/IPM14002
Rider DA (2014) Hymenoptera parasitoid records-list by parasitoid species (http://www.ndsu.nodak.edu/ndsu/rider/Pentatomoidea/Natural_Enemies/parasitoid_Hymen_Host.htm). Accessed 16 Feb 2015
Strand MR, Quarles JM, Meola SM, Vinson SB (1985) Cultivation of teratocytes of the egg parasitoid Telenomus heliothidis (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 21:361–367
Strand MR, Meola SM, Vinson SB (1986) Correlating pathological symptoms in Heliothis virescens eggs with development of the parasitoid Telenomus heliothidis. J Insect Physiol 32:389–402
Talamas EJ, Buffington M, Hoelmer K (2013) New synonymy of Trissolcus halyomorphae Yang. J Hymenopt Res 33:113–117
Talamas EJ, Johnson NF, Buffington ML (2015) Key to Nearctic species of Trissolcus Ashmead, natural enemies of native and invasive stink bugs (Pentatomidae). J Hymenopt Res 43:119–128
Thompson W. R. (1944) A catalogue of the parasites and predators of insect pests. Section I. Parasite host catalogue. Part 3. Parasites of the Hemiptera. Imperial Agriculture of Bureau Institute Entomologist Parasite Service, Ontario
Toepfer S, Kuhlmann U (2004) Survey for natural enemies of the invasive alien chrysomelid, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera, in Central Europe. Biocontrol 49:385–395
United States Apple Association (2010) Asian pest inflicting substantial losses, raising alarm in eastern apple orchards. Apple News 41:488
van Lenteren JC, Bale J, Bigler F, Hokkanen HMT, Loomans AJM (2006) Assessing risks of releasing exotic biological control agents of arthropods pests. Annu Rev Entomol 51:609–634
Vétek G, Papp V, Haltrich A, Redei D (2014) First record of the brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae), in Hungary, with description of the genitalia of both sexes. Zootaxa 3780:194–200
Vindstad OPL, Schott T, Hagen SB, Jepsen JU, Kapari L, Ims RA (2013) How rapidly do invasive birch forest geometrids recruit larval parasitoids? Insights from comparison with a sympatric native geometrid. Biol Invasions 15:1573–1589
Vinson SB (1990) How parasitoids deal with the immune system of their host: an overview. Arch Insect Biochem 13:3–27
Yang ZQ, Yao YX, Qiu LF, Li ZF (2009) A new species of Trissolcus (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) parasitizing eggs of Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in China with comments on its biology. Ann Entomol Soc Am 102:39–47
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all Swiss homeowners and farmers who kindly allowed us to collect stink bugs on their property. We would like to thank Alyson Carter, Léna Durocher-Granger, Dennis Quach and Sara Abdallah for technical assistance in the field and in the laboratory. We would like to thank Paul Abram for useful comments and suggestions on our manuscript. We appreciate the taxonomic guidance offered by Lubomir Masner (Canadian National Collection of Insects, Arachnids and Nematodes, Ottawa) and Elijah Talamas (Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC, USA).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals (vertebrates) performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Traugott.
Author Contribution Statement
TH and TG designed the study. TH, SF and JZ conducted field and laboratory experiments. TH, TG and SF wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haye, T., Fischer, S., Zhang, J. et al. Can native egg parasitoids adopt the invasive brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae), in Europe?. J Pest Sci 88, 693–705 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-015-0671-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-015-0671-1