Abstract
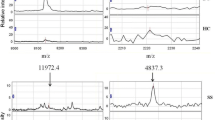
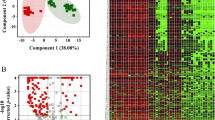
To establish a serological classification tree model for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), protein/peptide profiles of serum were detected by matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) combined with weak cationic exchange (WCX) from Cohort 1, including 65 patients with RA and 41 healthy controls (HC). The samples were randomly divided into a training set and a test set. Twenty-four differentially expressed peaks (P < 0.05) were identified in the training set and 4 of them, namely m/z 3,939, 5,906, 8,146, and 8,569 were chosen to set up our model. This model exhibited a sensitivity of 100.0 % and a specificity of 96.0 % for differentiating RA patients from HC. The test set reproduced these high levels of sensitivity and specificity, which were 100.0 and 81.2 %, respectively. Cohort 2, which include 228 RA patients, was used to further verify the classification efficiency of this model. It came out that 97.4 % of them were classified as RA by this model. In conclusion, MALDI-TOF-MS combined with WCX magnetic beads was a powerful method for constructing a classification tree model for RA, and the model we established was useful in recognizing RA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365:2205–2219
O’Dell James R (2004) Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 350:2502–2591
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 31:315–324
Sekhon LJ (2011) Using the new ACR criteria for early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. JAAPA 24(32–5):58
Mease PJ (2011) The potential roles for novel biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis assessment. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:567–574
Avouac J, Gossec L, Dougados M (2006) Diagnostic and predictive value of anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Ann Rheum Dis 65:845–851
Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y et al (2007) Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 146:797–808
Giusti L, Baldini C, Ciregia F et al (2012) Is GRP78/BiP a potential salivary biomarker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Proteomics Clin Appl 4:315–324
Li YZ, Hu CJ, Leng XM, Zhao GF, Li N, Xu Y (2009) Promising diagnostic biomarkers for primary biliary cirrhosis identified with magnetic beads and MALDI-TOF-MS. Anat Rec 292:455–460
Wang QT, Li YZ, Liang YF et al (2009) Construction of a multiple myeloma diagnostic model by magnetic bead-based MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry of serum and pattern recognition software. Anat Rec 292:604–610
Huang Z, Shi Y, Cai B et al (2009) MALDI-TOF MS combined with magnetic beads for detecting serum protein biomarkers and establishment of boosting decision tree model for diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 48:626–631
Deng C, Lin M, Hu C et al (2011) Establishing a serologic decision tree model of extrapulmonary tuberculosis by MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 71:144–150
Deng C, Lin M, Hu C et al (2011) Exploring serological classification tree model of active pulmonary tuberculosis by magnetic beads pretreatment and MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Scand J Immunol 74:397–405
Issaq HJ, Veenstra TD, Conrads TP, Felschow D (2002) The SELDI-TOF MS approach to proteomics: protein profiling and biomarker identification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 292:587–592
Bazzichi L, Rossi P, Giacomelli C et al (2012) A proposal of simple calculation (ERI calculator) to predict the early response to TNF-α blockers therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 32:349–356
Baggerly KA, Morris JS, Coombes KR (2004) Reproducibility of SELDI-TOF protein patterns in serum: comparing datasets from different experiments. Bioinformatics 20:777–785
Diamandis EP (2004) Mass spectrometry as a diagnostic and a cancer biomarker discovery tool: opportunities and potential limitations. Mol Cell Proteomics 3:367–378
de Seny D, Fillet M, Meuwis MA et al (2005) Discovery of new rheumatoid arthritis biomarkers using the surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry ProteinChip approach. Arthr Rheum 52:3801–3812
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from “Early diagnosis and therapy strategy for Rheumatoid Arthritis” (No. 2008BAI59B01) of the 11th Five Years Key Programs for Science and Technology Development of China. And we thank Professor Deng Haiteng (The Proteomics Resource Center of Rockfeller University,New York, USA) for technology supported.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhang Yan, Hu Chaojun, and Deng Chuiwen have equally contributed to this work and should be considered the first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Chaojun, H., Chuiwen, D. et al. Establishing serological classification tree model in rheumatoid arthritis using combination of MALDI-TOF-MS and magnetic beads. Clin Exp Med 15, 19–23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-013-0265-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-013-0265-2