Abstract
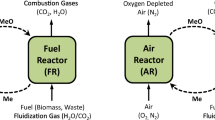
In this paper, the performances of two iron-based syngas-fueled chemical looping (SCL) systems for hydrogen (H2) and electricity production, with carbon dioxide (CO2) capture, using different reactor configurations were evaluated and compared. The first investigated system was based on a moving bed reactor configuration (SCL-MB) while the second used a fluidized bed reactor configuration (SCL-FB). Two modes of operation of the SCL systems were considered, namely, the H2 production mode, when H2 was the desired product from the system, and the combustion mode, when only electricity was produced. The SCL systems were modeled and simulated using Aspen Plus software. The results showed that the SCL system based on a moving bed reactor configuration is more efficient than the looping system with a fluidized bed reactor configuration. The H2 production efficiency of the SCL-MB system was 11 % points higher than that achieved in the SCL-FB system (55.1 % compared to 44.0 %). When configured to produce only electricity, the net electrical efficiency of the SCL-MB system was 1.4 % points higher than that of the SCL-FB system (39.9 % compared to 38.5 %). Further, the results showed that the two chemical looping systems could achieve >99 % carbon capture efficiency and emit ~2 kg CO2/MWh, which is significantly lower than the emission rate of conventional coal gasification-based plants for H2 and/or electricity generation with CO2 capture.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGR:
-
Acid gas removal
- AR:
-
Air reactor
- ASU:
-
Air separation unit
- CaL:
-
Calcium looping
- CCR:
-
Carbon capture rate (%)
- CGE:
-
Cold gas efficiency (%)
- CLC:
-
Chemical looping combustion
- FB:
-
Fluidized bed
- FR:
-
Fuel reactor
- HP:
-
High pressure
- HRSG:
-
Heat recovery steam generator
- IGCC:
-
Integrated gasification combined cycle
- IP:
-
Intermediate pressure
- LHV:
-
Lower heating value (MJ/kg)
- LP:
-
Low pressure
- MB:
-
Moving bed
- MDEA:
-
Methyldiethanolamine
- MEA:
-
Monoethanolamine
- OC:
-
Oxygen carrier
- PB:
-
Packed bed
- PC:
-
Pulverized coal
- PSA:
-
Pressure swing adsorption
- SCL:
-
Syngas chemical looping
- SE:
-
Specific emissions (kg/MWh)
- SR:
-
Steam reactor
- ST:
-
Steam turbine
- W:
-
Power (MW)
- \({\dot{m}}\) :
-
Mass flow rate (kg/s)
- ṅ :
-
Molar flow rate (kmol/s)
- η :
-
Efficiency (%)
- ar:
-
As received
- db:
-
Dry basis
References
Basavaraj RJ, Jayanti S (2015) Syngas-fueled, chemical-looping combustion-based power plant lay-out for clean energy generation. Clean Technol Envir 17(1):237–247. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0781-0
Basavaraja RJ, Jayanti S (2015) Comparative analysis of four gas-fired, carbon capture-enabled power plant layouts. Clean Technol Envir 17(8):2143–2156. doi:10.1007/s10098-015-0936-7
CAESAR (2011) D 4.9 European best practice guidelines for assessment of CO2 capture technologies. Available from: http://caesar.ecn.nl/fileadmin/caesar/user/documents/D_4.9_best_practice_guide.pdf
Cebrucean D, Cebrucean V, Ionel I (2014) CO2 capture and storage from fossil fuel power plants. Energy Procedia 63:18–26. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.003
Cho P, Mattisson T, Lyngfelt A (2004) Comparison of iron-, nickel-, copper- and manganese-based oxygen carriers for chemical-looping combustion. Fuel 83(9):1215–1225. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2003.11.013
Cormos CC (2010) Evaluation of iron based chemical looping for hydrogen and electricity co-production by gasification process with carbon capture and storage. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35(6):2278–2289. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.01.033
Cormos CC (2011a) Evaluation of power generation schemes based on hydrogen-fuelled combined cycle with carbon capture and storage (CCS). Int J Hydrogen Energy 36(5):3726–3738. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.12.042
Cormos CC (2011b) Hydrogen production from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage based on chemical looping systems. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36(10):5960–5971. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.01.170
Cormos CC (2012) Evaluation of syngas-based chemical looping applications for hydrogen and power co-generation with CCS. Int J Hydrogen Energy 37(18):13371–13386. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.06.090
Cormos CC, Cormos AM (2013) Assessment of calcium-based chemical looping options for gasification power plants. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38(5):2306–2317. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.11.128
DYNAMIS (2007a) D 3.1.3 DYNAMIS CO2 quality recommendations. Available from: http://www.sintef.no/globalassets/project/dynamis-hypogen/publications/d3-1-3-dynamis-co2-quality-recommendations1.pdf
DYNAMIS (2007b) D 3.2.2 DYNAMIS H2 quality recommendations. Available from: http://www.sintef.no/globalassets/project/dynamis-hypogen/publications/d3-2-2-dynamis-h2-quality-recommendations1.pdf
Fan LS (2010) Chemical looping systems for fossil energy conversions. Wiley, Hoboken
Gnanapragasam NV, Reddy BV, Rosen MA (2009) Hydrogen production from coal using coal direct chemical looping and syngas chemical looping combustion systems: assessment of system operation and resource requirements. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34(6):2606–2615. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.01.036
Gupta P, Velazquez-Vargas LG, Fan LS (2007) Syngas redox (SGR) process to produce hydrogen from coal derived syngas. Energy Fuel 21(5):2900–2908. doi:10.1021/ef060512k
Hamers HP, Romano MC, Spallina V, Chiesa P, Gallucci F, van Sint Annaland M (2014) Comparison on process efficiency for CLC of syngas operated in packed bed and fluidized bed reactors. Int J Greenh Gas Control 28:65–78. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2014.06.007
Henderson C (2010) Chemical looping combustion of coal. IEA Clean Coal Centre, CCC/178
Higman C, van der Burgt M (2008) Gasification, 2nd edn. Elsevier Inc, Burlington
Hossain MM, de Lasa HI (2008) Chemical-looping combustion (CLC) for inherent CO2 separations—a review. Chem Eng Sci 63(18):4433–4451. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2008.05.028
IEA (2010) Cost and performance of carbon dioxide capture from power generation. OECD/IEA. Available from: http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/costperf_ccs_powergen.pdf
IEA (2012a) World energy outlook. OECD/IEA. Available from: http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/WEO2012_free.pdf
IEA (2012b) Energy technology perspective 2012. Pathways to a clean energy system. OECD/IEA. Available from: http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/ETP2012_free.pdf
IEA (2014a) Key world energy statistics. OECD/IEA. Available from: http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/KeyWorld2014.pdf
IEA (2014b) CO2 emissions from fuel combustion. Highlights. OECD/IEA. Available from: http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/CO2EmissionsFromFuelCombustionHighlights2014.pdf
IEAGHG (2007) Co-production of hydrogen and electricity by coal gasification with CO2 capture. Report 2007/13, September 2007. Available from: http://www.ieaghg.org/docs/General_Docs/Reports/2007-13%20Co-production%20of%20hydrogen%20and.pdf
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2014: Mitigation of climate change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press. Available from: http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar5/wg3/ipcc_wg3_ar5_full.pdf
Jayanti S, Kareemulla D (2016) Detailed plant layout studies of oxy-enriched CO2 pulverized coal combustion-based power plant with CO2 enrichment. Clean Technol Environ. doi:10.1007/s10098-016-1125-z
Jerndal E, Mattisson T, Lyngfelt A (2006) Thermal analysis of chemical-looping combustion. Chem Eng Res Des 84(9):795–806. doi:10.1205/cherd05020
Li F, Kim HR, Sridhar D, Wang F, Zeng L, Chen J, Fan LS (2009) Syngas chemical looping gasification process: oxygen carrier particle selection and performance. Energ Fuel 23(8):4182–4189. doi:10.1021/ef900236x
Li F, Zeng L, Velazquez-Vargas LG, Yoscovits Z, Fan LS (2010) Syngas chemical looping gasification process: bench-scale studies and reactor simulations. AIChE J 56(8):2186–2199. doi:10.1002/aic.12093
Markewitz P, Kuckshinrichs W, Leitner W, Linssen J, Zapp P, Bongartz R, Schreiber A, Muller TE (2012) Worldwide innovations in the development of carbon capture technologies and the utilization of CO2. Energy Environ Sci 5(6):7281–7305. doi:10.1039/c2ee03403d
Mattisson T, Garcia-Labiano F, Kronberger B, Lyngfelt A, Adanez J, Hofbauer H (2007) Chemical-looping combustion using syngas as fuel. Int J Greenh Gas Control 1(2):158–169. doi:10.1016/s1750-5836(07)00023-0
Mukherjee S, Kumar P, Hosseini A, Yang A, Fennell P (2014) Comparative assessment of gasification based coal power plants with various CO2 capture technologies producing electricity and hydrogen. Energy Fuel 28(2):1028–1040. doi:10.1021/ef4024299
Mukherjee S, Kumar P, Yang A, Fennell P (2015) A systematic investigation of the performance of copper-, cobalt-, iron-, manganese- and nickel-based oxygen carriers for chemical looping combustion technology through simulation models. Chem Eng Sci 130:79–91. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2015.03.009
NETL (2013) Cost and performance baseline for fossil energy plants. Volume 1: Bituminous coal and natural gas to electricity. DOE/NETL-2010/1397, Revision 2a, September 2013. Available from: http://www.netl.doe.gov/File%20Library/Research/Energy%20Analysis/OE/BitBase_FinRep_Rev2a-3_20130919_1.pdf
Padurean A, Cormos CC, Cormos AM, Agachi PS (2011) Multicriterial analysis of post-combustion carbon dioxide capture using alkanolamines. Int J Greenh Gas Con 5(4):676–685. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2011.02.001
Prosser NM, Shah MM (2011) Current and future oxygen (O2) supply technologies for oxy-fuel combustion. In: Zheng L (ed) Oxy-fuel combustion for power generation and carbon dioxide (CO2) capture. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 195–227. doi:10.1533/9780857090980.2.195
Skorek-Osikowska A, Bartela L, Kotowicz J, Job M (2013) Thermodynamic and economic analysis of the different variants of a coal-fired, 460 MW power plant using oxy-combustion technology. Energy Convers Manag 76:109–120. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2013.07.032
Sorgenfrei M, Tsatsaronis G (2014) Design and evaluation of an IGCC power plant using iron-based syngas chemical-looping (SCL) combustion. Appl Energy 113:1958–1964. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.03.089
Spallina V, Romano MC, Chiesa P, Gallucci F, van Sint Annaland M, Lozza G (2014) Integration of coal gasification and packed bed CLC for high efficiency and near-zero emission power generation. Int J Greenh Gas Control 27:28–41. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2014.04.029
Spliethoff H (2010) Power generation from solid fuels. Springer, Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-02856-4
Sridhar D, Tong A, Kim H, Zeng L, Li F, Fan LS (2012) Syngas chemical looping process: design and construction of a 25 kWth subpilot unit. Energy Fuel 26(4):2292–2302. doi:10.1021/ef202039y
Svoboda K, Slowinski G, Rogut J, Baxter D (2007) Thermodynamic possibilities and constraints for pure hydrogen production by iron based chemical looping process at lower temperatures. Energy Convers Manage 48(12):3063–3073. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2007.05.019
Svoboda K, Siewiorek A, Baxter D, Rogut J, Pohorely M (2008) Thermodynamic possibilities and constraints for pure hydrogen production by a nickel and cobalt-based chemical looping process at lower temperatures. Energy Convers Manage 49(2):221–231. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2007.06.036
Tong A, Sridhar D, Sun Z, Kim HR, Zeng L, Wang F, Wang D, Kathe MV, Luo S, Sun Y, Fan LS (2013) Continuous high purity hydrogen generation from a syngas chemical looping 25 kWth sub-pilot unit with 100 % carbon capture. Fuel 103:495–505. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2012.06.088
Tong A, Bayham S, Kathe MV, Zeng L, Luo SW, Fan LS (2014) Iron-based syngas chemical looping process and coal-direct chemical looping process development at Ohio State University. Appl Energy 113:1836–1845. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.05.024
Urech J, Tock L, Harkin T, Hoadley A, Marechal F (2014) An assessment of different solvent-based capture technologies within an IGCC-CCS power plant. Energy 64:268–276. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2013.10.081
Xiang W, Chen S, Xue Z, Sun X (2010) Investigation of coal gasification hydrogen and electricity co-production plant with three-reactors chemical looping process. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35(16):8580–8591. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.04.167
ZEP (2015) European Technology Platform for Zero Emission Fossil Fuel Power Plants. http://www.zeroemissionsplatform.eu. Accessed 17 Apr 2015
Acknowledgements
This work was partly carried out by the first author at the Institute for Energy Systems (Technical University of Munich) as part of his postdoctoral research program under the TUFF Grant. Second author would like to acknowledge the financial support through the strategic grant POSDRU107/1.5/S/77265 provided by the Ministry of Labor, Family and Social Protection (Romania), and co-financed by the European Social Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cebrucean, D., Cebrucean, V., Ionel, I. et al. Performance of two iron-based syngas-fueled chemical looping systems for hydrogen and/or electricity generation combined with carbon capture. Clean Techn Environ Policy 19, 451–470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1231-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1231-y