Abstract
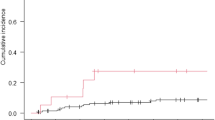
The aim of the study is to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of hypofractionated frameless stereotactic radiotherapy (HSRT) with whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) for the treatment of 1–3 brain metastases. 38 patients with a total of 58 brain metastases were treated at Ghent University Hospital with WBRT (10 × 3 Gy) followed by HSRT (5 × 6 Gy). Patients with RPA class I (n = 8) and II (n = 30) were eligible for HSRT. Acute toxicity was scored with the RTOG toxicity criteria. Response rates were scored every 3 months using the McDonald criteria. Overall survival (OS), brain-specific survival, local and distant brain control were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Patient (age, Karnofsky performance score, KPS, RPA class) and tumor characteristics (number of lesions, extracranial metastases, brain tumor volume, primary cancer status, histology) were tested in univariate and multivariate analysis. Survival at 6 and 12 months was 65 and 35 %, respectively. On univariate analysis KPS < 90, number of lesions, a histologic diagnosis of adenocarcinoma and uncontrolled primary cancer status were statistic significant predictors for poor OS. Four patients (11 %) developed a grade 3 toxicity. Rates of complete remission, partial remission, no change and progressive disease were 30, 40, 23 and 5 %, respectively. Median survival was 7.6 months. The actuarial brain-specific survival was 97 % at 6 months and 91 % at 1 year of follow-up. The 1-year actuarial local and distant brain control was 66 and 75 %, respectively. WBRT + HSRT is an effective treatment for patients with up to three brain metastases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scoccianti S, Ricardi U (2011) Treatment of brain metastases: Review of phase III randomized controlled trials. Radiother Oncol 102(2):168–179 (epub 2011/10/15)
Soffietti R, Ducati A, Ruda R (2012) Brain metastases. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 105, pp 747–755 (epub 2012/01/11)
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T et al (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37(4):745–751 (epub 1997/03/01)
Kondziolka D, Patel A, Lunsford LD, Kassam A, Flickinger JC (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45(2):427–434 (epub 1999/09/16)
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Regine WF, Dempsey RJ, Mohiuddin M, Kryscio RJ et al (1998) Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA 280(17):1485–1489 (epub 1998/11/11)
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363(9422):1665–1672 (epub 2004/05/26)
Sneed PK, Suh JH, Goetsch SJ, Sanghavi SN, Chappell R, Buatti JM et al (2002) A multi-institutional review of radiosurgery alone vs. radiosurgery with whole brain radiotherapy as the initial management of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53(3):519–526 (epub 2002/06/14)
Linskey ME, Andrews DW, Asher AL, Burri SH, Kondziolka D, Robinson PD et al (2010) The role of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 96(1):45–68 (epub 2009/12/05)
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(2):291–298 (epub 2000/05/10)
Powers WE, Tolmach LJ (1963) A multicomponent x-ray survival curve for mouse lymphosarcoma cells irradiated in vivo. Nature 197:710–711 (epub 1963/02/16)
Brenner DJ, Martel MK, Hall EJ (1991) Fractionated regimens for stereotactic radiotherapy of recurrent tumors in the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21(3):819–824 (epub 1991/08/01)
Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Sauer R, Grabenbauer G (2006) Phase II trial of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: results and toxicity. Radiother Oncol 81(1):18–24 (epub 2006/09/19)
Guckenberger M, Baier K, Guenther I, Richter A, Wilbert J, Sauer O et al (2007) Reliability of the bony anatomy in image-guided stereotactic radiotherapy of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69(1):294–301 (epub 2007/08/21)
Withers HR, Thames HD Jr, Peters LJ (1983) A new isoeffect curve for change in dose per fraction. Radiother Oncol 1(2):187–191 (epub 1983/11/01)
Cox JD, Stetz J, Pajak TF (1995) Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31(5):1341–1346 (epub 1995/03/30)
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase-II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8(7):1277–1280
Khuntia D, Brown P, Li J, Mehta MP (2006) Whole-brain radiotherapy in the management of brain metastasis. J Clin Oncol 24(8):1295–1304 (epub 2006/03/10)
Aoki M, Abe Y, Hatayama Y, Kondo H, Basaki K (2006) Clinical outcome of hypofractionated conventional conformation radiotherapy for patients with single and no more than three metastatic brain tumors, with noninvasive fixation of the skull without whole brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64(2):414–418 (epub 2005/11/08)
Kwon AK, Dibiase SJ, Wang B, Hughes SL, Milcarek B, Zhu Y (2009) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of brain metastases. Cancer 115(4):890–898 (epub 2009/01/10)
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29(2):134–141 (epub 2010/11/03)
Giubilei C, Ingrosso G, D’Andrea M, Benassi M, Santoni R (2009) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in combination with whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 91(2):207–212 (epub 2008/09/23)
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Onimaru R, Kagei K, Ikeda J, Ishii N et al (2003) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone without whole-brain irradiation for patients with solitary and oligo brain metastasis using noninvasive fixation of the skull. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56(3):793–800 (epub 2003/06/06)
Narayana A, Chang J, Yenice K, Chan K, Lymberis S, Brennan C et al (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using intensity-modulated radiotherapy in patients with one or two brain metastases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85(2–3):82–87 (epub 2006/12/15)
Rodrigues G, Eppinga W, Lagerwaard F, de Haan P, Haasbeek C, Perera F et al (2011) A pooled analysis of arc-based image-guided simultaneous integrated boost radiation therapy for oligometastatic brain metastases. Radiother Oncol 102(2):180–186 (epub 2011/06/07)
Marchetti M, Milanesi I, Falcone C, De Santis M, Fumagalli L, Brait L et al (2011) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for oligometastases in the brain: a single-institution experience. Neurol Sci 32(3):393–399 (epub 2011/01/15)
Lindvall P, Bergstrom P, Lofroth PO, Henriksson R, Bergenheim AT (2005) Hypofractionated conformal stereotactic radiotherapy alone or in combination with whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with cerebral metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61(5):1460–1466 (epub 2005/04/09)
Aoyama H, Tago M, Kato N, Toyoda T, Kenjyo M, Hirota S et al (2007) Neurocognitive function of patients with brain metastasis who received either whole brain radiotherapy plus stereotactic radiosurgery or radiosurgery alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68(5):1388–1395 (epub 2007/08/07)
Masi L, Casamassima F, Polli C, Menichelli C, Bonucci I, Cavedon C (2008) Cone beam CT image guidance for intracranial stereotactic treatments: comparison with a frame guided set-up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71(3):926–933 (epub 2008/06/03)
Boda-Heggemann J, Walter C, Rahn A, Wertz H, Loeb I, Lohr F et al (2006) Repositioning accuracy of two different mask systems-3D revisited: comparison using true 3D/3D matching with cone-beam CT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 66(5):1568–1575 (epub 2006/11/28)
Manning MA, Cardinale RM, Benedict SH, Kavanagh BD, Zwicker RD, Amir C et al (2000) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy as an alternative to radiosurgery for the treatment of patients with brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(3):603–608 (epub 2000/06/06)
Fahrig A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Grabenbauer G, Kleinert G, Sauer R et al (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases–results from three different dose concepts. Strahlenther Onkol 183(11):625–630 (epub 2007/10/26)
Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Sauer R, Grabenbauer G (2006) Phase II trial of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: results and toxicity. Radiother Oncol 81(1):18–24 (epub 2006/09/19)
Lindvall P, Bergstrom P, Lofroth PO (2009) Tommy Bergenheim A. A comparison between surgical resection in combination with WBRT or hypofractionated stereotactic irradiation in the treatment of solitary brain metastases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151(9):1053–1059 (epub 2009/04/25)
Ethical standards
This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of good clinical practices (ICH/GCP) and the Helsinki declaration (version 2000) developed to protect human subjects participating in clinical studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Potter, B., De Meerleer, G., De Neve, W. et al. Hypofractionated frameless stereotactic intensity-modulated radiotherapy with whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of 1–3 brain metastases. Neurol Sci 34, 647–653 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1091-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-1091-0