Abstract
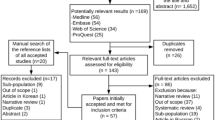
The objective of the study was to determine by meta-analysis whether polymorphisms of the gene encoding peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) are associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). A literature review was conducted to identify data sets that described analyses of genetic association between PADI4 polymorphisms and RA. Data sets were collated and a meta-analysis was performed, with a specific focus on associations within Caucasian and Asian populations. A total of 15,947 RA cases and 22,696 controls that were taken from 28 studies in 24 papers were included in this study. Meta-analysis showed a significant association between allele 2 of the PADI4_94 polymorphism and RA in the overall population (odds ratio [OR] = 1.155, 95 % confidence interval [CI] = 1.069–1.249, p = 2.7 × 10−5). Stratification by ethnicity revealed an association between PADI4_94 allele 2 and RA in Asians (OR = 1.273, 95 % CI = 1.193–1.359, p < 1.0 × 10−9), but not in Caucasians (OR = 1.024, 95 % CI = 0.973–1.078, p = 0.358). However, meta-analysis using homozygote contrast showed an association between PADI4_94 allele 2 and RA in both Asians (OR = 2.311, 95 % CI = 1.1.858–2.875, p < 1.0 × 10−9) and Caucasians (OR = 1.523, 95 % CI = 1.157–2.004, p = 0.008). Meta-analysis also revealed an association between allele 2 of the PADI4_104 polymorphism and RA in both Asians (OR = 1.547, 95 % CI = 1.247–1.919, p = 7.1 × 10−6) and Caucasians (OR = 1.096, 95 % CI = 1.025–1.172, p = 0.008). Finally, meta-analysis showed an association between allele 2 of the PADI4_92 polymorphism and RA in Asians (OR = 1.263, 95 % CI = 1.153–1.384, p = 5.8 × 10−8), but not in Caucasians (OR = 1.123, 95 % CI = 0.980–1.287, p = 0.095). Meta-analysis indicated no association between allele 2 of either the PADI4_90 or PADI4_89 polymorphisms and RA in Asians. This meta-analysis revealed that the PADI4_94 and PADI_104 polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to RA in Asians and Caucasians, and that the PADI4_92 polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to RA in Asians, but not in Caucasians.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SJ, Rho YH, Ji JD, Song GG, Lee YH (2006) Genome scan meta-analysis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 45:166–170
Deighton CM, Walker DJ, Griffiths ID, Roberts DF (1989) The contribution of HLA to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Genet 36:178–182
Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, van Venrooij WJ (2000) The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum 43:155–163
Vossenaar ER, Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ (2003) PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. BioEssays 25:1106–1118
Zhou Z, Menard HA (2002) Autoantigenic posttranslational modifications of proteins: does it apply to rheumatoid arthritis? Curr Opin Rheumatol 14:250–253
Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, Tokuhiro S, Sawada T, Suzuki M, Nagasaki M, Nakayama-Hamada M, Kawaida R, Ono M, Ohtsuki M, Furukawa H, Yoshino S, Yukioka M, Tohma S, Matsubara T, Wakitani S, Teshima R, Nishioka Y, Sekine A, Iida A, Takahashi A, Tsunoda T, Nakamura Y, Yamamoto K (2003) Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 34:395–402
Zavala-Cerna MG, Gonzalez-Montoya NG, Nava A, Gamez-Nava JI, Moran-Moguel MC, Rosales-Gomez RC, Gutierrez-Rubio SA, Sanchez-Corona J, Gonzalez-Lopez L, Davalos-Rodriguez IP, Salazar-Paramo M (2013) PADI4 haplotypes in association with RA Mexican patients, a new prospect for antigen modulation. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:383681
Li Q, Lin KQ, Li Q, Wang J, Yu J, Yu L, Yi W, Huang XQ, Chu JY, Yang ZQ (2013) [Association of polymorphisms of PTPN22 and PADI4 genes with rheumatoid arthritis in Yunnan]. Zhonghua yi xue yi chuan xue za 30:111–115
Panati K, Pal S, Rao KV, Reddy VD (2012) Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of PADI4 gene with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Indian population. Genes Genet Syst 87:191–196
Cheng J, Zhang H, Zhuang C, Liu R (2012) Peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 and methyl-CpG binding domain 4 polymorphisms in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 39:1159–1165
Ben Hassine H, Zemni R, Bouagina E, Zaglaoui H, Ben Fradj H, Slama F, Boukadida J, Sghiri R (2012) Lack of association between PADI4 polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis in the Tunisian population. Joint Bone Spine 79:329–330
Abd-Allah SH, el Shal AS, Shalaby SM, Pasha HF, AM A e-S, el Najjar AR, el Shahawy EE (2012) PADI4 polymorphisms and related haplotype in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Joint Bone Spine 79:124–128
El-Gabalawy HS, Robinson DB, Daha NA, Oen KG, Smolik I, Elias B, Hart D, Bernstein CN, Sun Y, Lu Y, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Siminovitch KA (2011) Non-HLA genes modulate the risk of rheumatoid arthritis associated with HLA-DRB1 in a susceptible North American Native population. Genes Immun 12:568–574
Chen R, Wei Y, Cai Q, Duan S, Ren D, Shen J, He D, Fang M, Lv K, Cheng N, Sun S (2011) The PADI4 gene does not contribute to genetic susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese Han population. Rheumatol Int 31:1631–1634
Burr ML, Naseem H, Hinks A, Eyre S, Gibbons LJ, Bowes J, Wilson AG, Maxwell J, Morgan AW, Emery P, Steer S, Hocking L, Reid DM, Wordsworth P, Harrison P, Thomson W, Worthington J, Consortium B, Consortium Y, Barton A (2010) PADI4 genotype is not associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a large UK Caucasian population. Ann Rheum Dis 69:666–670
Fan LY, Wang WJ, Wang Q, Zong M, Yang L, Zhang H, Sun LS, Lu TB, Han J (2008) A functional haplotype and expression of the PADI4 gene associated with increased rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Chinese. Tissue Antigens 72:469–473
Takata Y, Inoue H, Sato A, Tsugawa K, Miyatake K, Hamada D, Shinomiya F, Nakano S, Yasui N, Tanahashi T, Itakura M (2008) Replication of reported genetic associations of PADI4, FCRL3, SLC22A4 and RUNX1 genes with rheumatoid arthritis: results of an independent Japanese population and evidence from meta-analysis of East Asian studies. J Hum Genet 53:163–173
Poor G, Nagy ZB, Schmidt Z, Brozik M, Meretey K, Gergely P Jr (2007) Genetic background of anticyclic citrullinated peptide autoantibody production in Hungarian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1110:23–32
Ikari K, Kuwahara M, Nakamura T, Momohara S, Hara M, Yamanaka H, Tomatsu T, Kamatani N (2005) Association between PADI4 and rheumatoid arthritis: a replication study. Arthritis Rheum 52:3054–3057
Martinez A, Valdivia A, Pascual-Salcedo D, Lamas JR, Fernandez-Arquero M, Balsa A, Fernandez-Gutierrez B, de la Concha EG, Urcelay E (2005) PADI4 polymorphisms are not associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the Spanish population. Rheumatology 44:1263–1266
Harney SM, Meisel C, Sims AM, Woon PY, Wordsworth BP, Brown MA (2005) Genetic and genomic studies of PADI4 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 44:869–872
Barton A, Bowes J, Eyre S, Spreckley K, Hinks A, John S, Worthington J (2004) A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population is not associated in a United Kingdom population. Arthritis Rheum 50:1117–1121
Plenge RM, Padyukov L, Remmers EF, Purcell S, Lee AT, Karlson EW, Wolfe F, Kastner DL, Alfredsson L, Altshuler D, Gregersen PK, Klareskog L, Rioux JD (2005) Replication of putative candidate-gene associations with rheumatoid arthritis in >4,000 samples from North America and Sweden: association of susceptibility with PTPN22, CTLA4, and PADI4. Am J Hum Genet 77:1044–1060
Costenbader KH, Chang SC, De Vivo I, Plenge R, Karlson EW (2008) Genetic polymorphisms in PTPN22, PADI-4, and CTLA-4 and risk for rheumatoid arthritis in two longitudinal cohort studies: evidence of gene-environment interactions with heavy cigarette smoking. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R52
Feng Z, Niu H, Liang Y, Niu Y, Wen H (2010) Association between rheumatoid arthritis and single nucleotide polymorphisms of padi4-104 in Han population in Hebei province. J Mol Diagn Ther 2:244–247
Cui LFYW, Song HC, Shu R, Han YX, Liu YY (2007) Association of polymorphism of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 gene and rheumatoid arthritis in Han Population. Chin J Allergy Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1:158–162
Zhong BFY, Li H, Wan P, Yang F, Wang Y (2010) Correlation of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 gene polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis. J Third Mil Med Univ 32:1155–1157
Shi HXQL, Li XP, Li XM, Wang GS, Zhang H (2010) Association of polymorphism of peptidylarginine deaminase-4 gene and rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 14:336–339
Cui LFYW, Yang WH, Shu R, Song HC, Han YX et al (2011) Association of polymorphism of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) gene with rheumatoid arthritis and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody. Chin J Basic Med Tradit Chin Med 17:630–632
Kang CP, Lee HS, Ju H, Cho H, Kang C, Bae SC (2006) A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with increased rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Koreans. Arthritis Rheum 54:90–96
Caponi L, Petit-Teixeira E, Sebbag M, Bongiorni F, Moscato S, Pratesi F, Pierlot C, Osorio J, Chapuy-Regaud S, Guerrin M, Cornelis F, Serre G, Migliorini P, ECRAF (2005) A family based study shows no association between rheumatoid arthritis and the PADI4 gene in a white French population. Ann Rheum Dis 64:587–593
Lee YH, Woo JH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2009) Associations between osteoprotegerin polymorphisms and bone mineral density: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 37:227–234
Lee YH, Bae SC, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2010) Associations between vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 38:3643–3651
Lee YH, Ji JD, Song GG (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter -308 A/G polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: a metaanalysis. J Rheumatol 34:43–49
Lee YH, Rho YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG (2007) PADI4 polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 27:827–833
Hou S, Gao GP, Zhang XJ, Sun L, Peng WJ, Wang HF, Ge XJ, Huang W, Sun YH (2013) PADI4 polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Modern Rheumatol 23:50–60
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Duval S, Tweedie R (2000) Trim and fill: a simple funnel‐plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics 56:455–463
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN (1997) Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ 315:1533–1537
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. G. Song for serving as a third reviewer. This study was supported in part by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI13C2124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.H., Bae, SC. Association between susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and PADI4 polymorphisms: a meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 35, 961–971 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3098-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3098-4